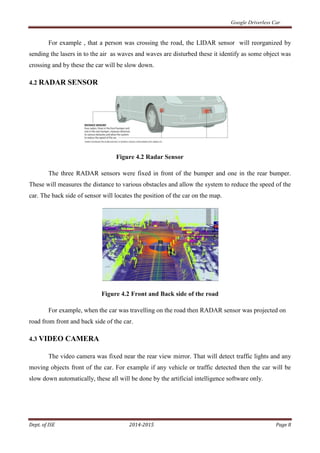
The document provides an overview of Google's driverless car technology. It describes the various sensors used in the car, including LIDAR, RADAR, video cameras, and a position estimator. The sensors gather information about the vehicle's environment and location. Artificial intelligence software integrates this sensor data and helps operate the vehicle without human assistance. The document discusses the history and development of driverless cars. It examines the components, working, advantages, disadvantages, and potential future applications and predictions for this emerging technology.



![Google Driverless Car
Dept. of ISE 2014-2015 Page 4
lawmakers about autonomous vehicle technology, according to federal records, nearing the $9.68
million it spent on lobbying in all of 2011. It is unclear how much Google has spent in total on
lobbying state officials; the company doesn’t disclose such data.
In most states, autonomous vehicles are neither prohibited nor permitted-a key reason why
Google’s fleet of autonomous cars secretly drove more than 100,000 miles on the road before the
company announced the initiative in fall 2010. Last month, Mr. Brin said he expects self-driving cars
to be publicly available within five years.
In January 2011, Mr. Goldwater approached Ms. Dondero Loop and the Nevada assembly
transportation committee about proposing a bill to direct the state’s department of motor vehicles to
draft regulations around the self-driving vehicles. “We’re not saying, ‘Put this on the road,’” he said
he told the lawmakers. “We’re saying, ‘This is legitimate technology,’ and we’re letting the DMV
test it and certify it.” Following the Nevada bill’s passage, legislators from other states began
showing interest in similar legislation. So Google repeated its original recipe and added an extra
ingredient: giving lawmakers the chance to ride in one of its about a dozen self-driving cars…In
California, an autonomous-vehicle bill became law last month despite opposition from the Alliance
of Automobile Manufacturers, which includes 12 top auto makers such as GM, BMW and Toyota.
The group had approved of the Florida bill. Dan Gage, a spokesman for the group, said the California
legislation would allow companies and individuals to modify existing vehicles with self-driving
technology that could be faulty, and that auto makers wouldn’t be legally protected from resulting
lawsuits.
“They’re not all Google, and they could convert our vehicles in a manner not intended,”
Mr. Gage said. But Google helped push the bill through after spending about $140,000 over the past
year to lobby legislators and California agencies, according to public records.
As with California’s recently enacted law, Cheh’s [Washington D.C.] bill requires that a
licensed driver be present in the driver’s seat of these vehicles. While seemingly inconsequential, this
effectively outlaws one of the more promising functions of autonomous vehicle technology: allowing
disabled people to enjoy the personal mobility that most people take for granted. Google highlighted
this benefit when one of its driverless cars drove a legally blind man to a Taco Bell. Bizarrely,
Cheh’s bill also requires that autonomous vehicles operate only on alternative fuels.
While the Google Self-Driving Car may manifest itself as an eco-conscious Prius, self-
driving vehicle technology has nothing to do with hybrids, plug-in electrics or vehicles fueled with](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newfinalreportdoc-150323123222-conversion-gate01/85/Google-s-Driverless-Car-report-4-320.jpg)








![Google Driverless Car
Dept. of ISE 2014-2015 Page 15
CHAPTER 9
REFERENCES
[1] Chea, T. California governor signs driverless cars bill [Internet]. The Associated Press; 2012 Sep 26 [cited
2013 Feb 2]. Available from:http://news.yahoo.com/california-governor-signs-driverless-cars-bill-225332278–
finance.html
[2] United States Department of Energy. 2005 Compare Side by Side: Fuel Economy [Internet]. Environmental
Protection Agency; 2005 [cited 2013 March 2]. Available
from: http://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/Find.do?action=sbs&id=20934
[3] United States Department of Energy. 2013 Most and Least Efficient Cars [Internet]. Environmental
Protection Agency; 2013 April 11 [cited 2013 March 1]. Available
from: http://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/best/bestworstNF.shtml
[4] Newman, G. A Future Filled with Driverless Cars [Internet]. Insurance Journal; 2013 Feb 11 [cited 2013
Mar 2]. Available from:http://www.insurancejournal.com/magazines/features/2013/02/11/280151.htm
[5] Odest Jenkins. 2013. March 26.
[6] Bertam, M., Jenkins, O., & Littman, M. Interviewed by Peseri, Alexandra. 2013. April 11.
[7] Use patterns among early adopters of adaptive cruise
control.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23156618
[8] Marcus, G. Moral Machines [Internet]. The New Yorker; 2012 Nov 27[cited 2013 April 15] 2012 Nov 27.
Available from:http://www.newyorker.com/online/blogs/newsdesk/2012/11/google-driverless-car-morality.html
[9] Wikipedia. Ernst Dickmanns [Internet]. Wikipedia; 2013 Mar 13 [cited 2013 April 11]. Available
from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ernst_Dickmanns
[10] Mariacher, E. 3 driverless cars trends in 2012 [Internet]. Blogger; 2013. Jan 2 [cited 2013 April 13].
Available from: http://driverless-cars.blogspot.com/2013/01/3-driverless-cars-trends-in-
2012.html#.UWoAenCrJ0o](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newfinalreportdoc-150323123222-conversion-gate01/85/Google-s-Driverless-Car-report-15-320.jpg)