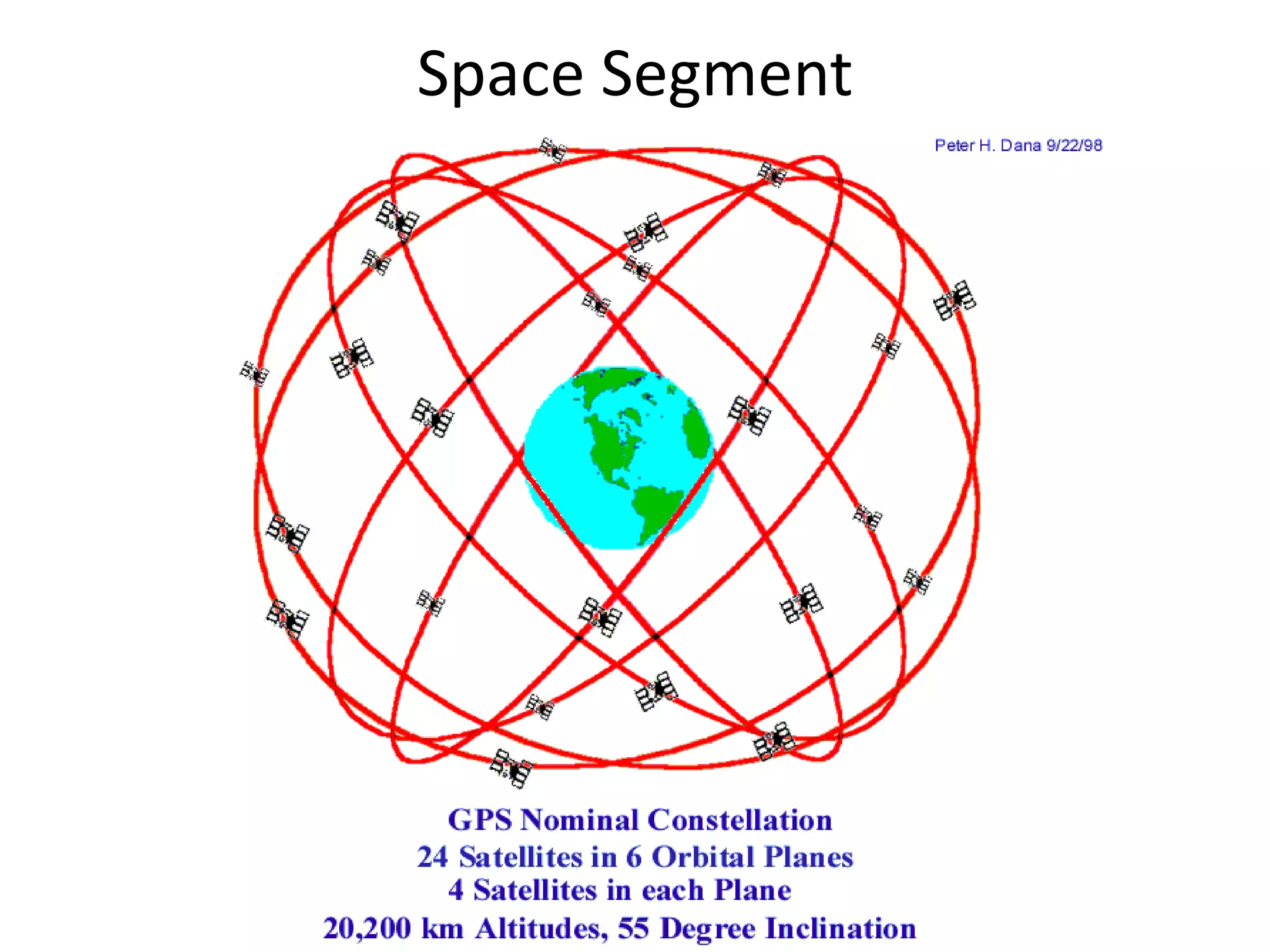
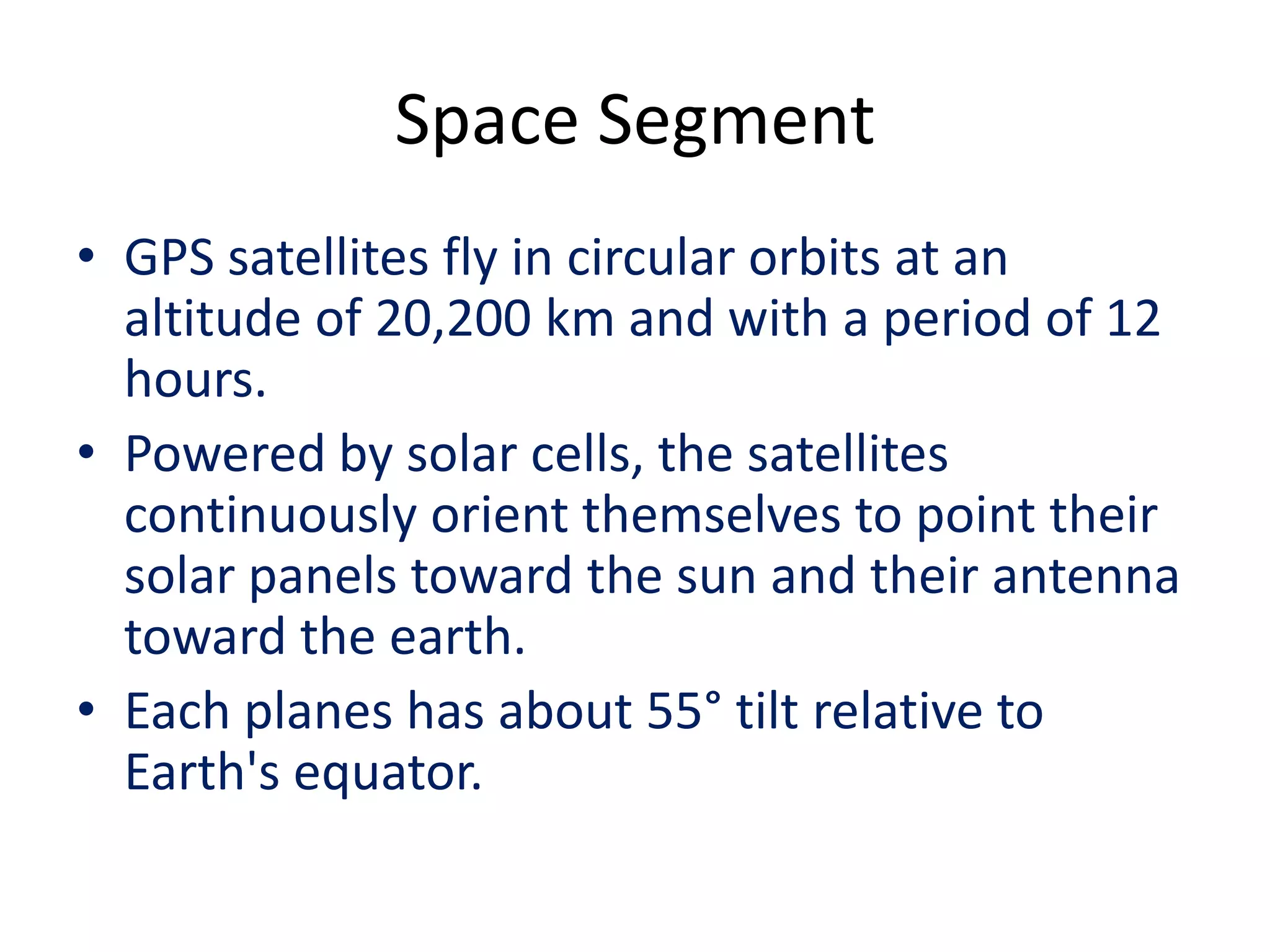
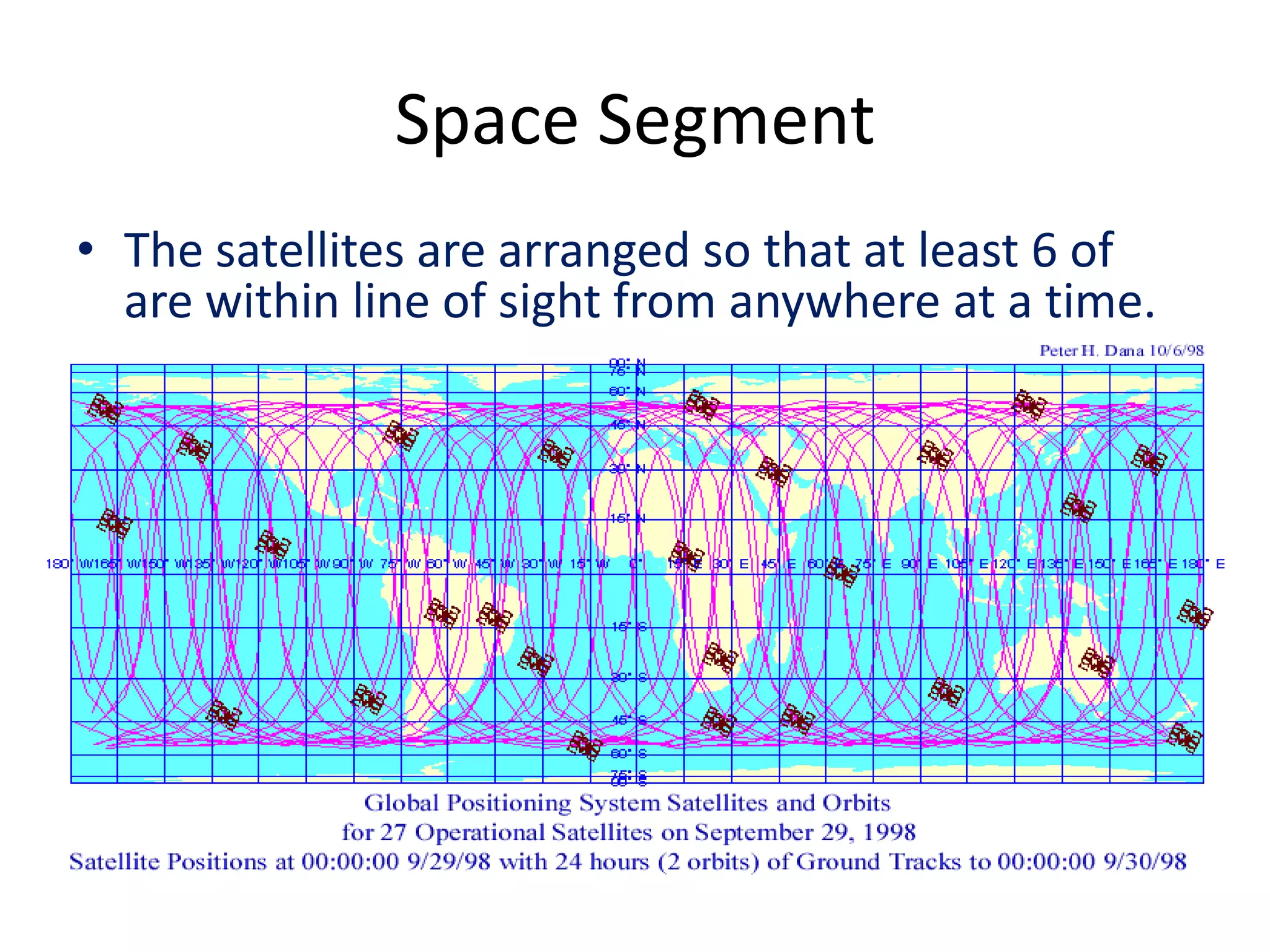
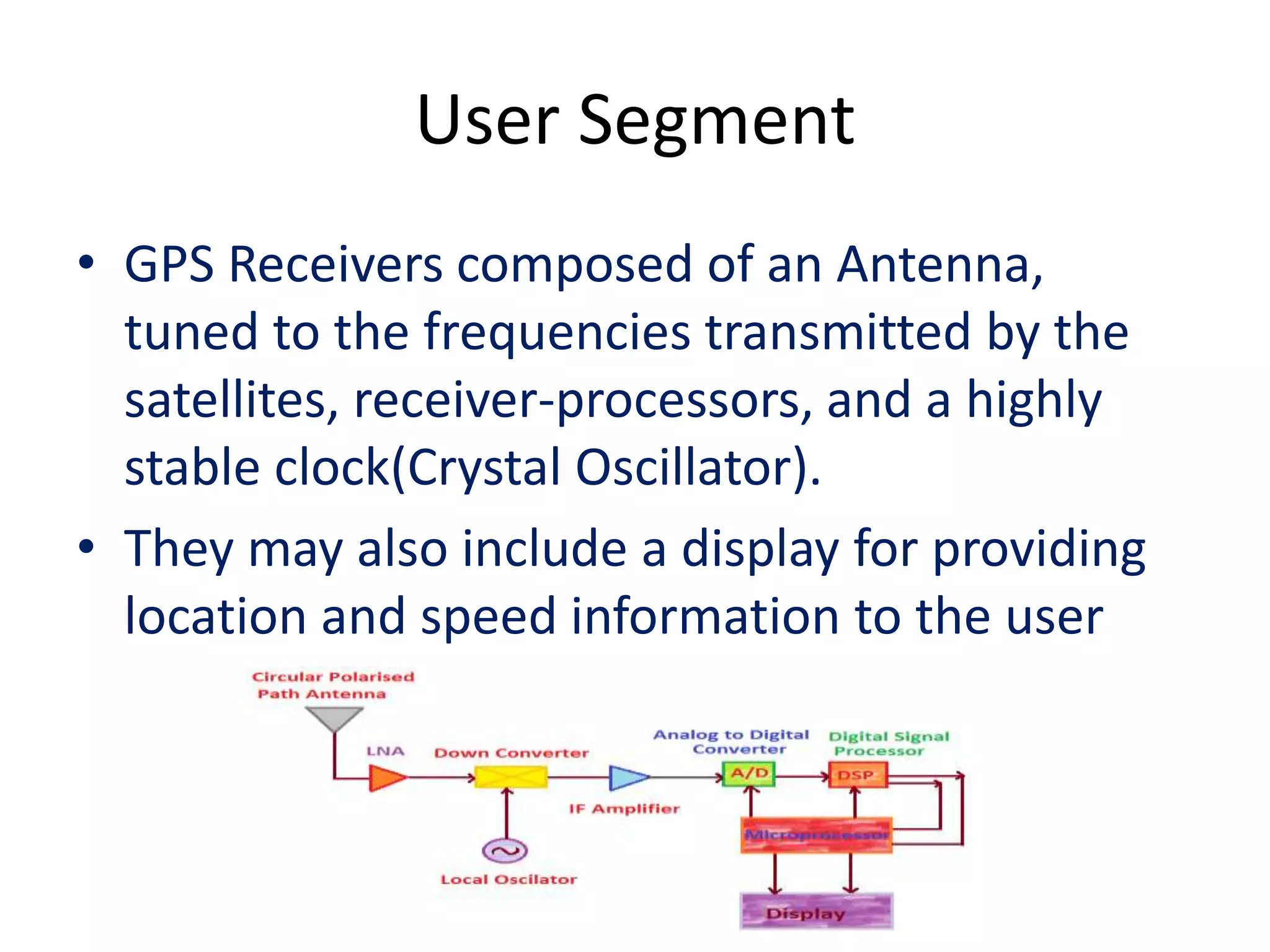
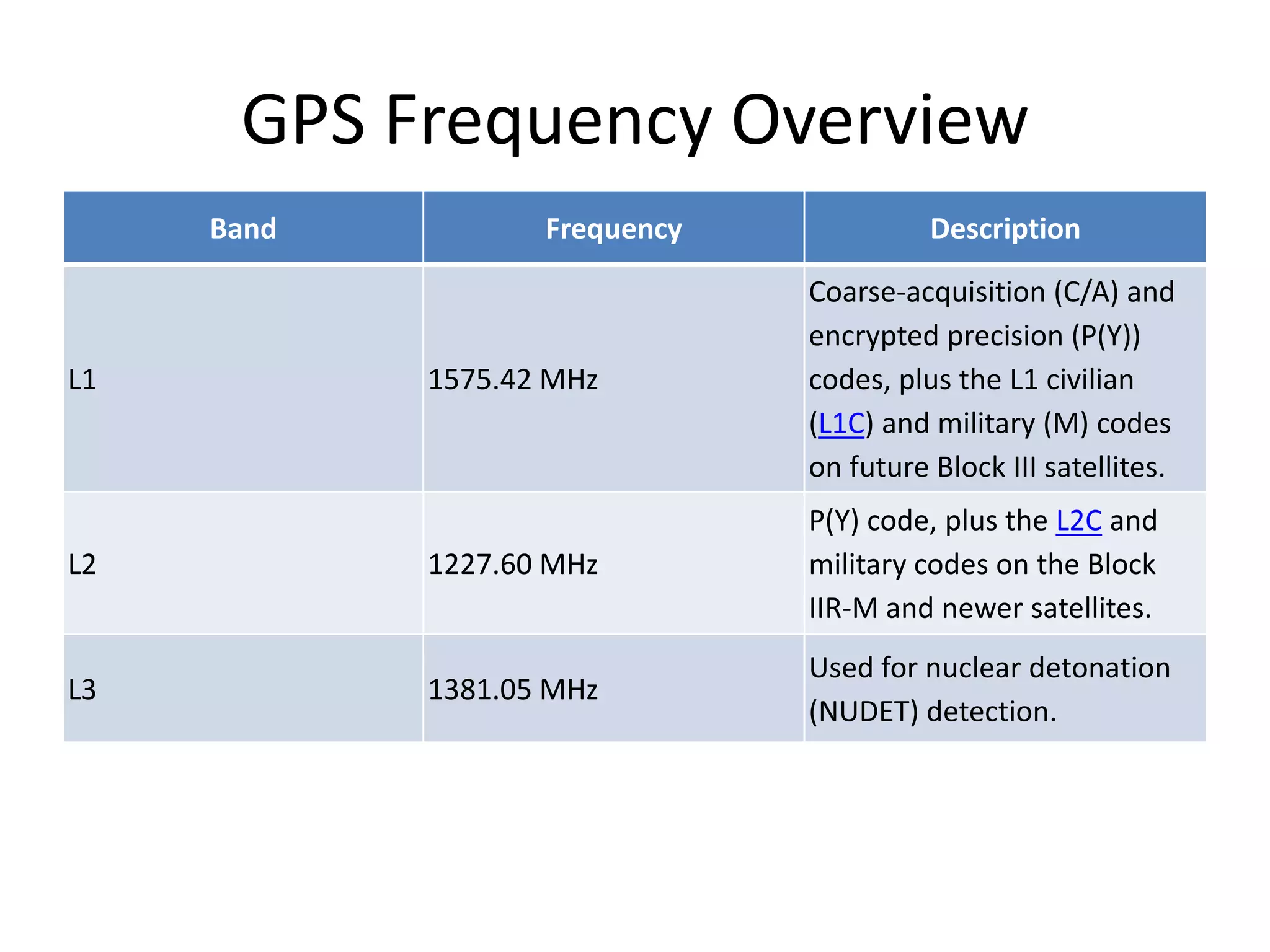
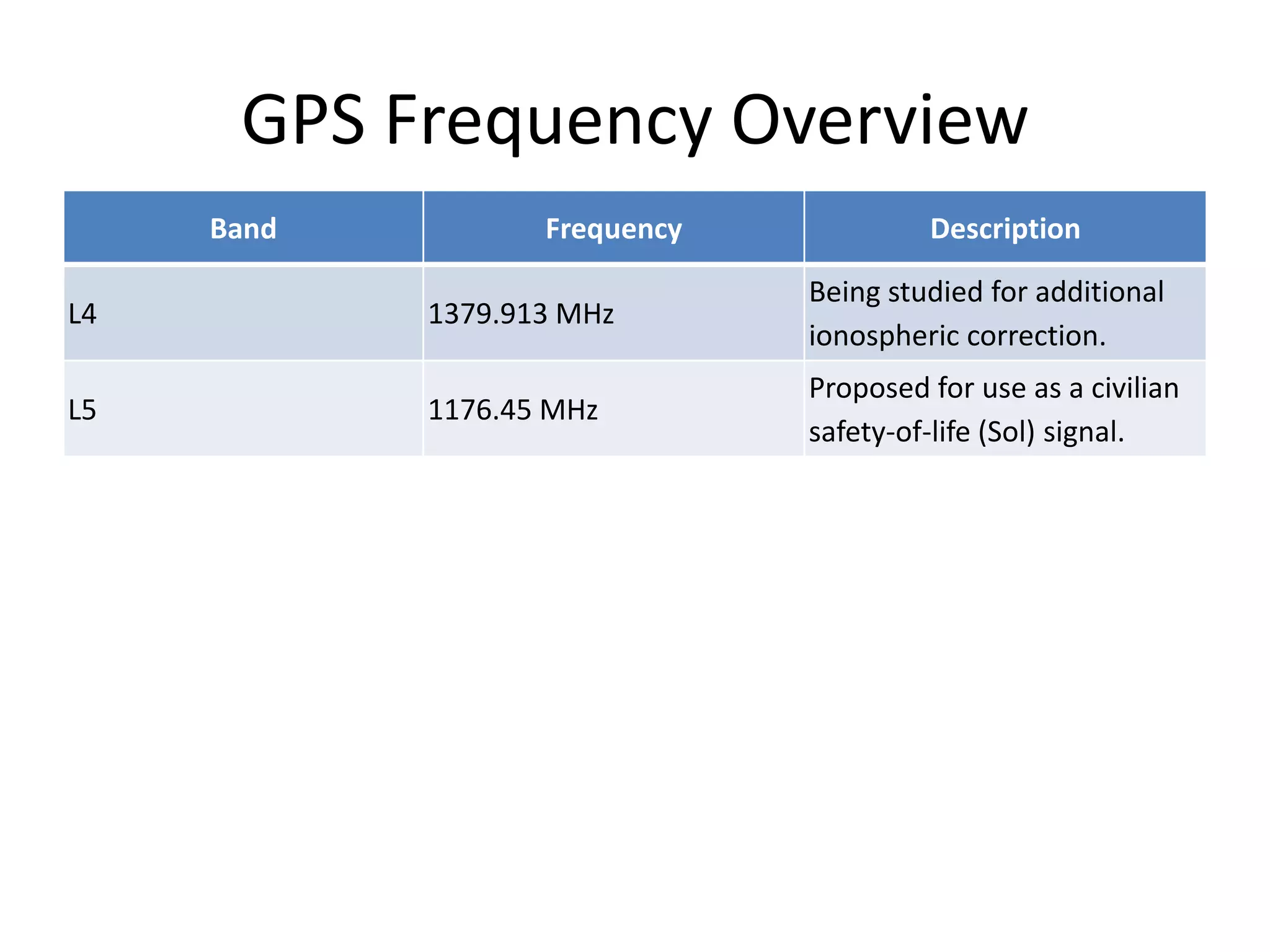
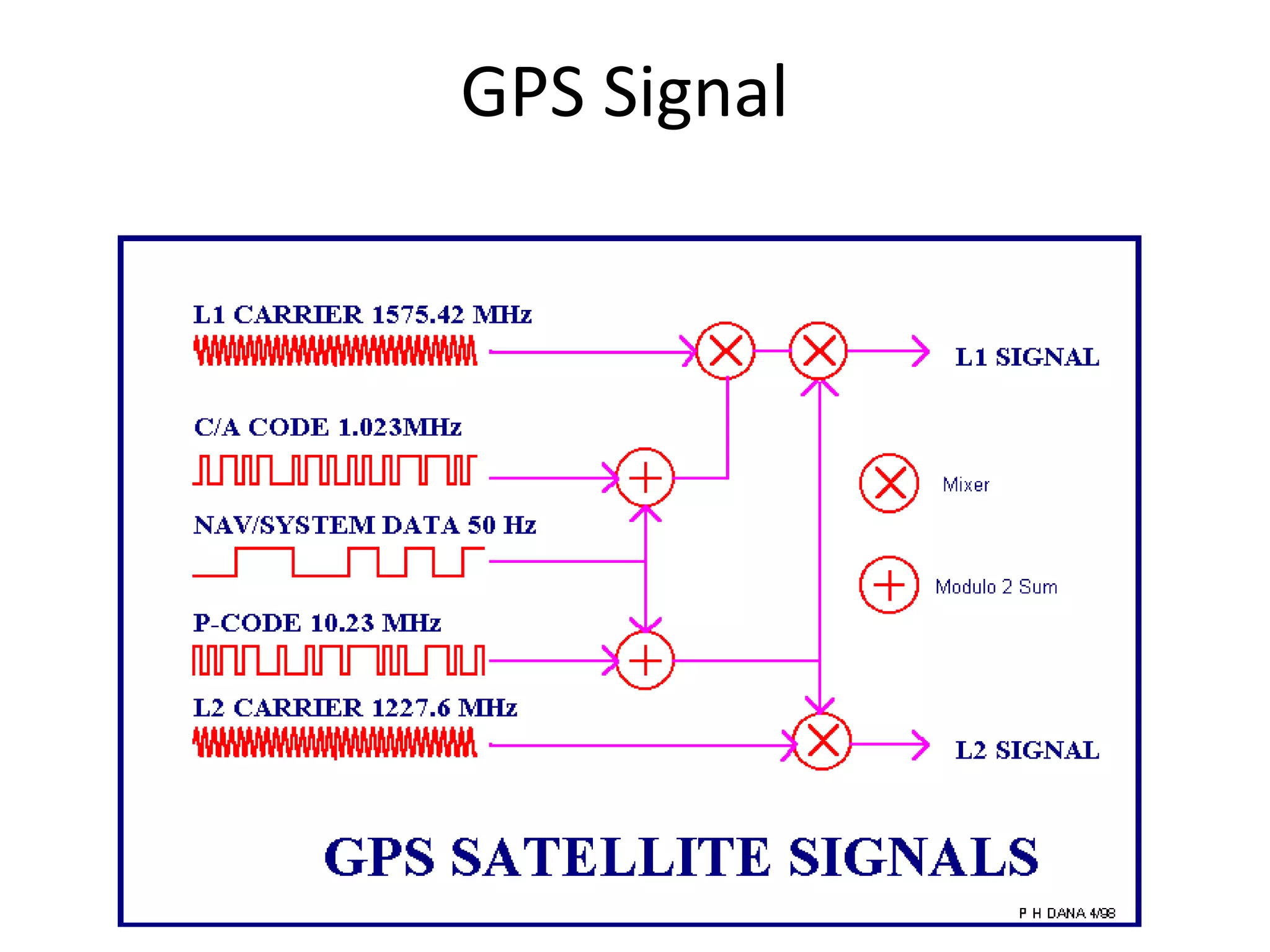
The seminar covered the Global Positioning System (GPS), its history, functionality, and applications. Initially developed by the U.S. Department of Defense for military use, GPS has evolved into a vital tool for navigation and surveying, consisting of a space segment with satellites, a control segment, and user receivers. Current developments include the Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) and expanding civilian applications across various fields.