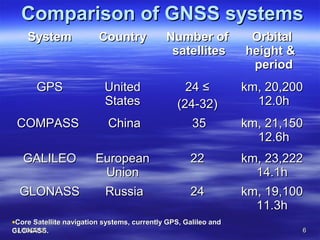
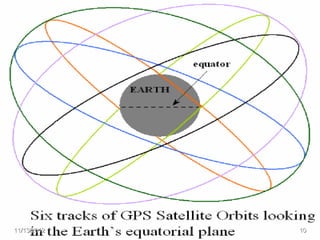
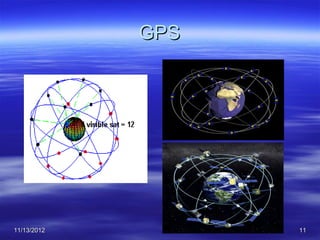
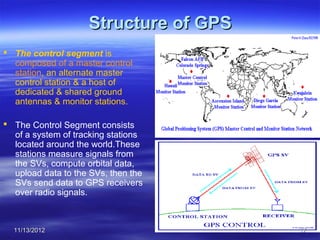
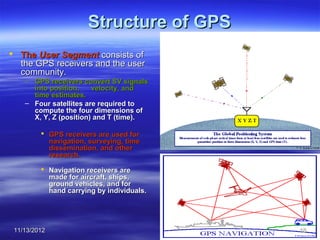
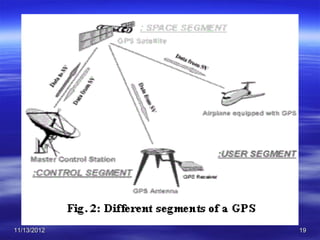
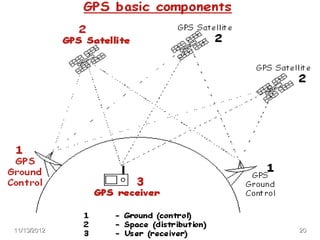
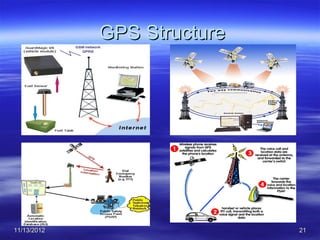
The document discusses Mohamed Mahmoud Ahmed El-shora's research on the Global Positioning System (GPS) supervised by Prof. Dr. Shadiya Taha El-khodary at Tanta University's Faculty of Science, Department of Geology. It provides an introduction to GPS, describing how it is a satellite-based system that uses precise timing signals from 24 to 32 satellites to determine the location of GPS receivers on Earth. The document then discusses the structure of GPS including its space, control, and user segments as well as its various applications in fields such as navigation, tracking, and scientific research.