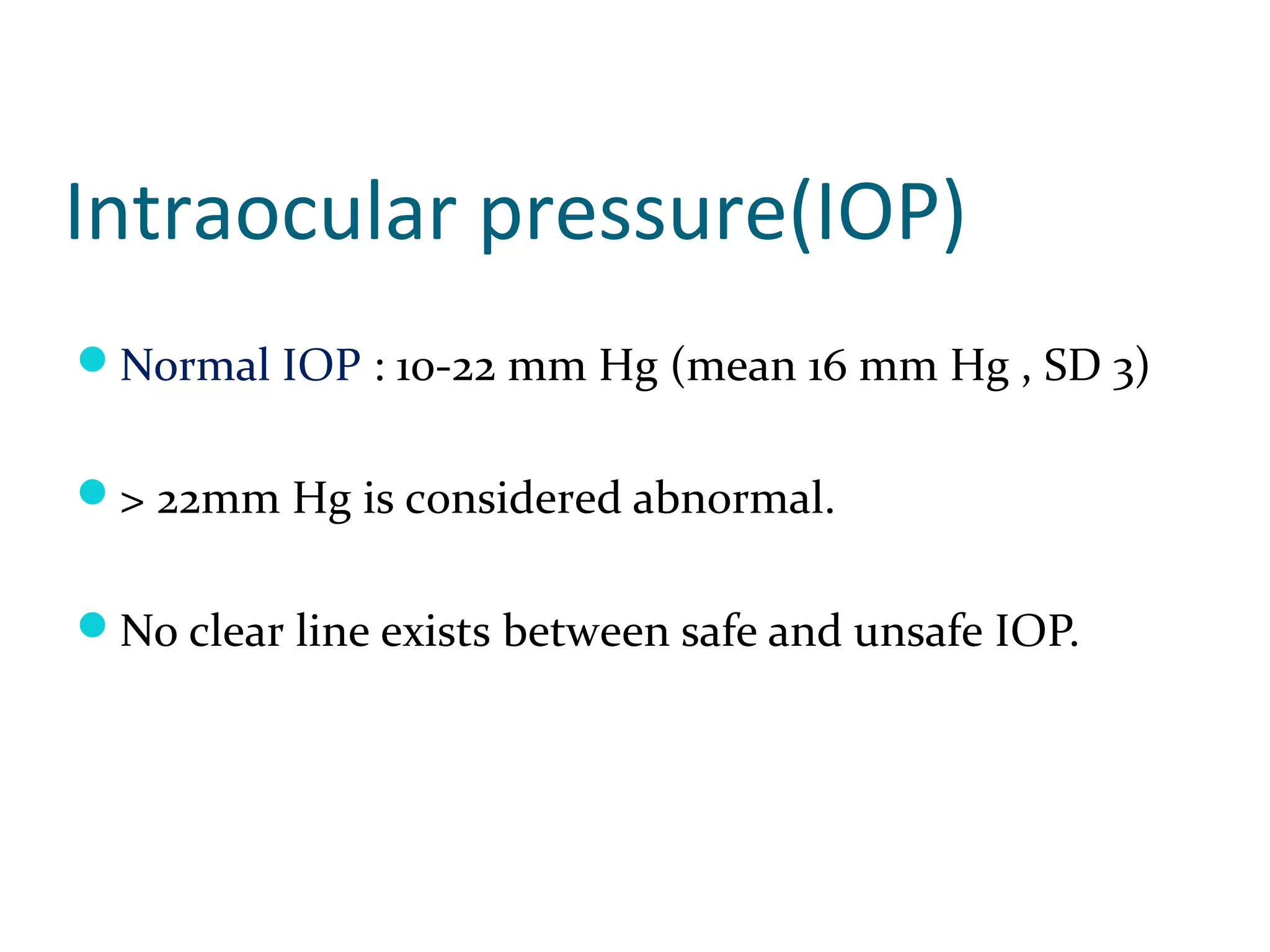
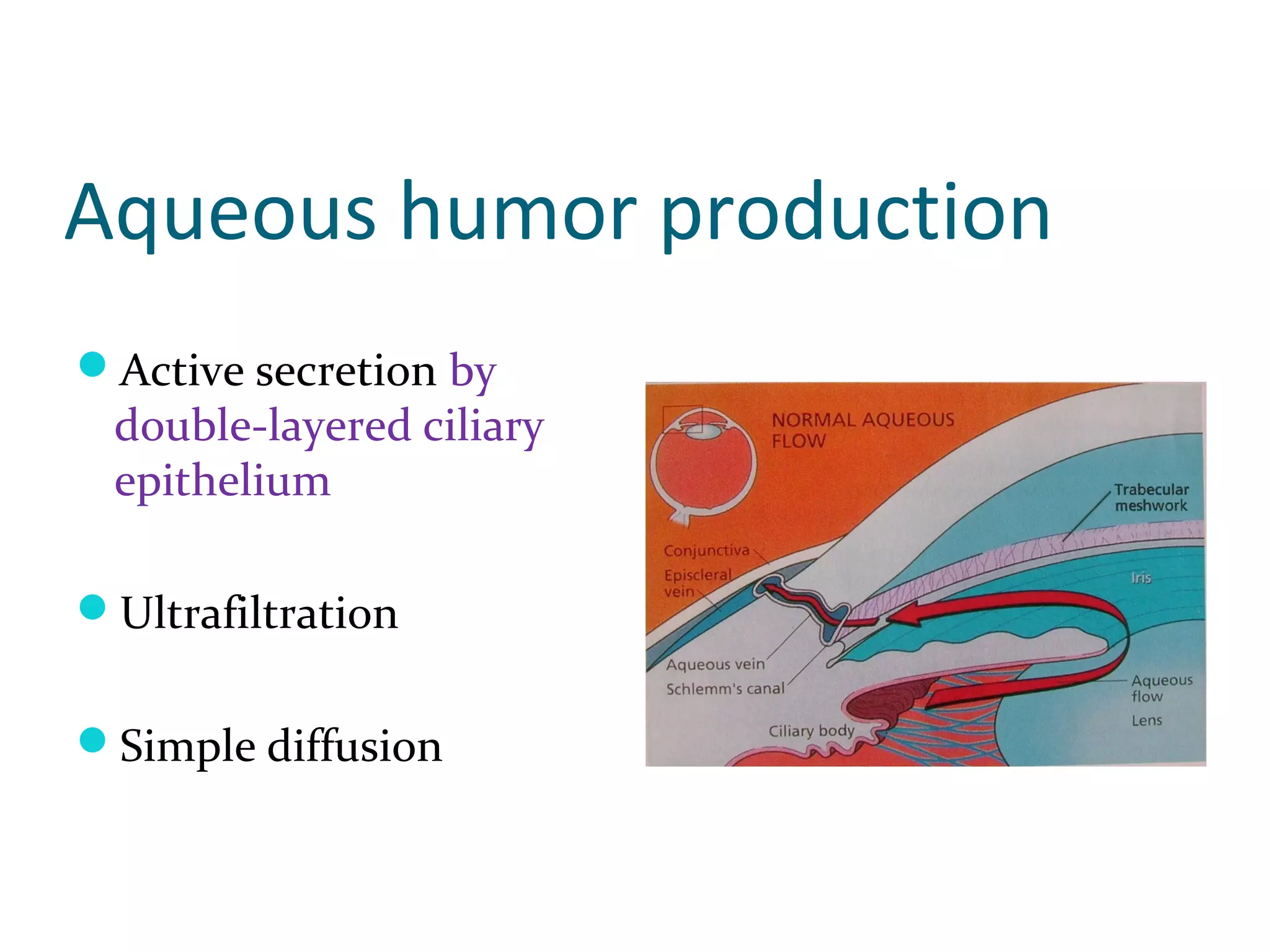
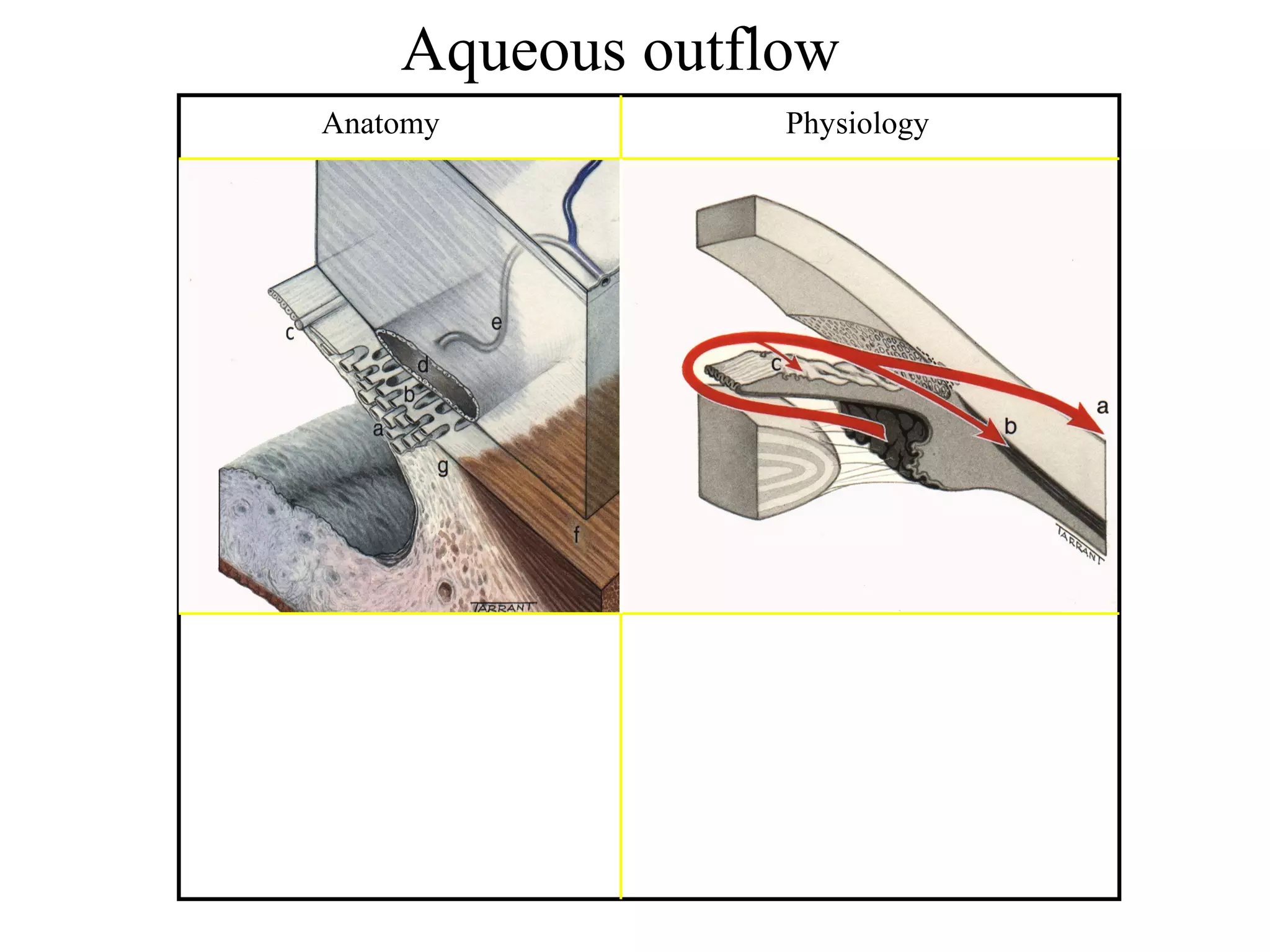
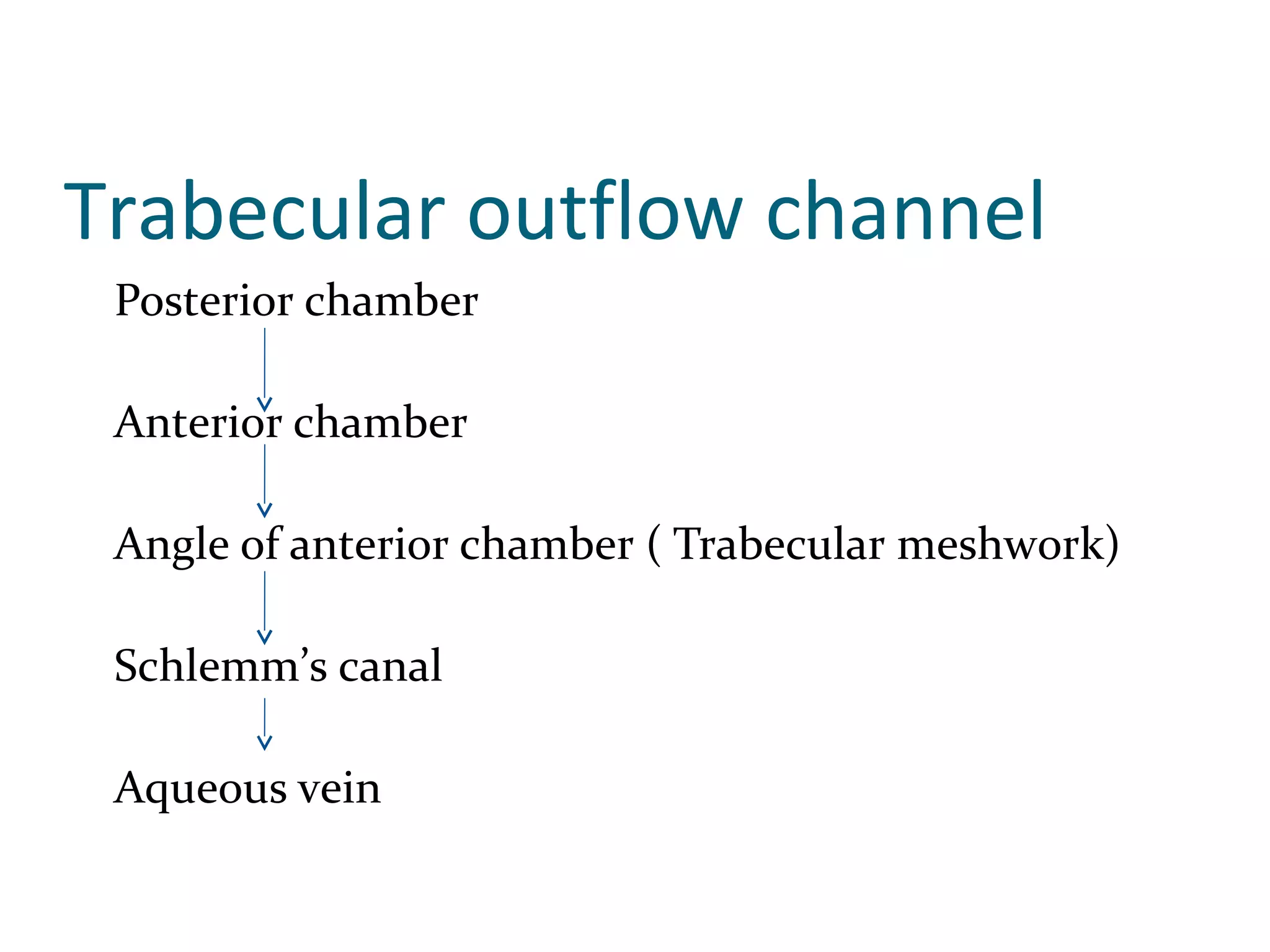
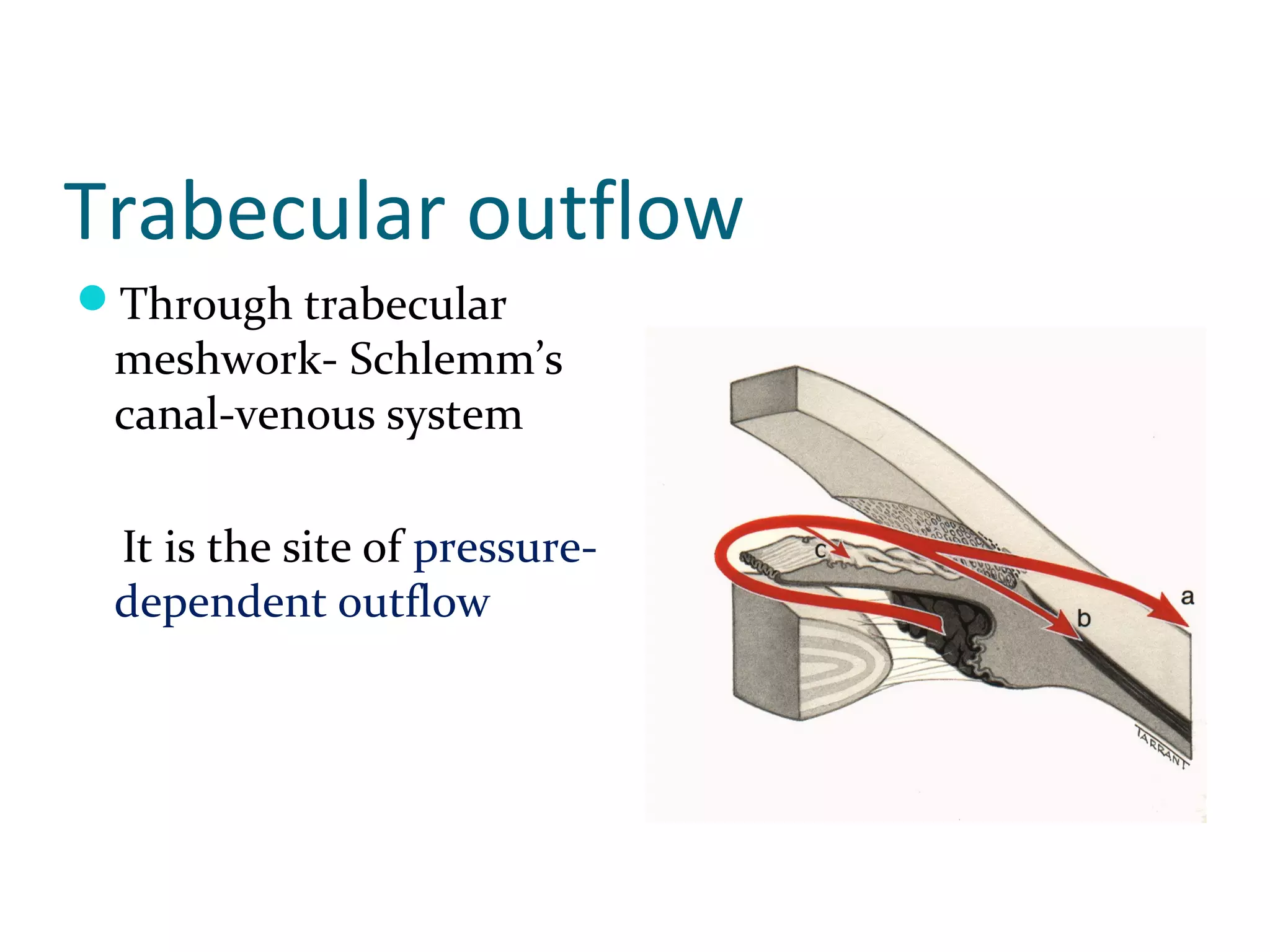
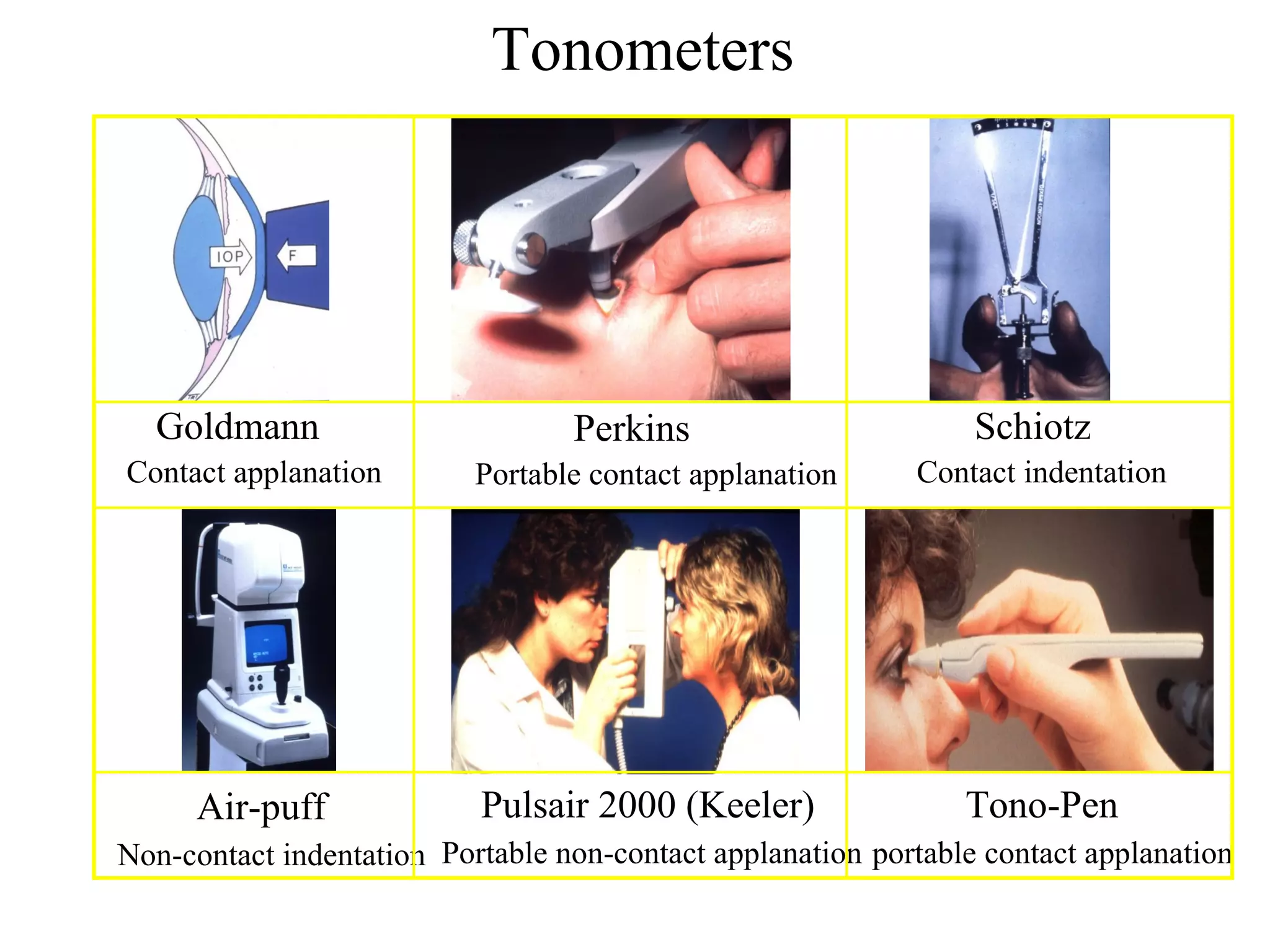
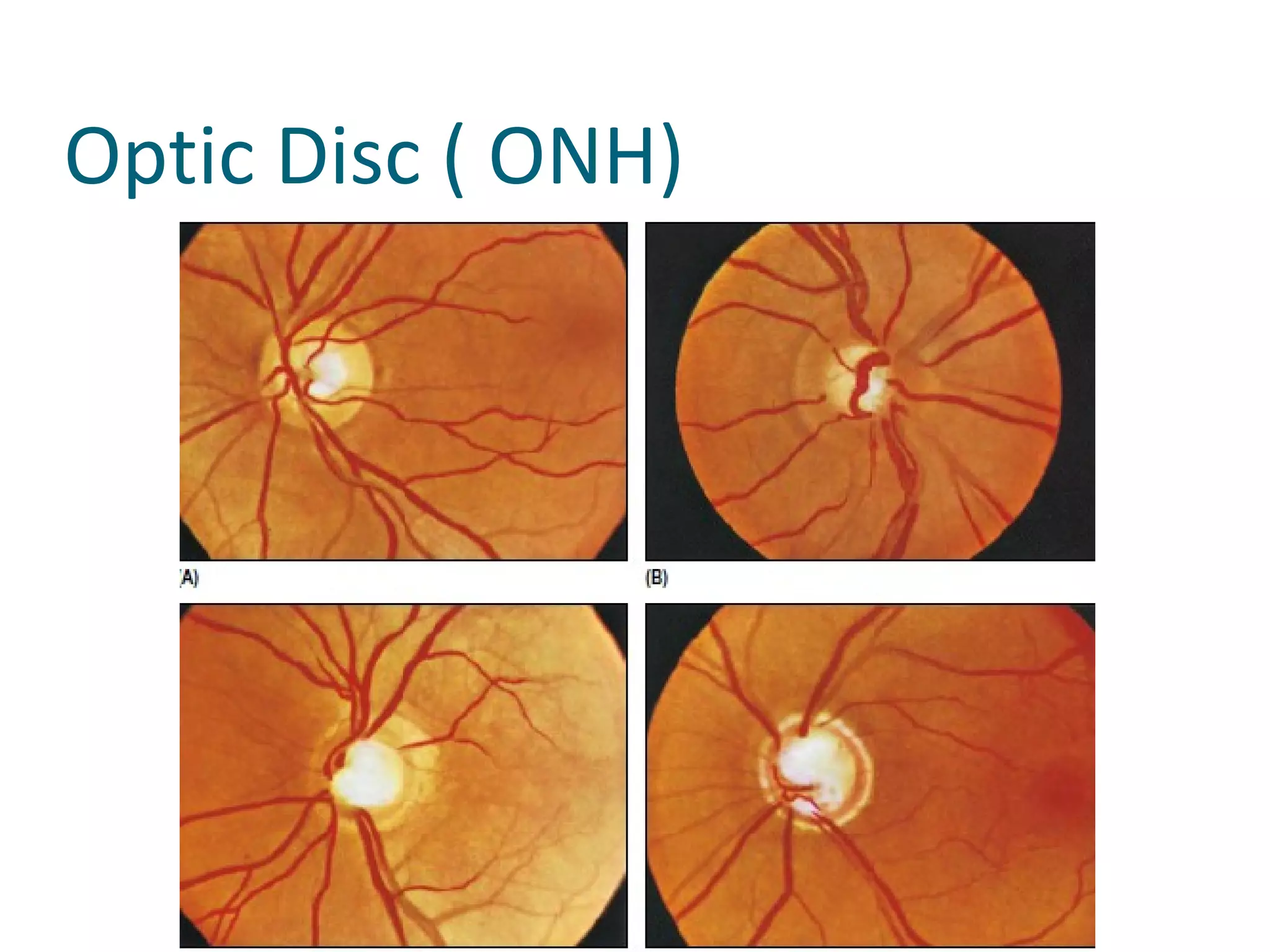
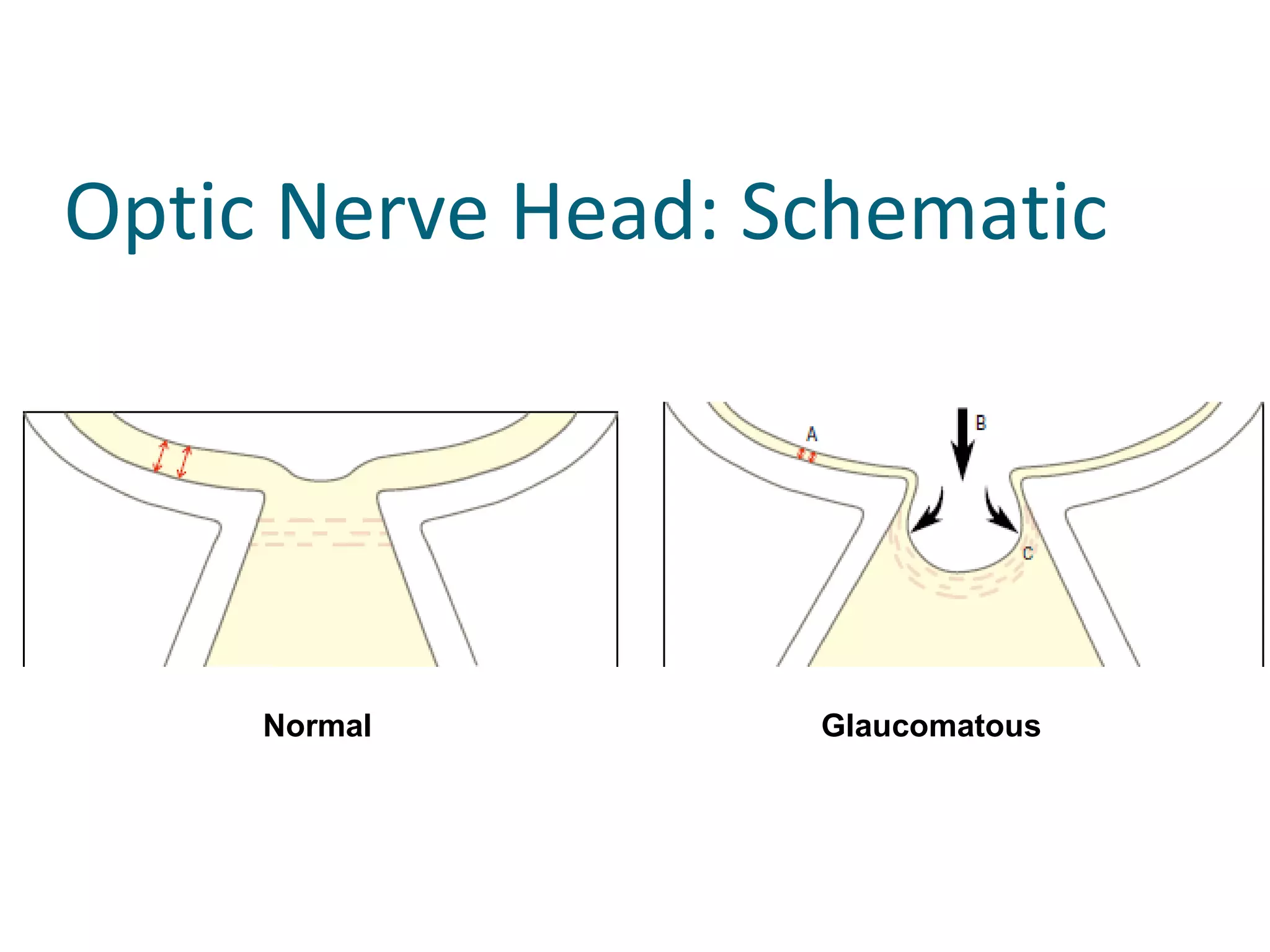
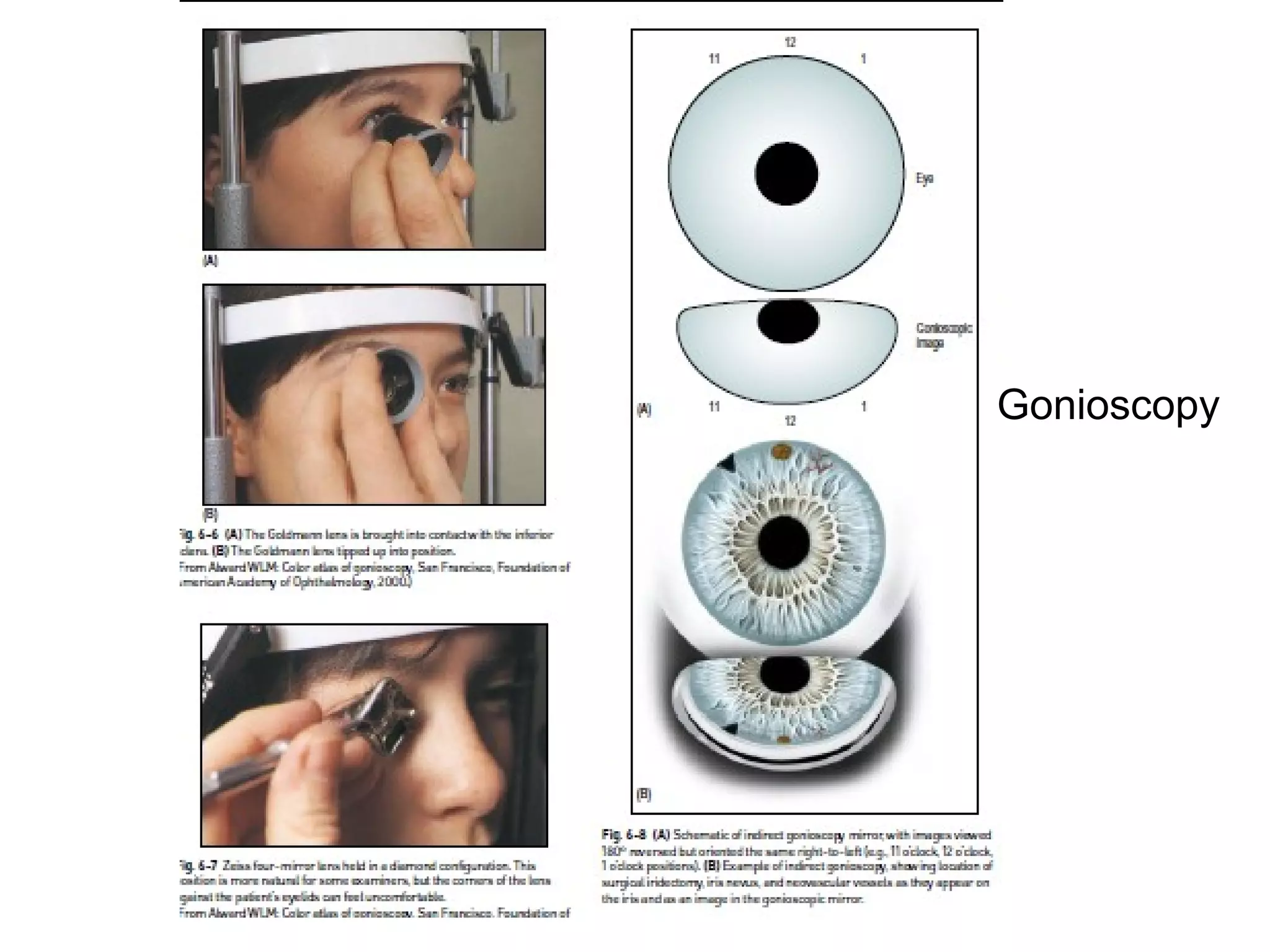
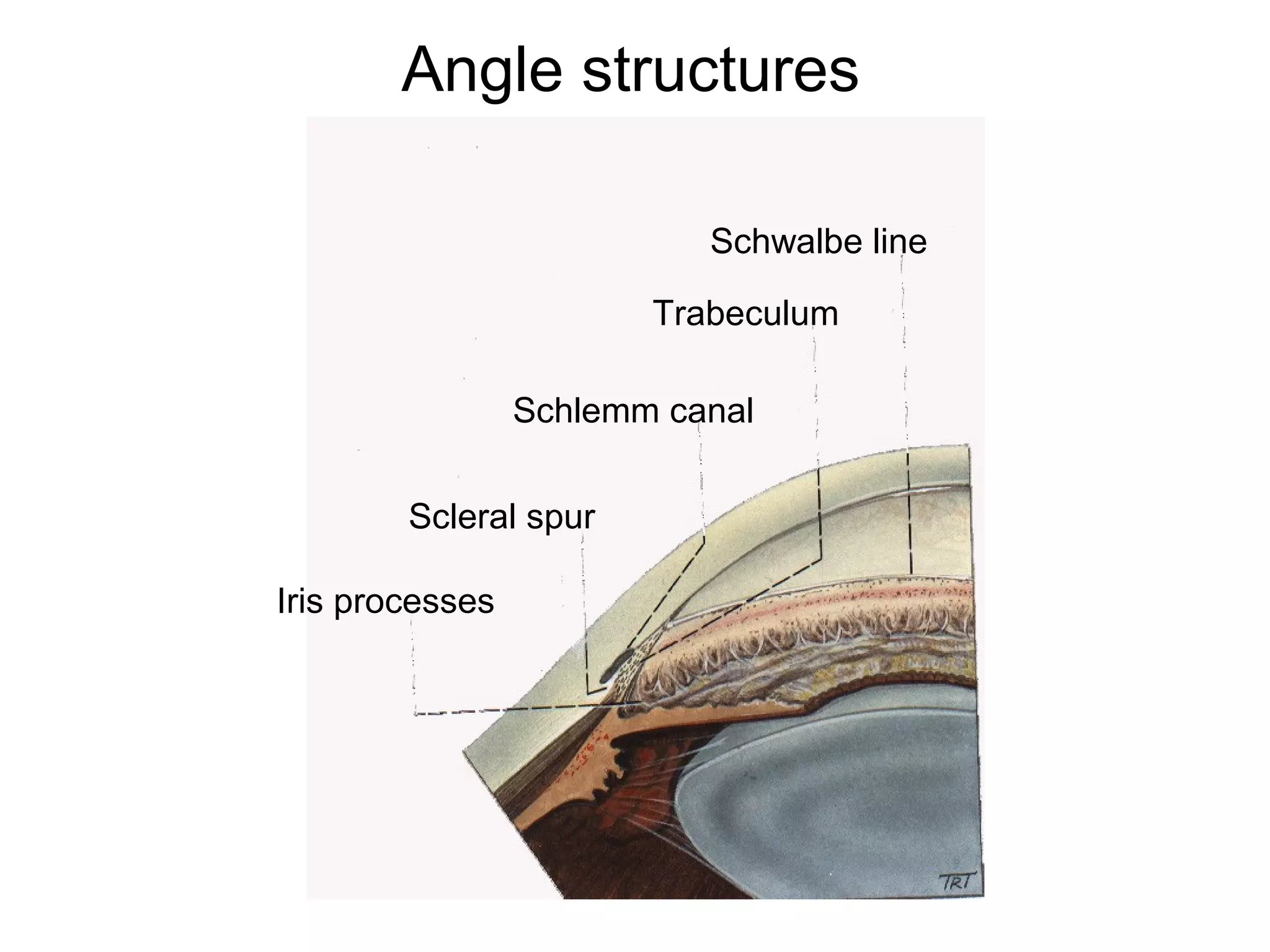
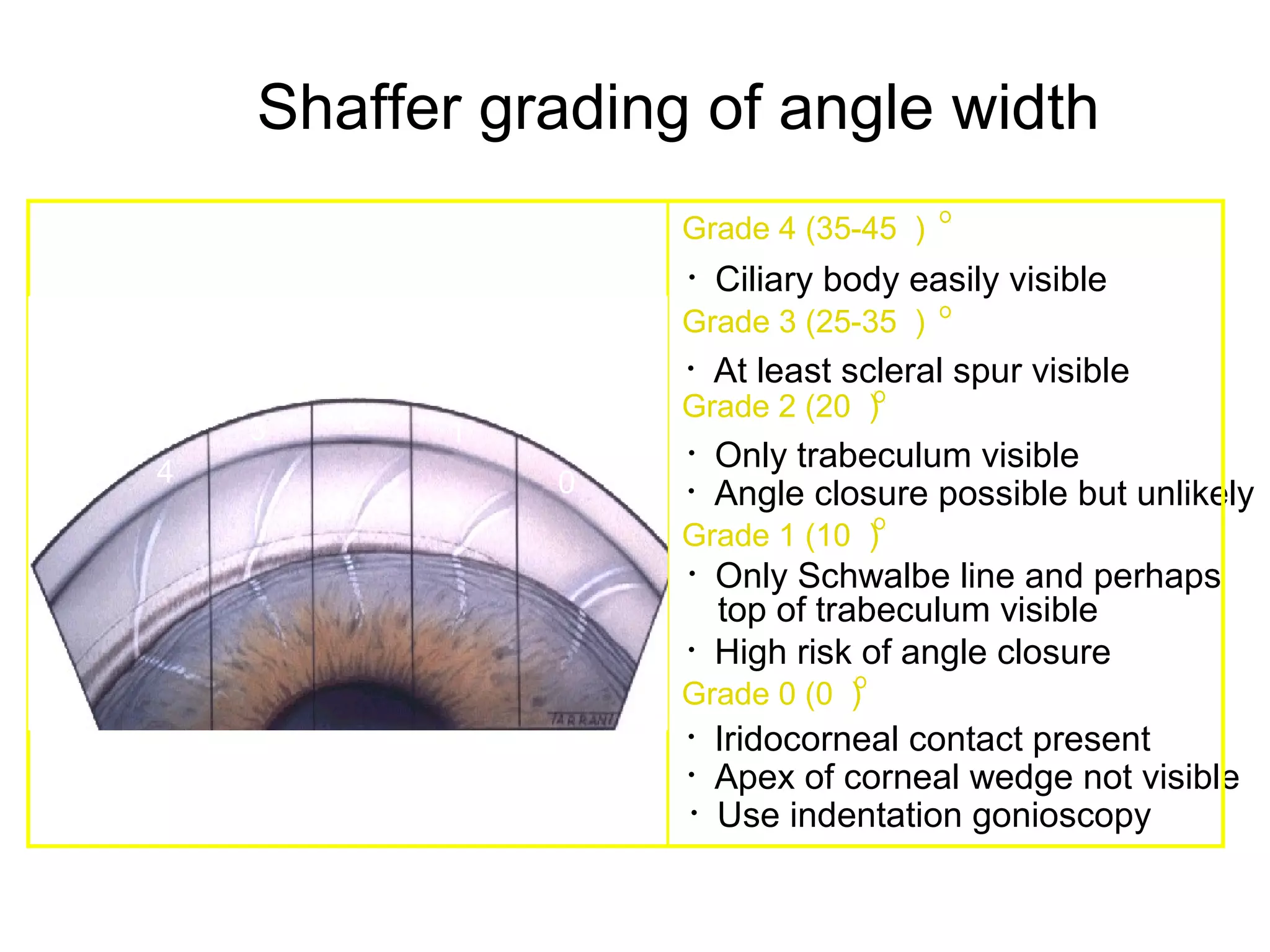
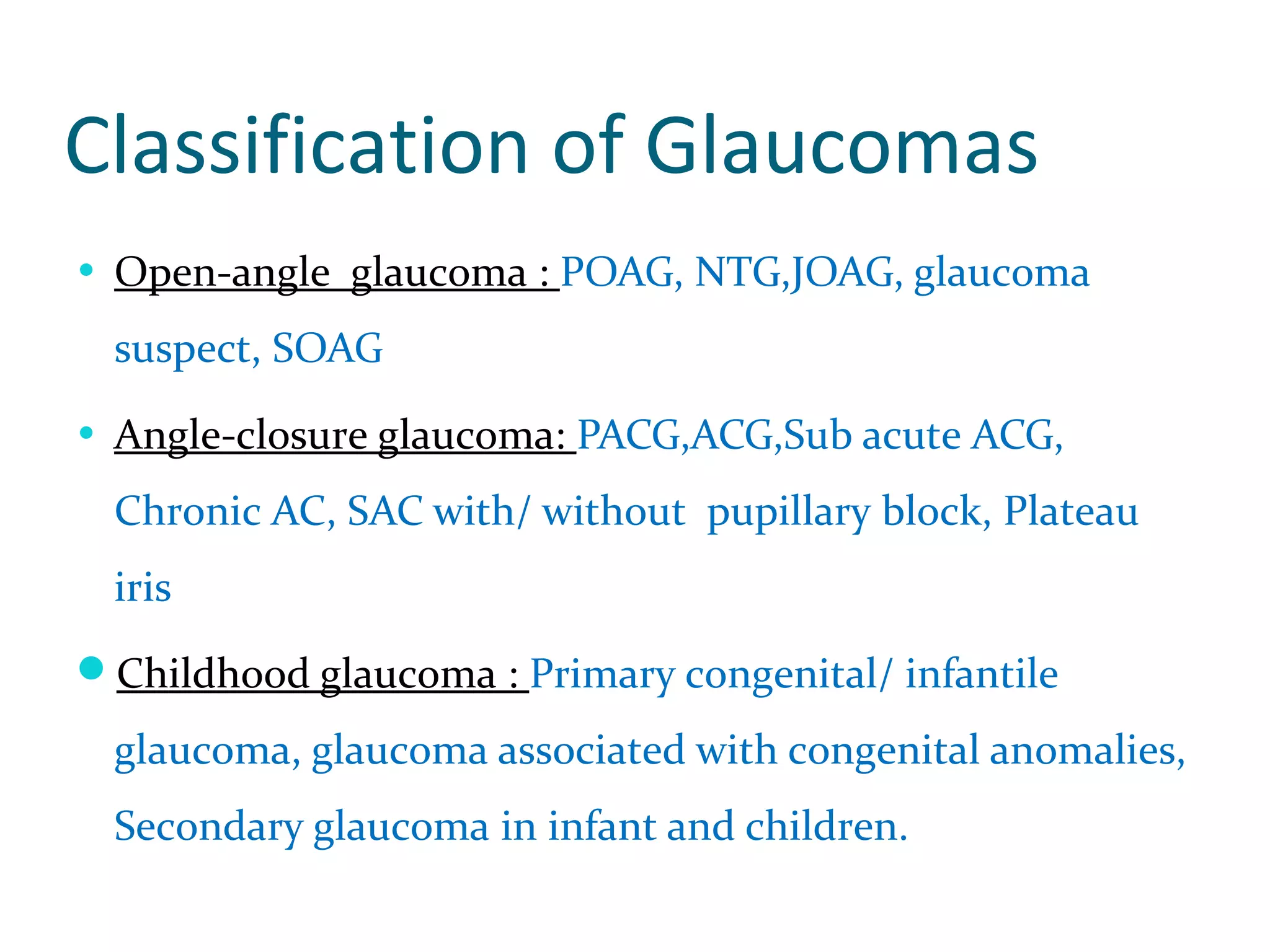
Glaucoma is defined as a group of diseases characterized by optic nerve damage and visual field loss. It is associated with elevated intraocular pressure but this is not required for diagnosis. The aqueous humor is produced by the ciliary body and drains through two pathways - the trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal or through the uveoscleral pathway. Investigations for glaucoma include tonometry, gonioscopy, optic nerve examination, and visual field testing. Glaucomas are classified as open-angle, angle-closure, childhood, and secondary to other conditions.