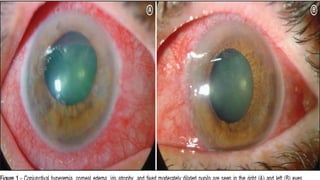
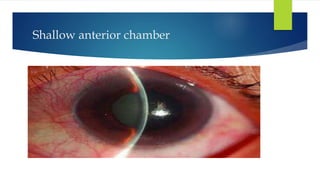
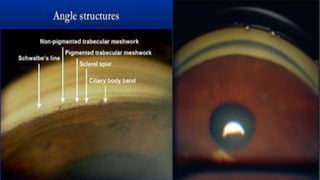
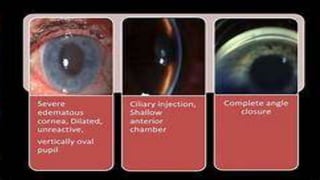
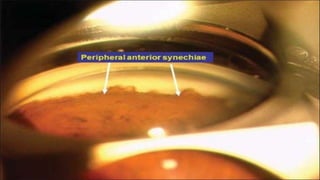
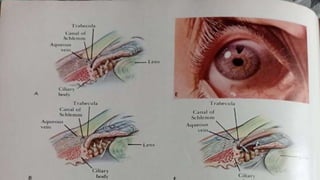
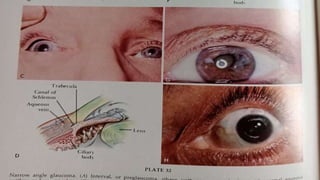
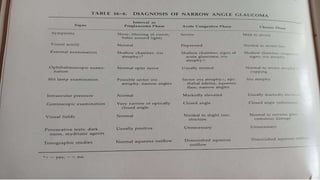
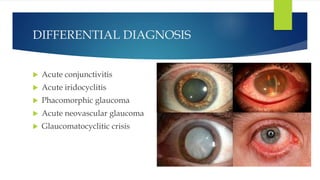
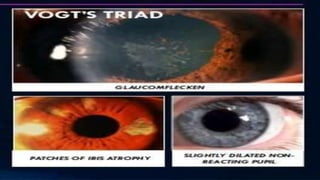
Acute congestive glaucoma is a sight-threatening emergency caused by sudden angle closure, leading to severe intraocular pressure (IOP) increase and resulting symptoms such as acute eye pain, headache, and visual impairment. Management involves immediate medical therapy to reduce IOP and definitive treatments like laser peripheral iridotomy or filtration surgery, especially for the asymptomatic fellow eye which has a high risk of developing the condition. Long-term follow-up and IOP management are crucial to prevent glaucomatous blindness.