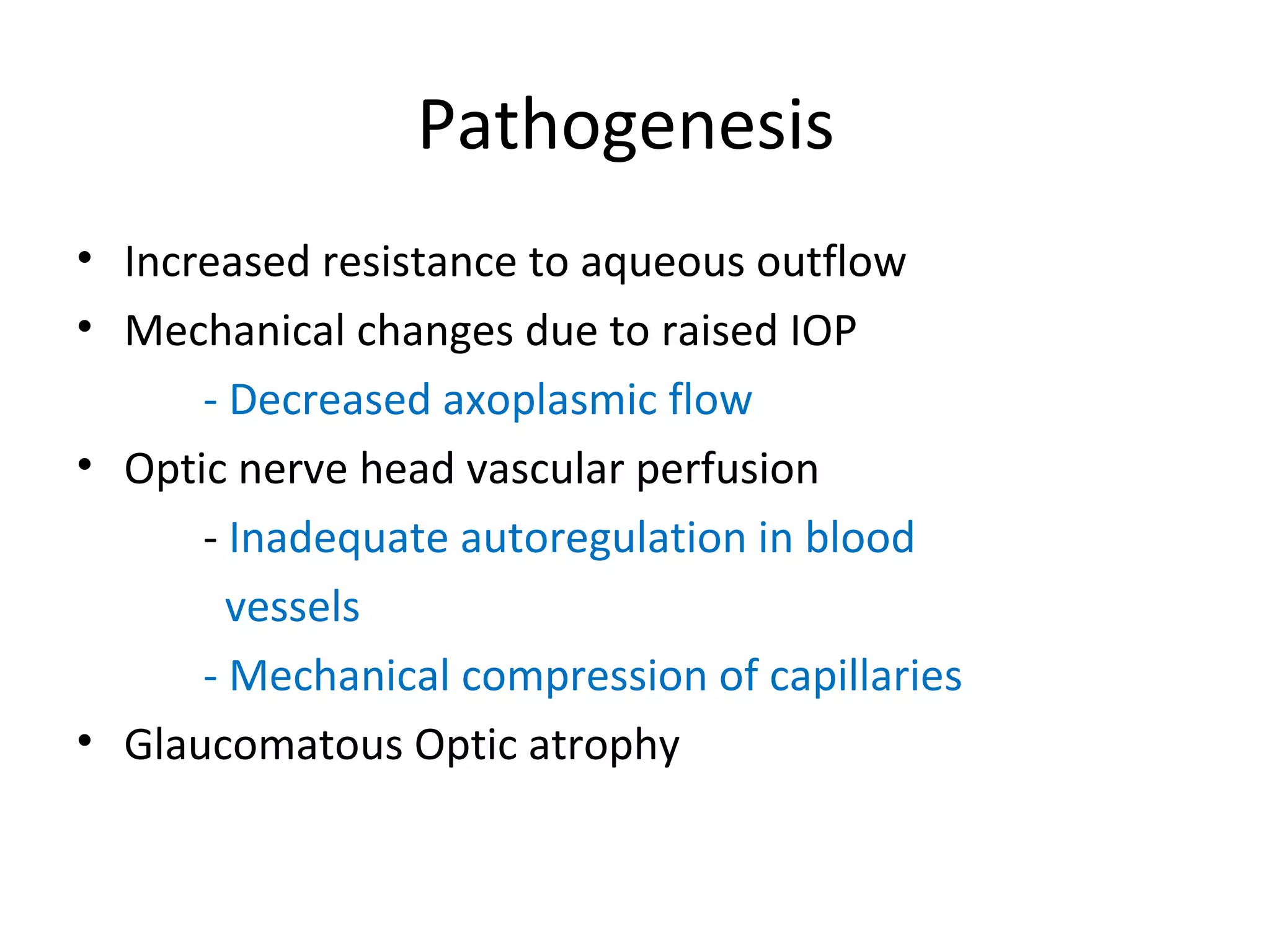
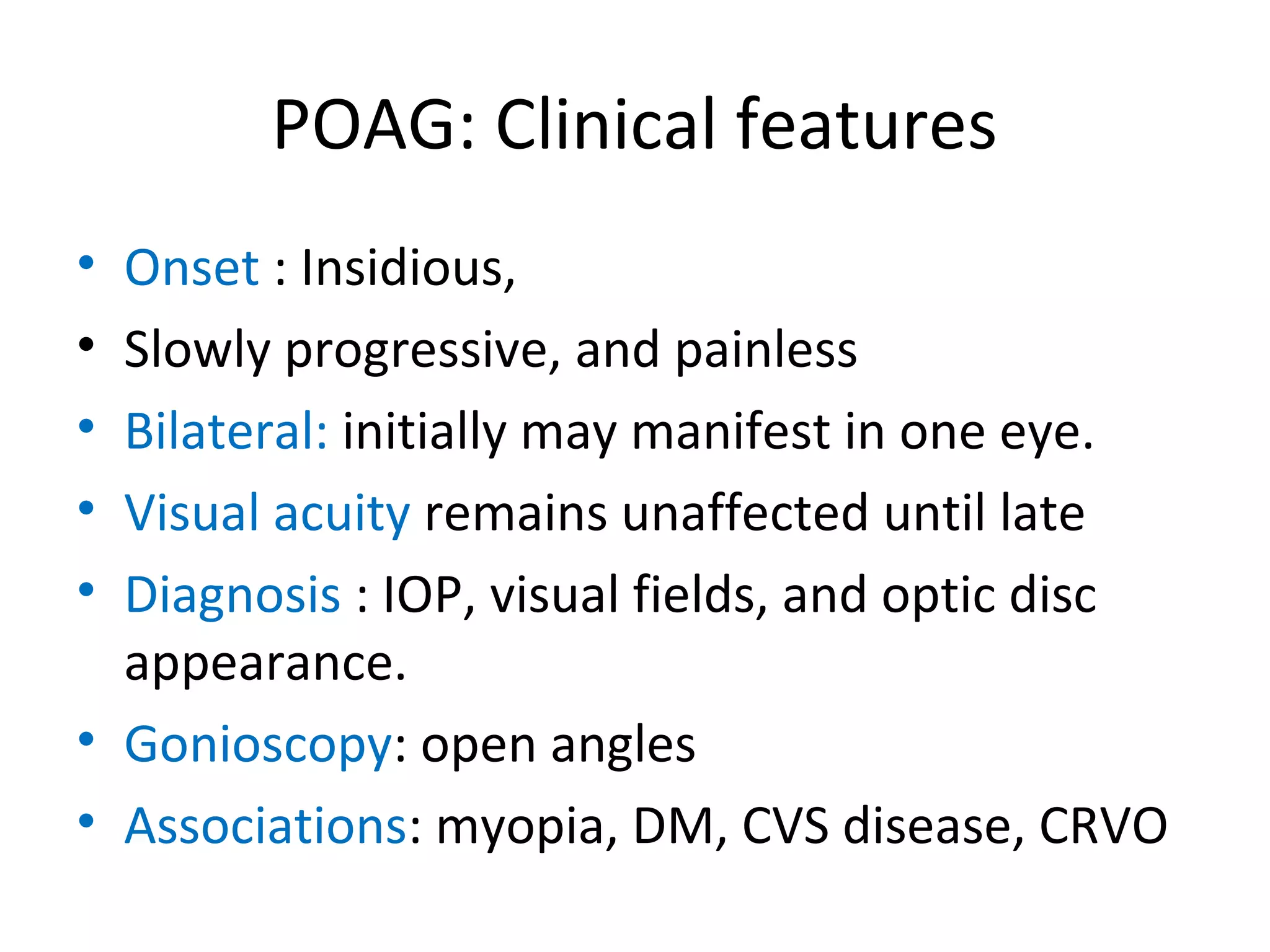
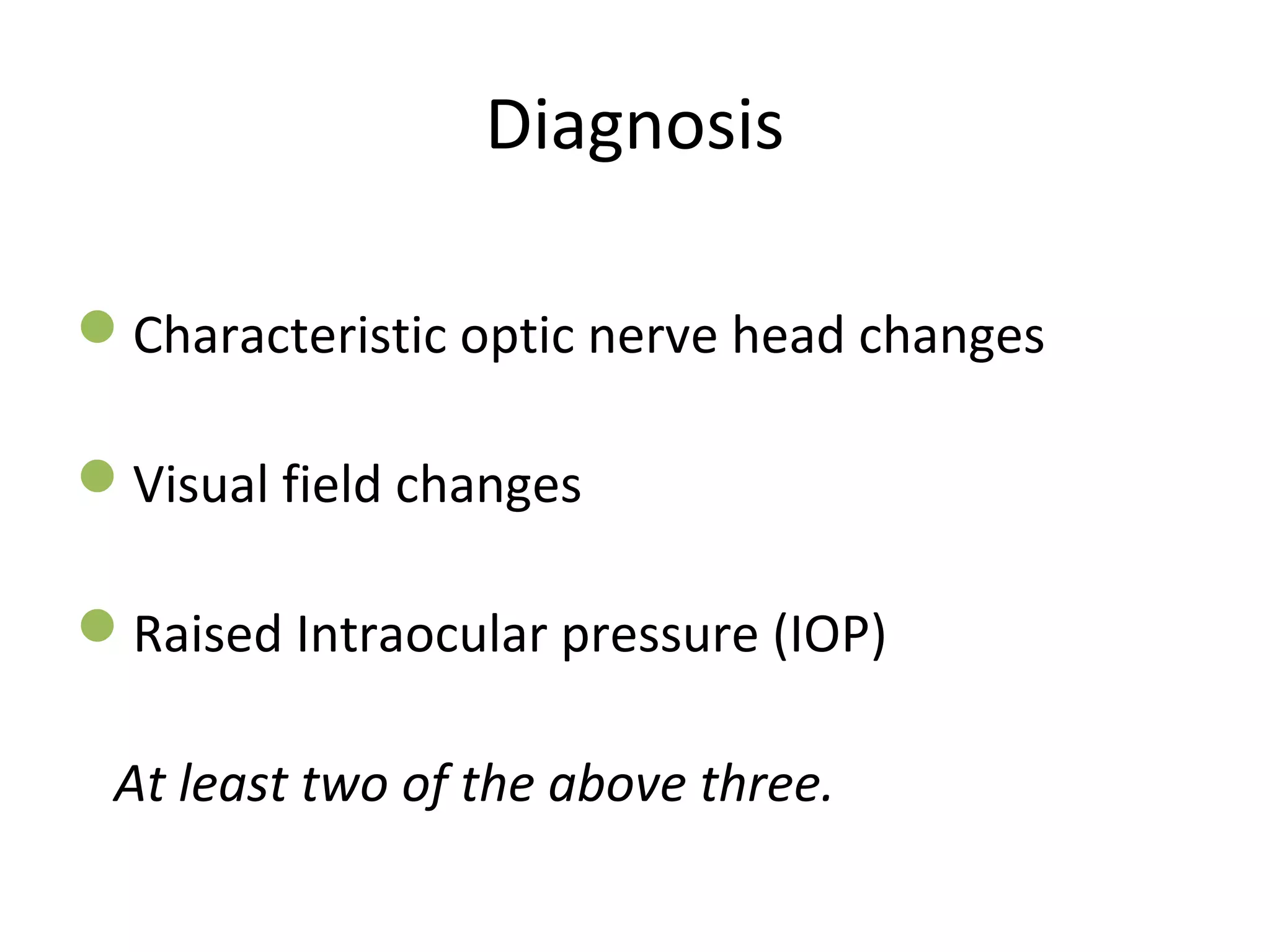
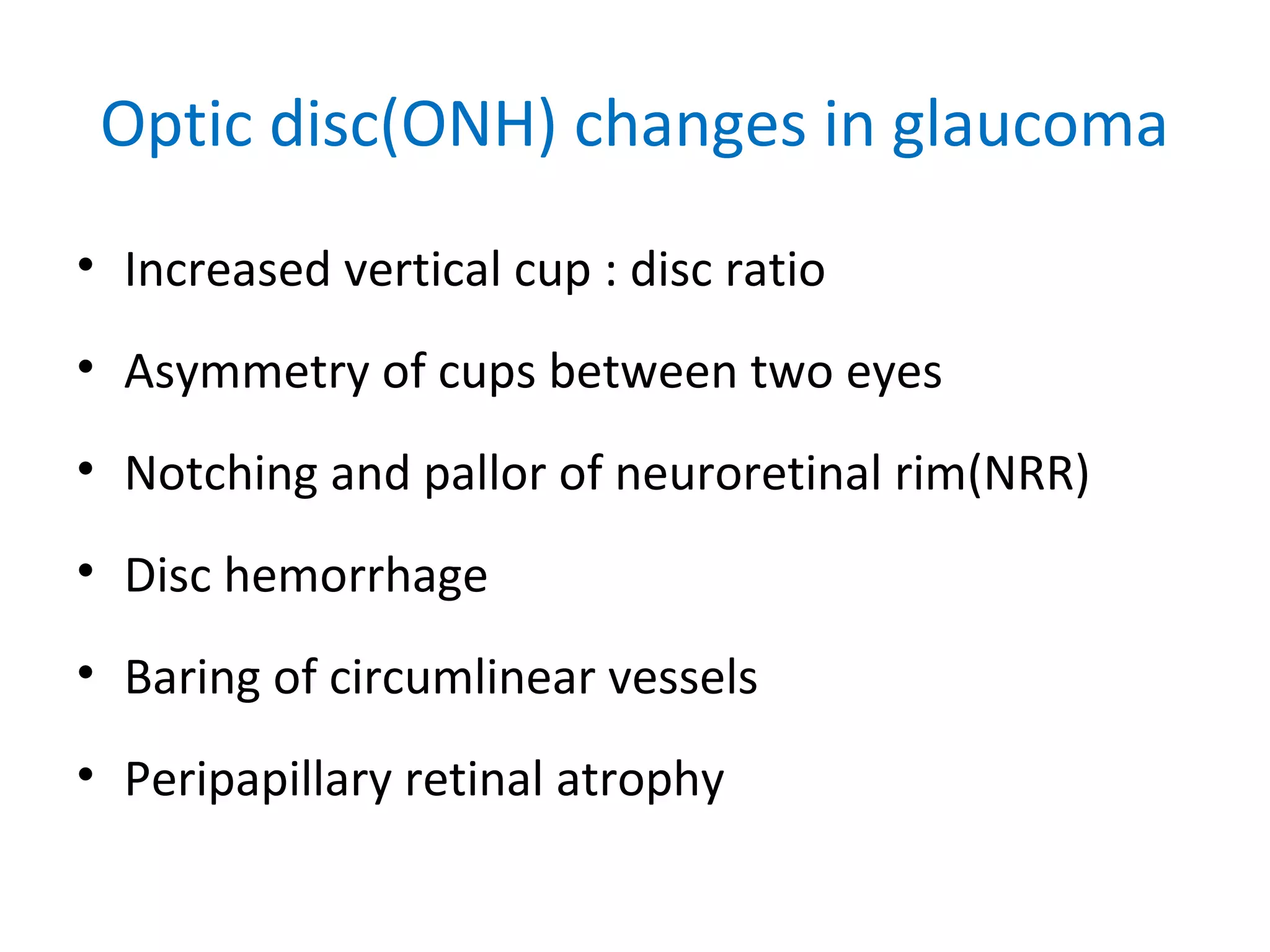
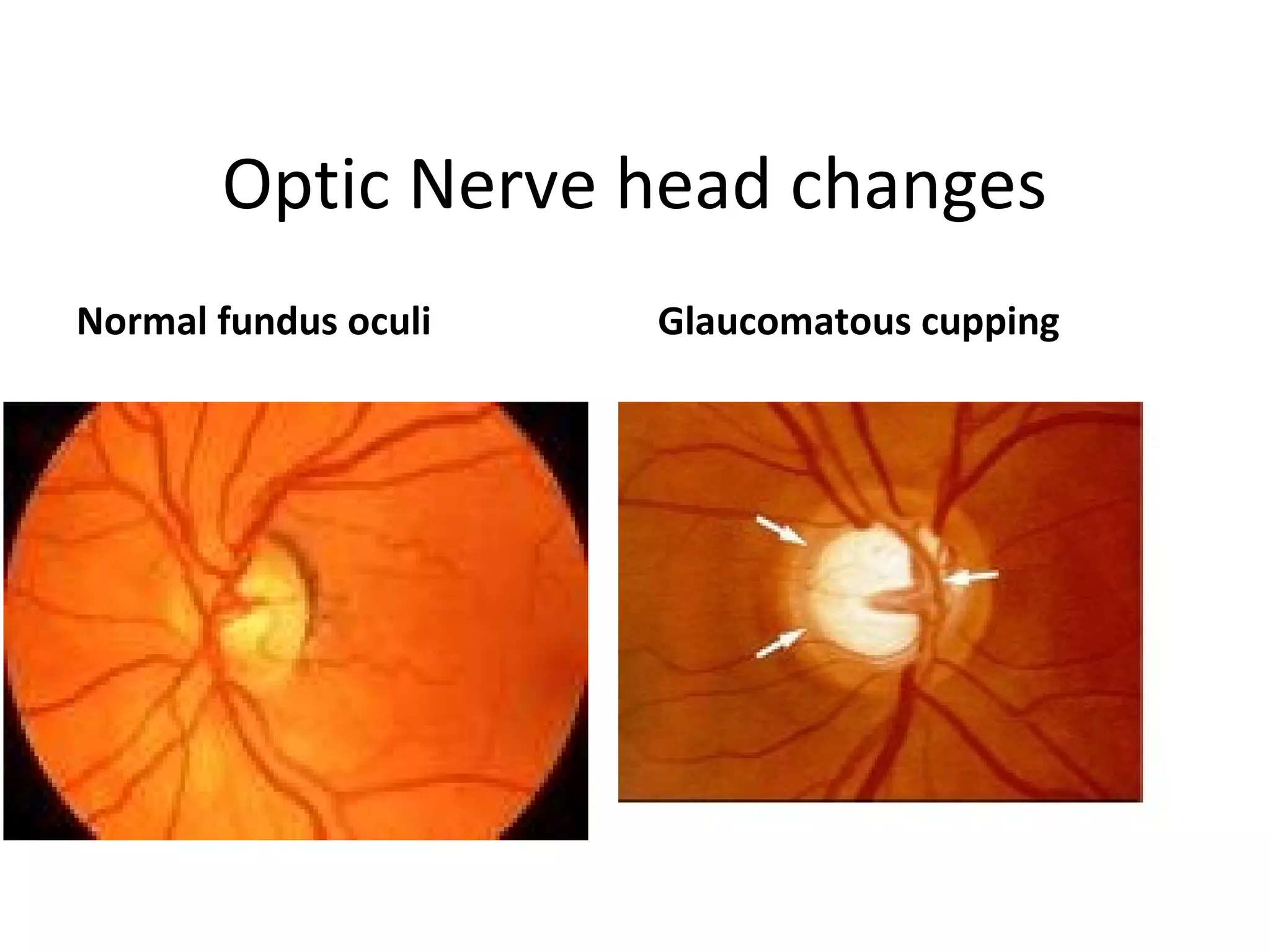
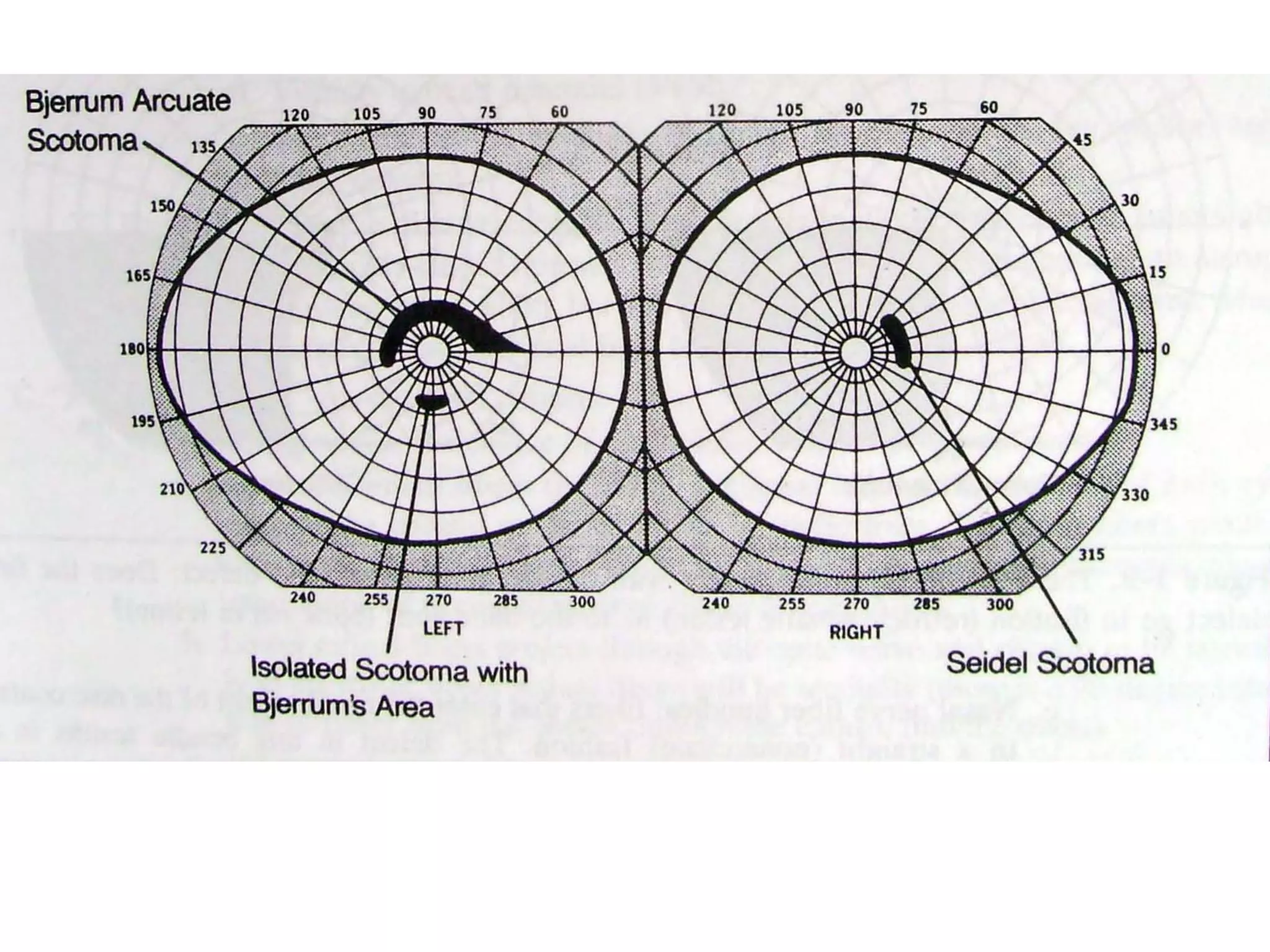
Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is characterized by optic nerve damage and visual field loss due to increased intraocular pressure without obstruction of the eye's drainage angle. It has no known cause but risks include older age, family history, and higher eye pressure. Diagnosis is based on optic nerve head changes, visual field testing showing blind spots, and elevated intraocular pressure. Treatment aims to lower pressure through eye drops, laser therapy, or surgery to slow progression and preserve vision. Regular monitoring of pressure and nerve changes is needed for long-term management.