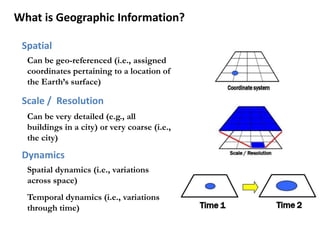
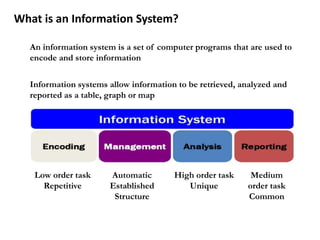
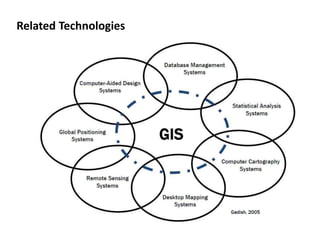
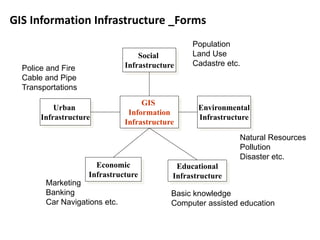
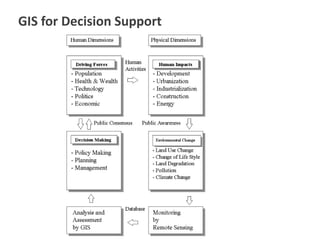
This document provides an overview of a Geographic Information Systems (GIS) course. It defines GIS as a computer tool that combines database and mapping technologies to create maps where every point, line, or polygon is connected to a database. GIS allows users to spend time reviewing, understanding, querying, and classifying geospatial data to solve problems with a spatial component. The document also outlines the key components, applications, related technologies, benefits, and basic functions of GIS systems.