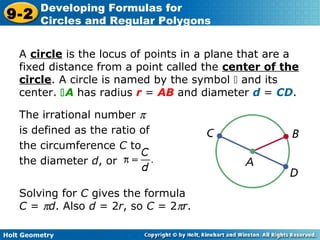
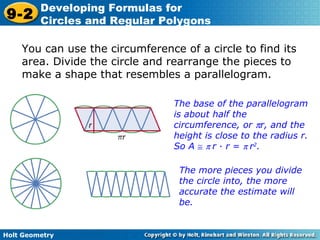
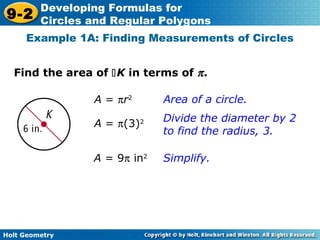
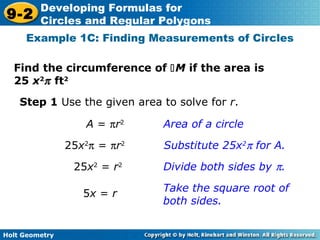
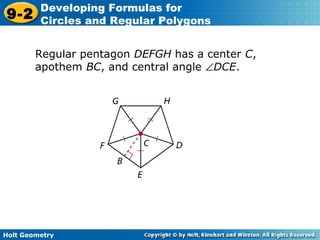
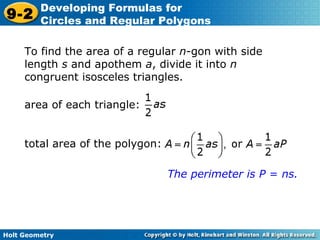
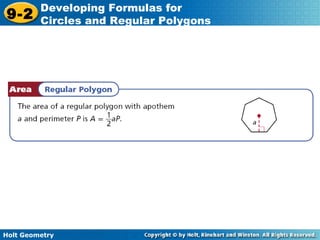
The document discusses formulas for circles and regular polygons. It defines key terms like radius, diameter, circumference, area, apothem, and central angle. Examples are provided for calculating circle measurements like circumference and area using formulas like C=2πr and A=πr^2. A formula is developed for the area of a regular polygon by dividing it into congruent triangles: A=(1/2)aps, where a is the apothem, p is the perimeter, and s is the side length. Worked examples demonstrate calculating measurements for circles and finding areas of regular polygons.