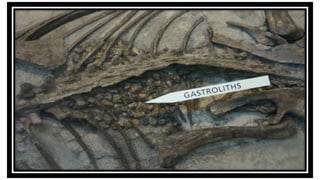
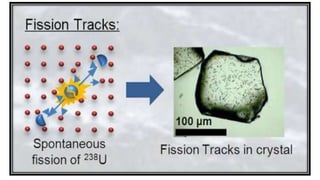
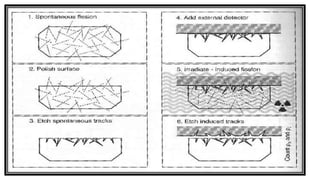
This document discusses different types of fossils and fission track dating. It describes various ways that organisms can be preserved as fossils, including their entire bodies, original hard parts, skeletons, altered hard parts, and traces. Examples are given for each type like insects preserved in amber. Fission track dating is also summarized as a technique used to date uranium-bearing minerals based on analyzing damage trails left by radioactive decay. Rocks suitable for this method include apatite, zircon, and granite. The document outlines the process of fission track dating and its applications in understanding mountain belts, sediment provenance, and basin thermal evolution.