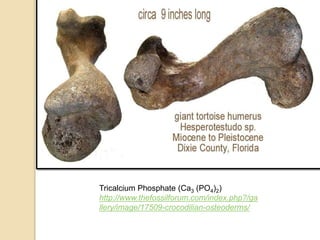
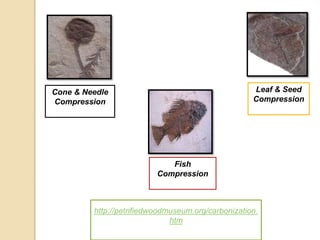
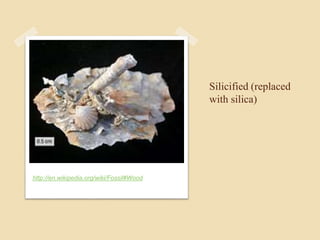
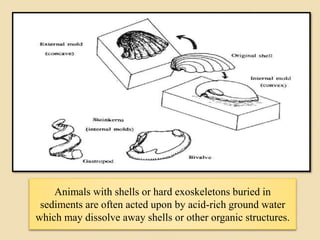
Fossilization is the process of preserving remains or traces of ancient organisms, crucial for paleontology. It includes body fossils, which preserve parts of organisms, and trace fossils, which consist of marks left by living organisms. Various conditions and materials, such as ice, amber, and volcanic ash, significantly affect fossilization and preservation outcomes.