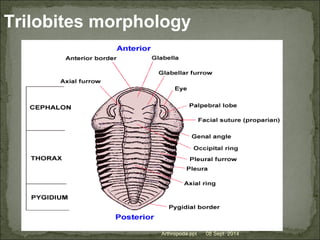
The document discusses the phylum Arthropoda, specifically the class Trilobita. Trilobites had a three-lobed body plan divided into three sections - the cephalon (head), thorax (body), and pygidium (tail). Their dorsal surface was protected by a calcareous exoskeleton. Trilobites first appeared in the Lower Cambrian period and became extinct by the end of the Paleozoic era. They exhibited changes over time including a reduction in thoracic segments and variations in eye and glabella morphology.