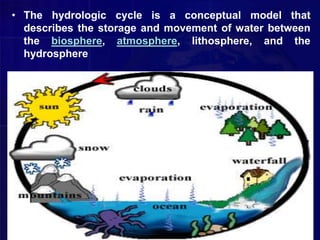
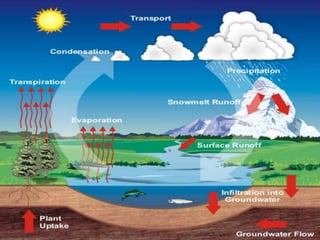
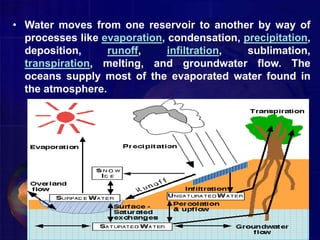
The hydrological cycle describes the storage and movement of water on Earth. Water moves between the biosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere through processes like evaporation, condensation, precipitation, deposition, runoff, infiltration, sublimation, transpiration, melting, and groundwater flow. The oceans supply most of the water that evaporates into the atmosphere. Water then falls as precipitation, runs off into streams and rivers, and eventually flows back into the oceans, completing the cycle.