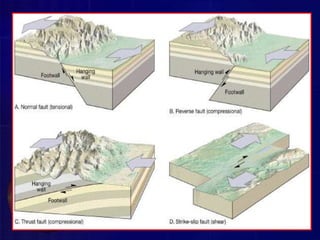
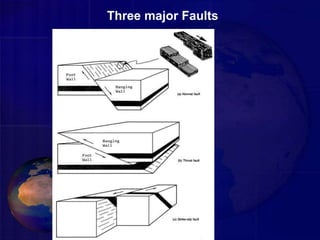
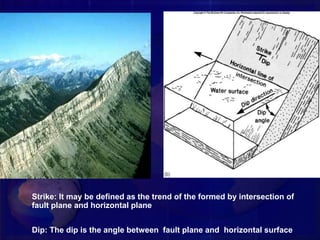
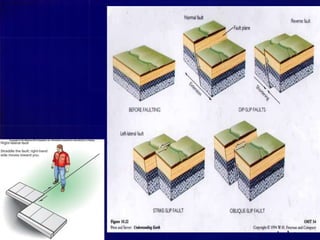
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock where one side has moved relative to the other. A fault divides the rock into a hanging wall and footwall. There are three major types of faults: normal faults, where the hanging wall has dropped down relative to the footwall; strike-slip faults, where the blocks move horizontally parallel to the strike of the fault; and oblique-slip faults, where there is both vertical and horizontal displacement at an angle. Faults can cause problems for civil engineering projects because the crushed rock in the fault zone is weak, unstable, and permeable.