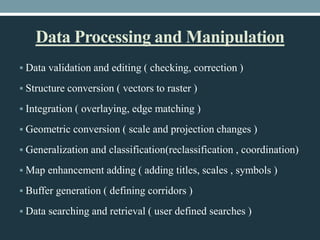
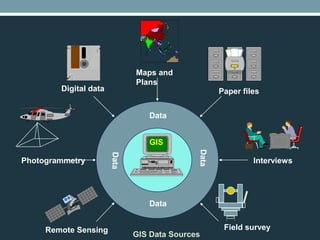
This document defines geographical information systems (GIS) and describes their key components and functions. GIS is defined as a system for capturing, storing, analyzing and managing data that is tied to specific locations. The key components of GIS are hardware, software, procedures, data and people. Hardware includes computers and input/output devices. Popular GIS software packages are listed. Procedures involve creating and editing maps and data. Data includes geospatial and attribute data from various sources. GIS has various functions including data processing, analysis, display and database management to support decision making.