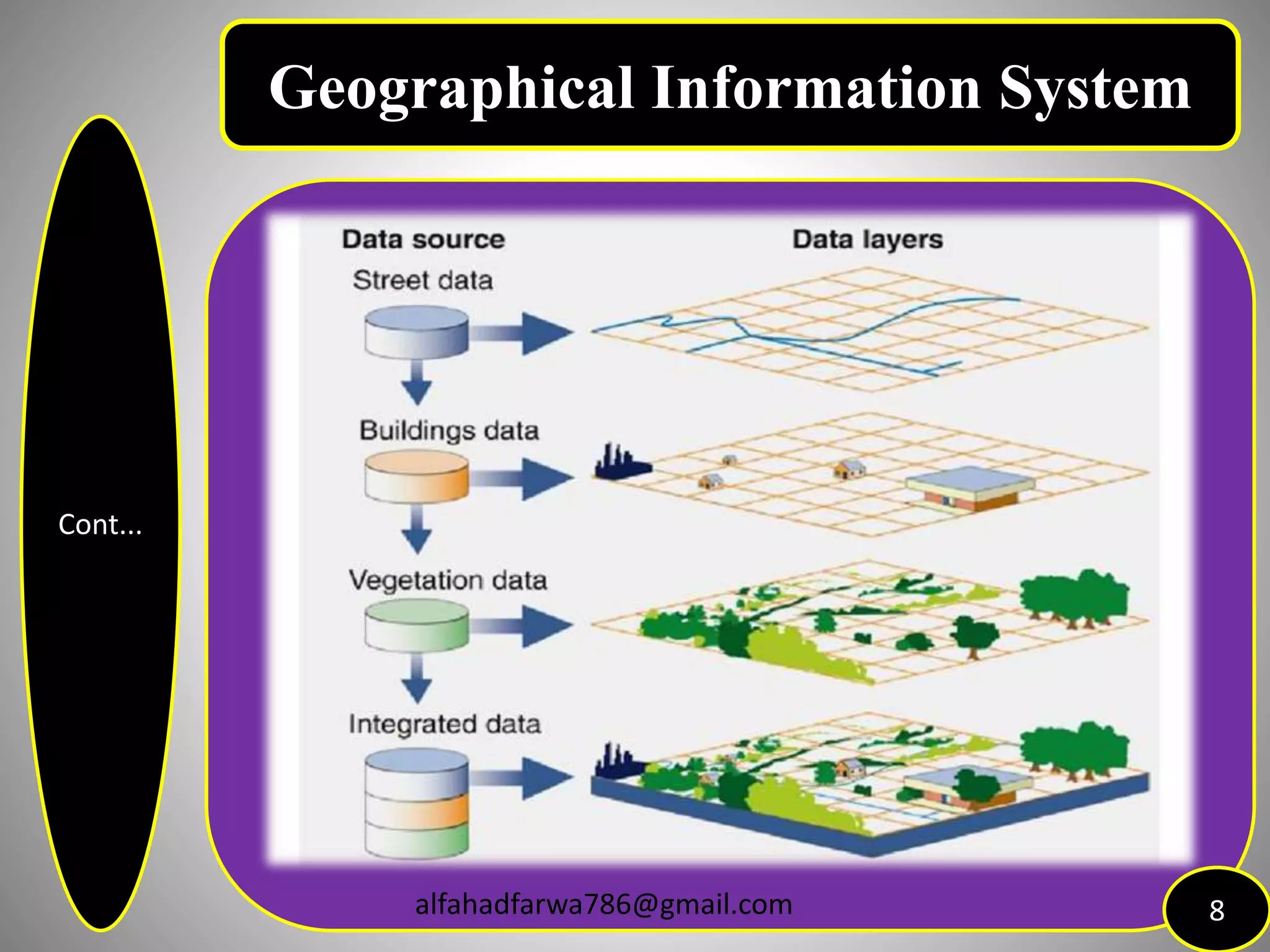
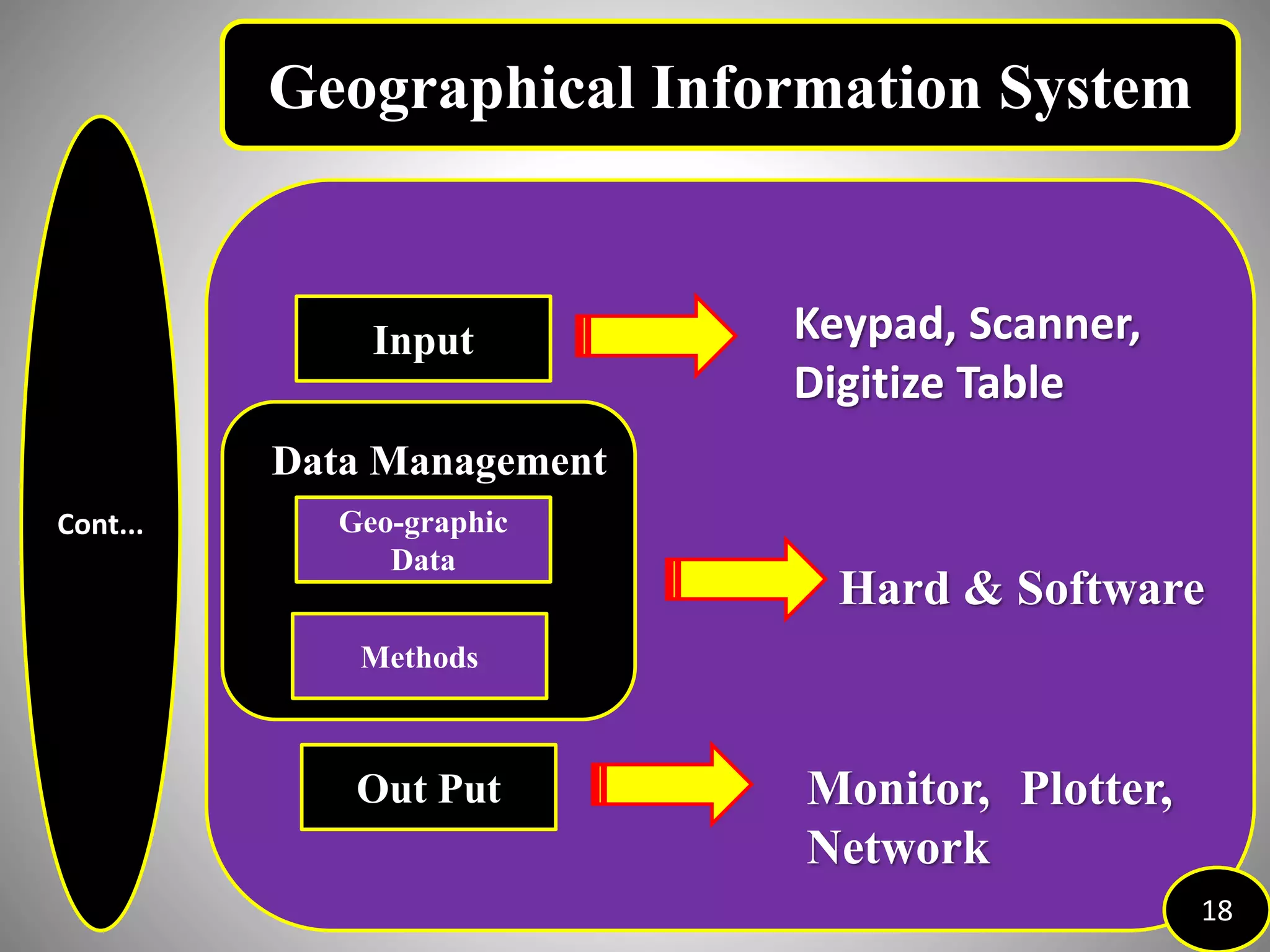
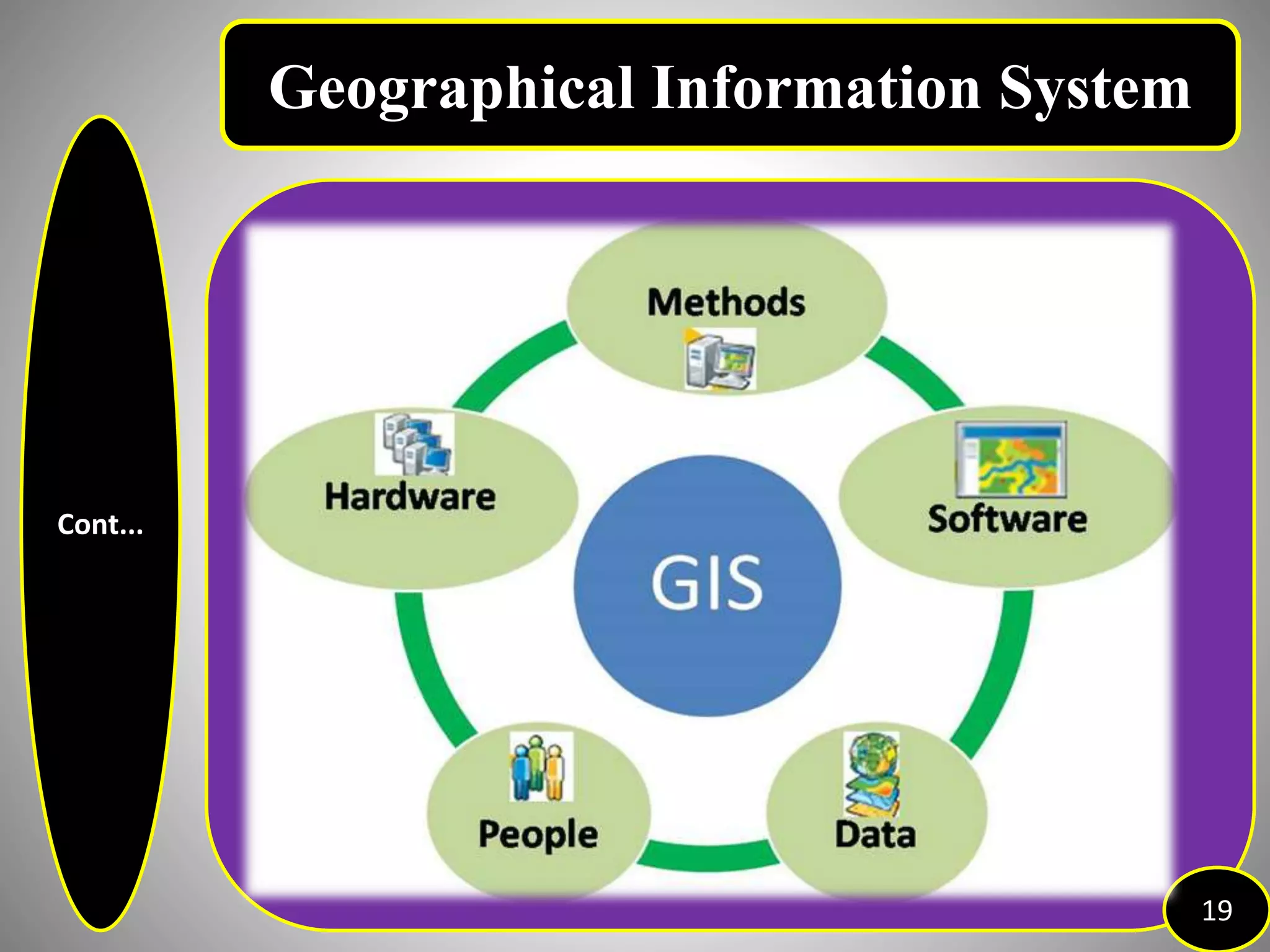
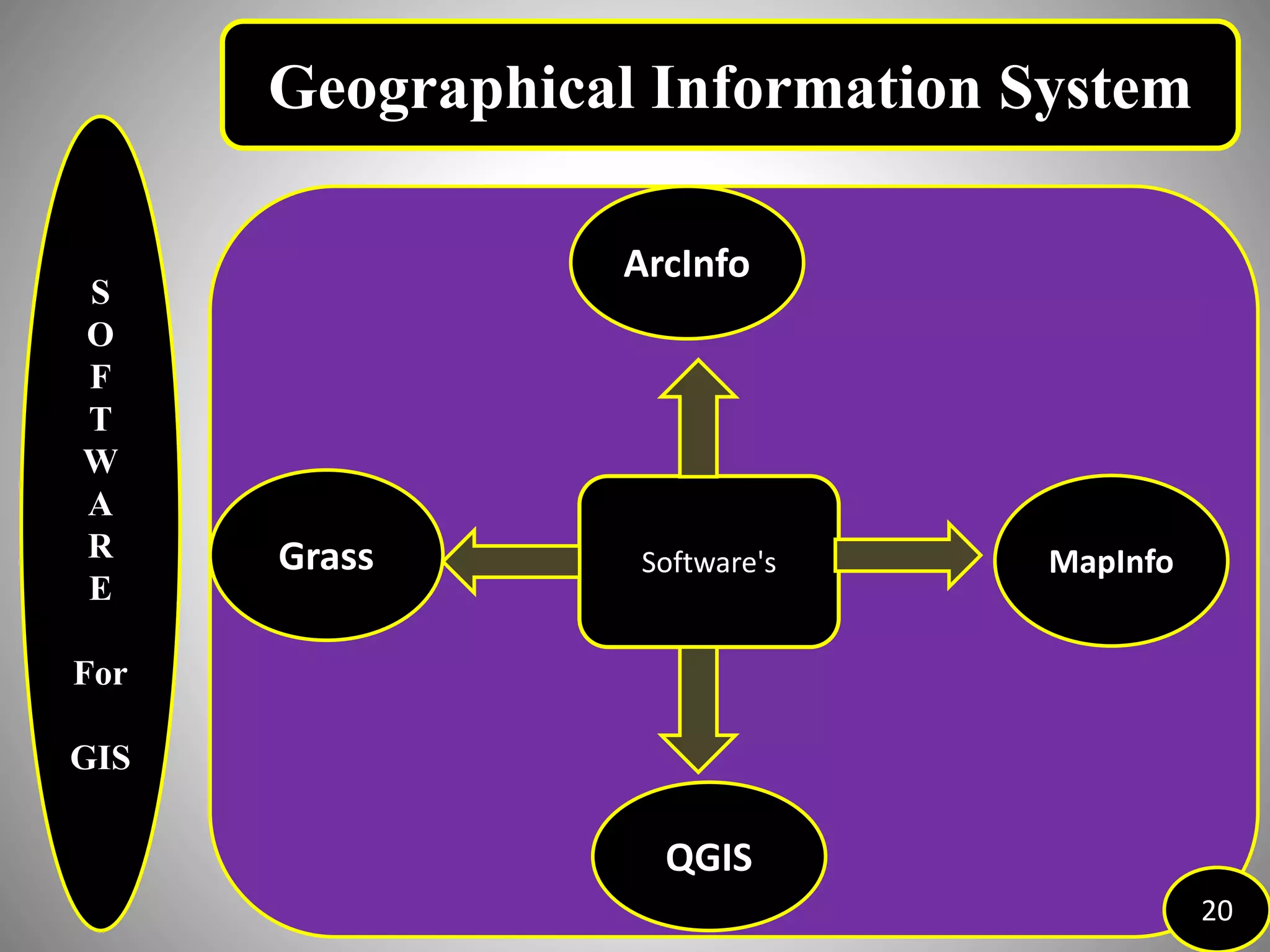
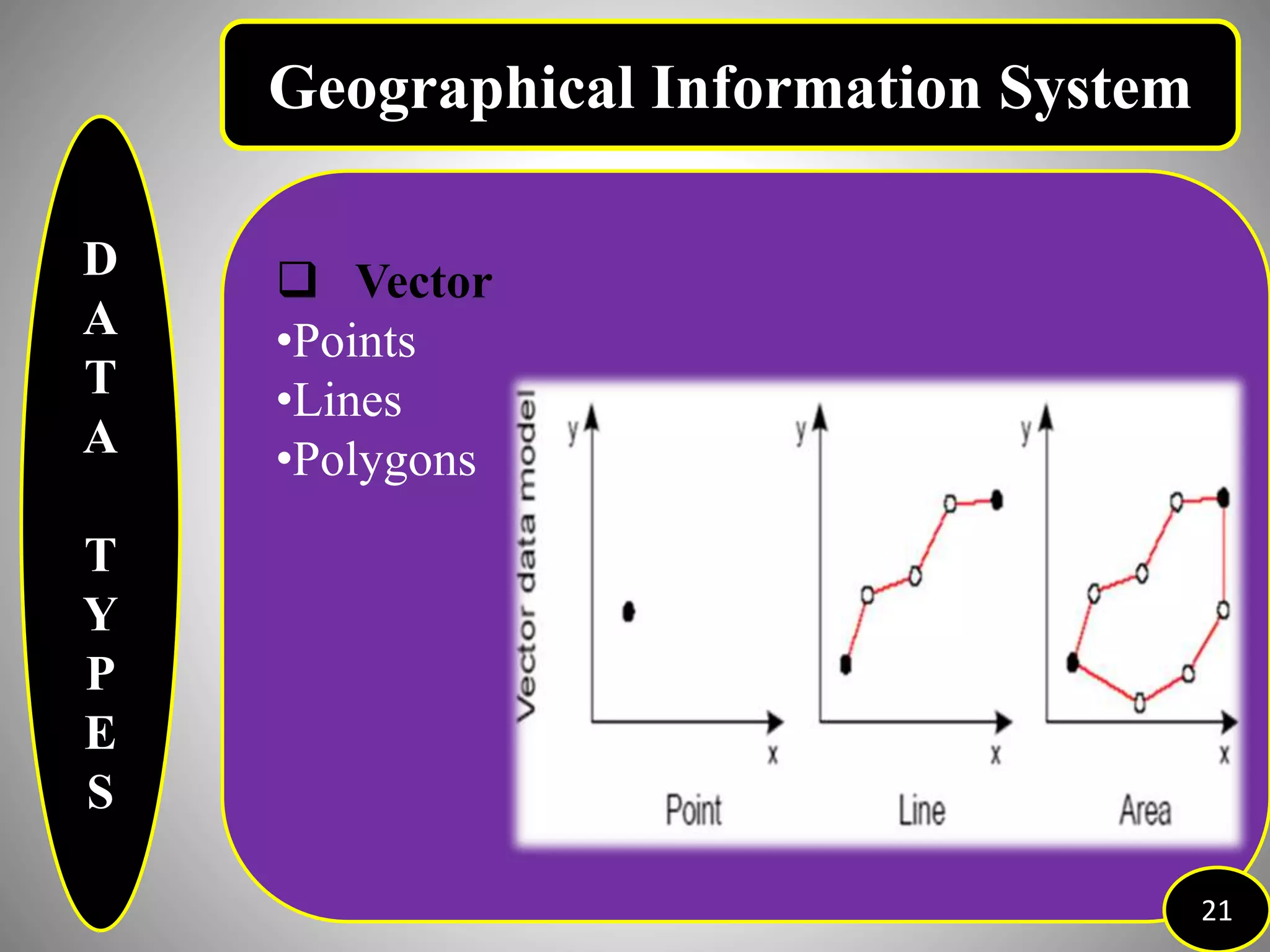
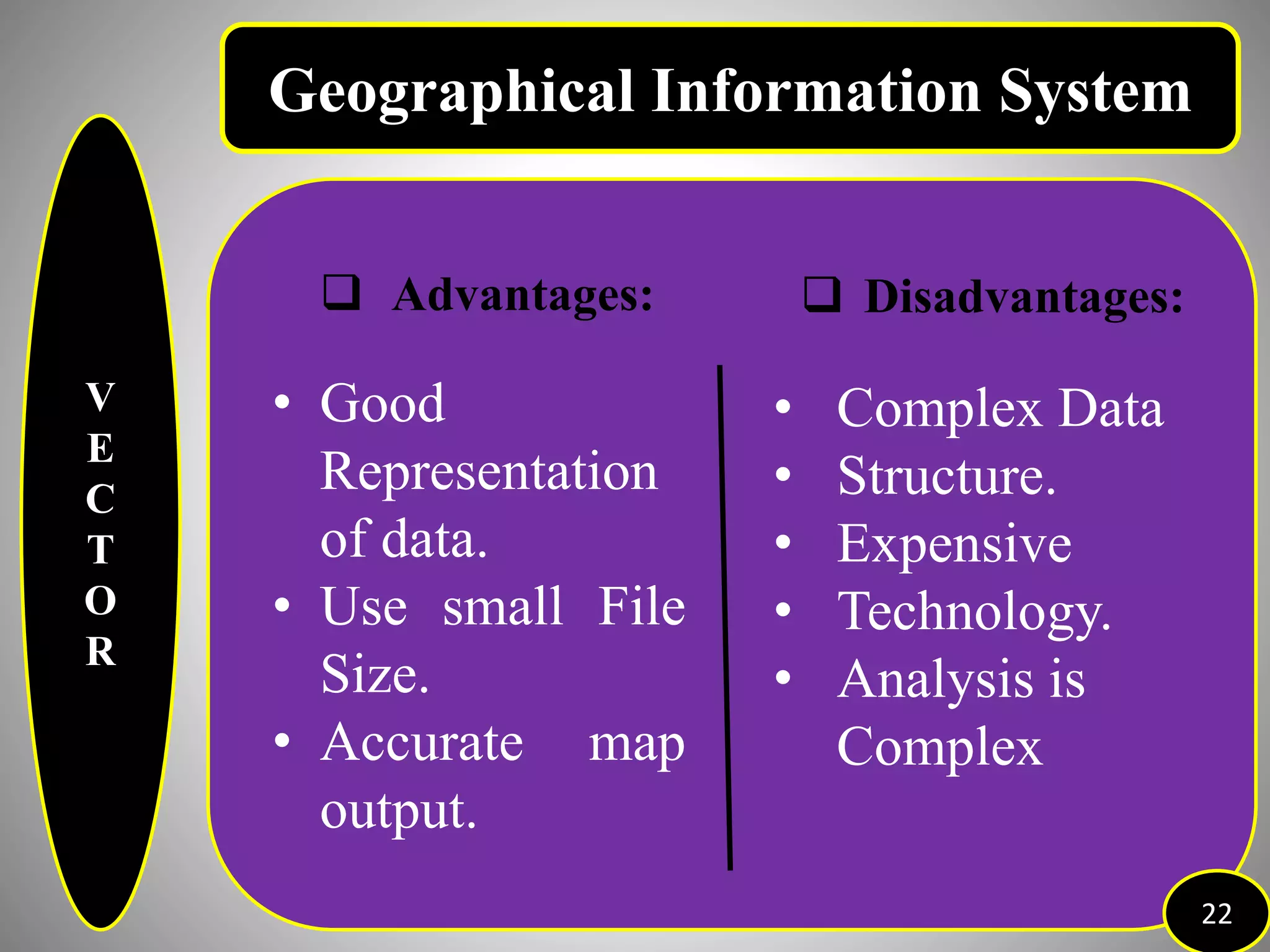
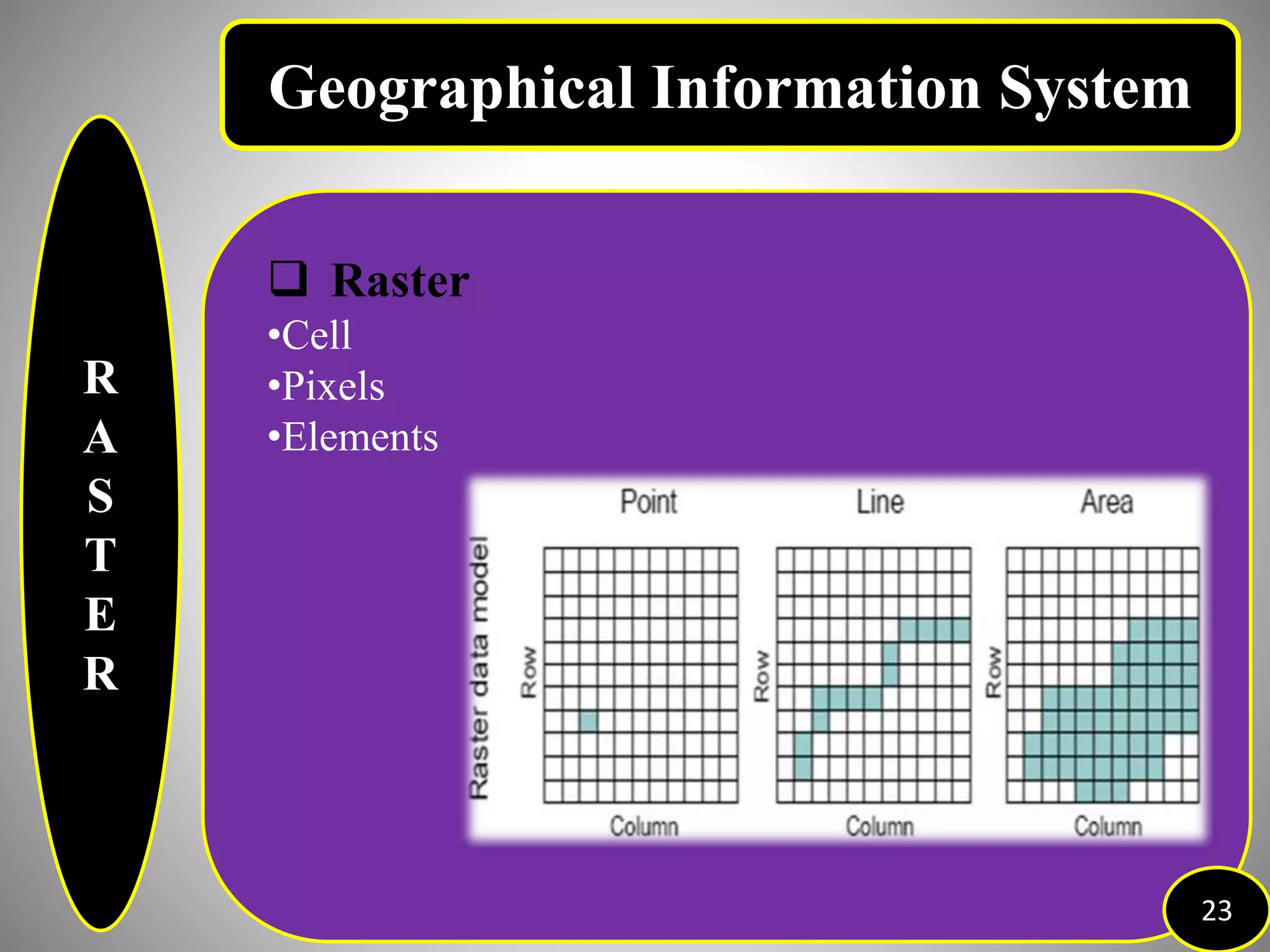
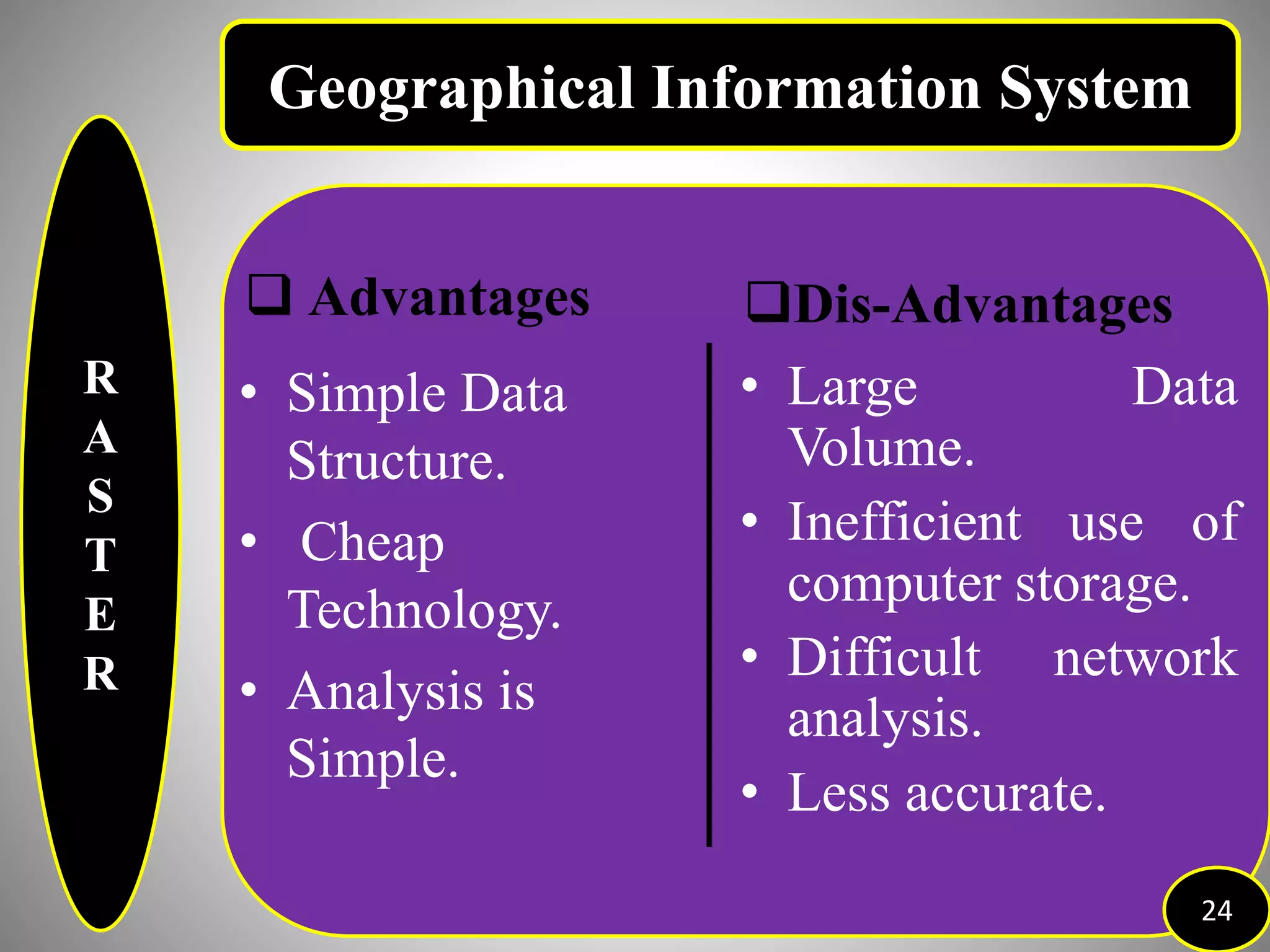
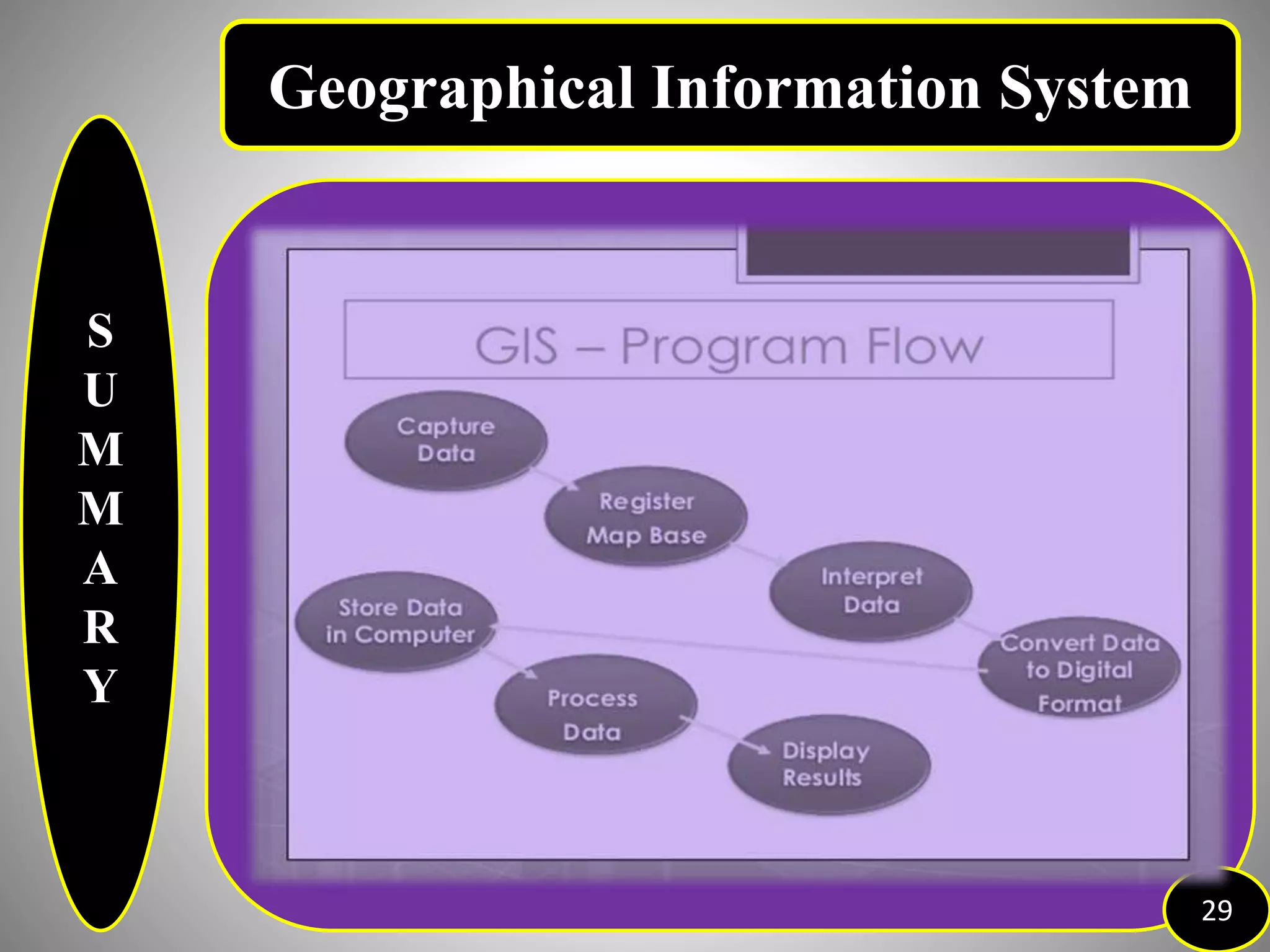
The document provides an overview of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), detailing its definition, history, functions, advantages, and disadvantages. GIS is a system for collecting, storing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data, which has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s. It outlines various existing GIS systems, proposed functionalities for improved user experiences, and the importance of data types, capturing methods, and software utilized in the field.