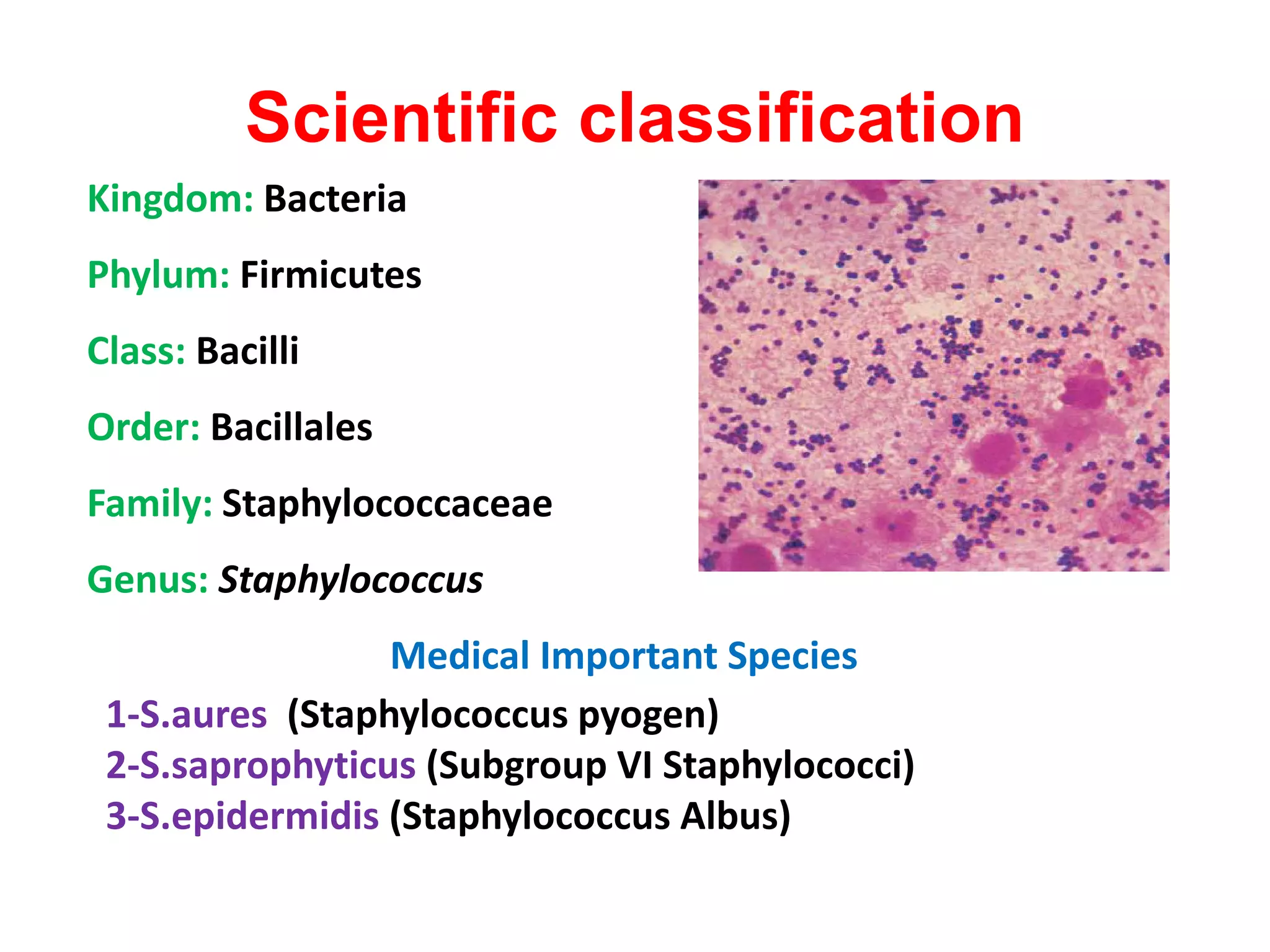
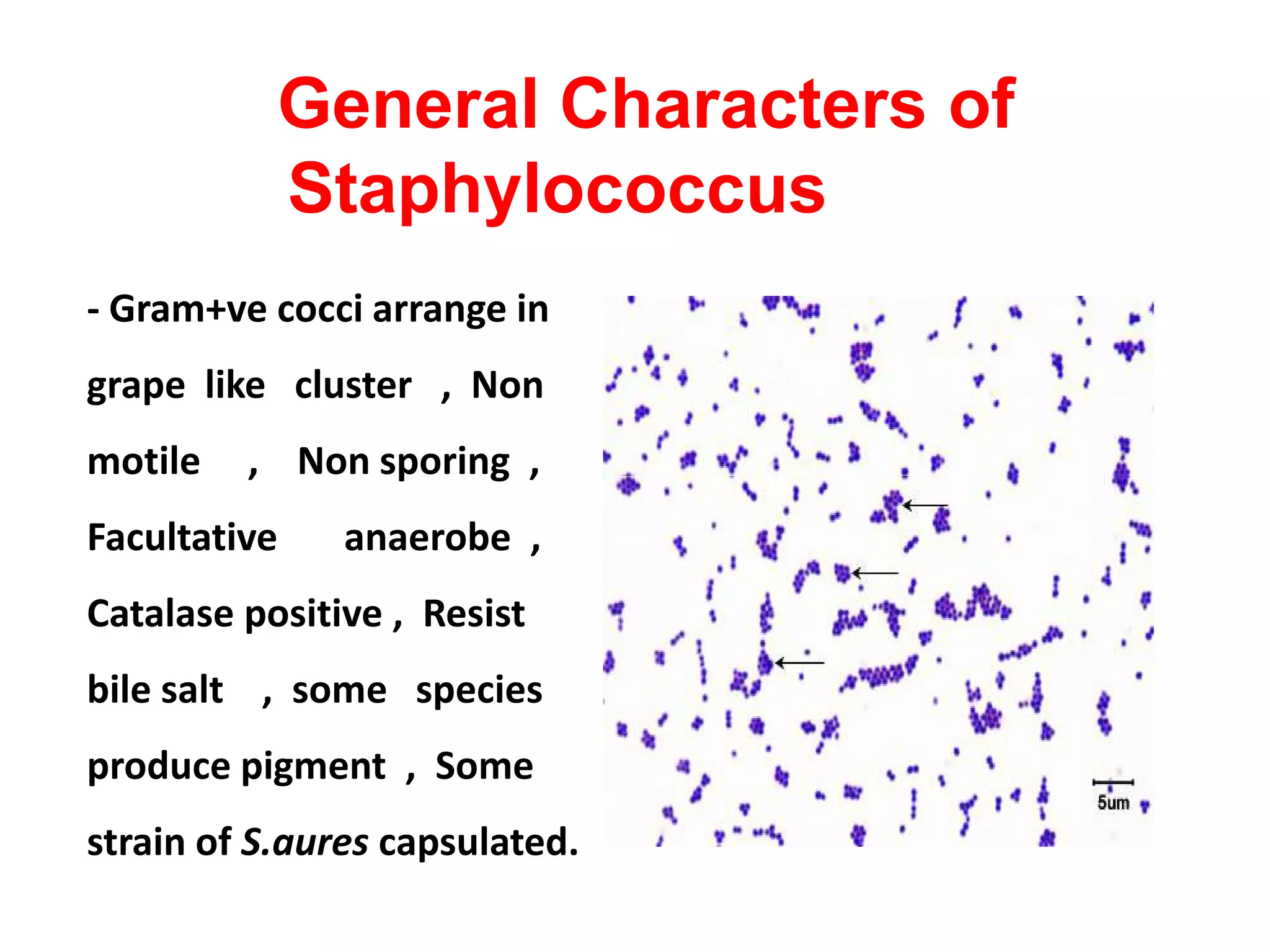
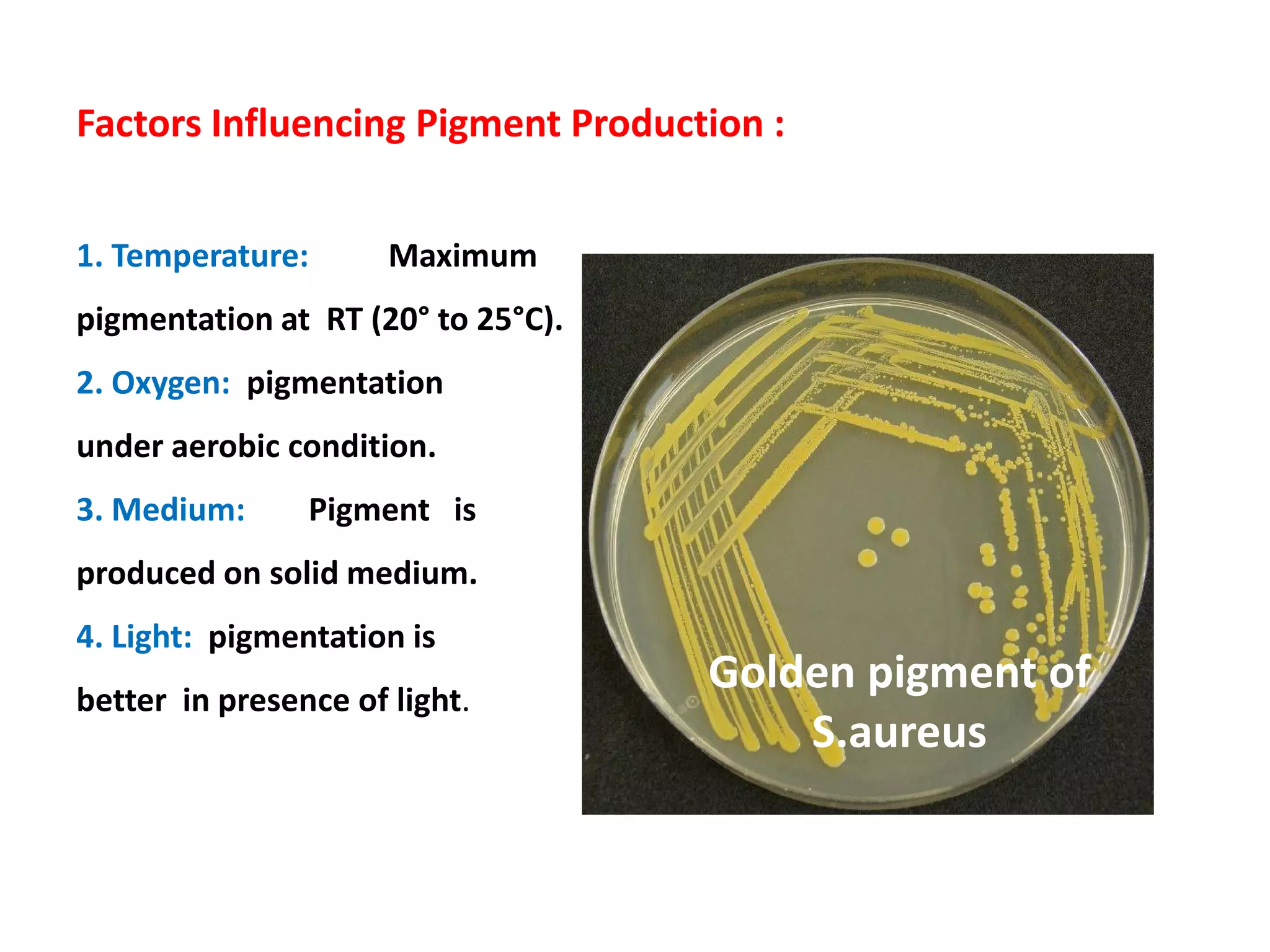
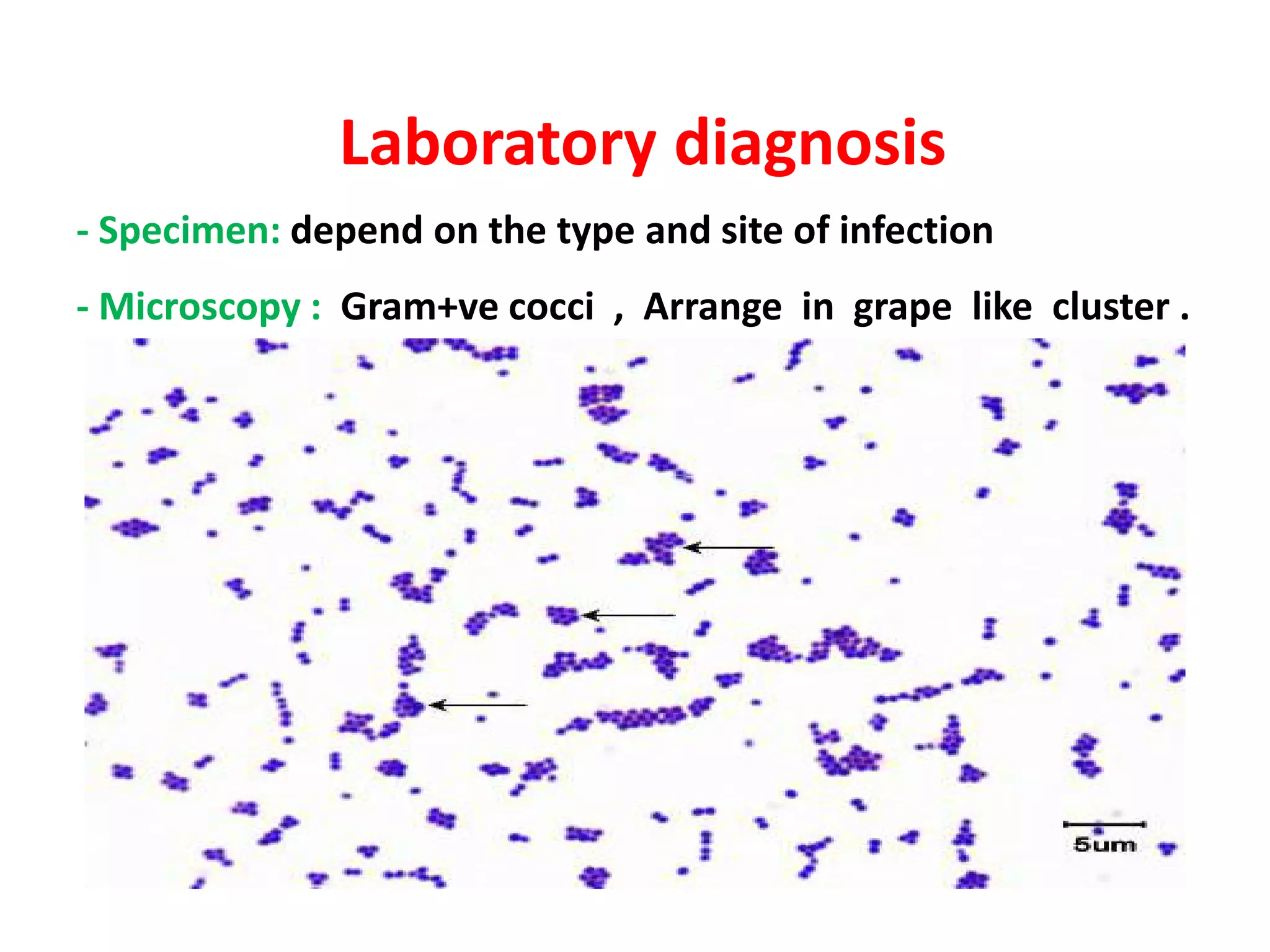
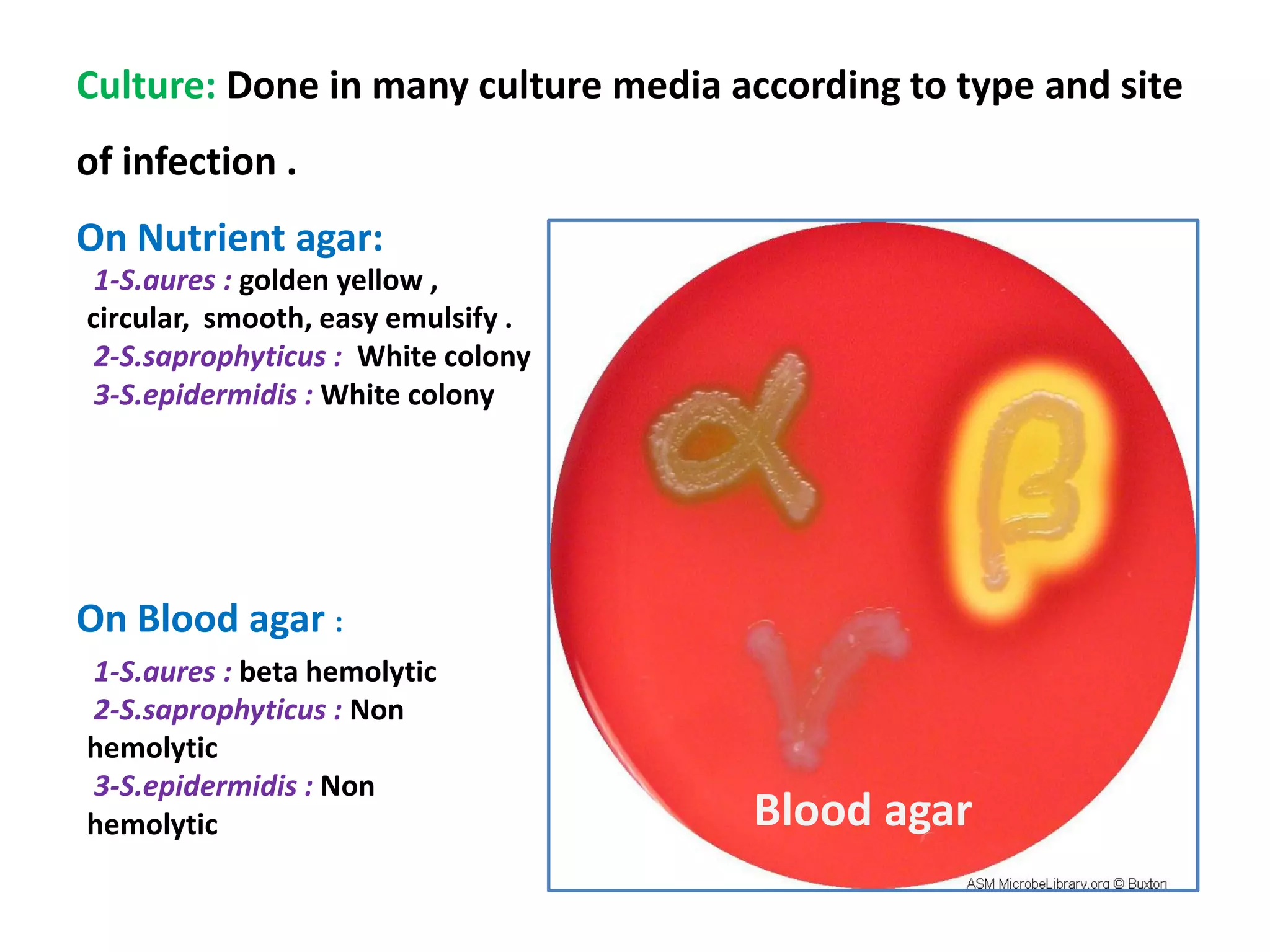
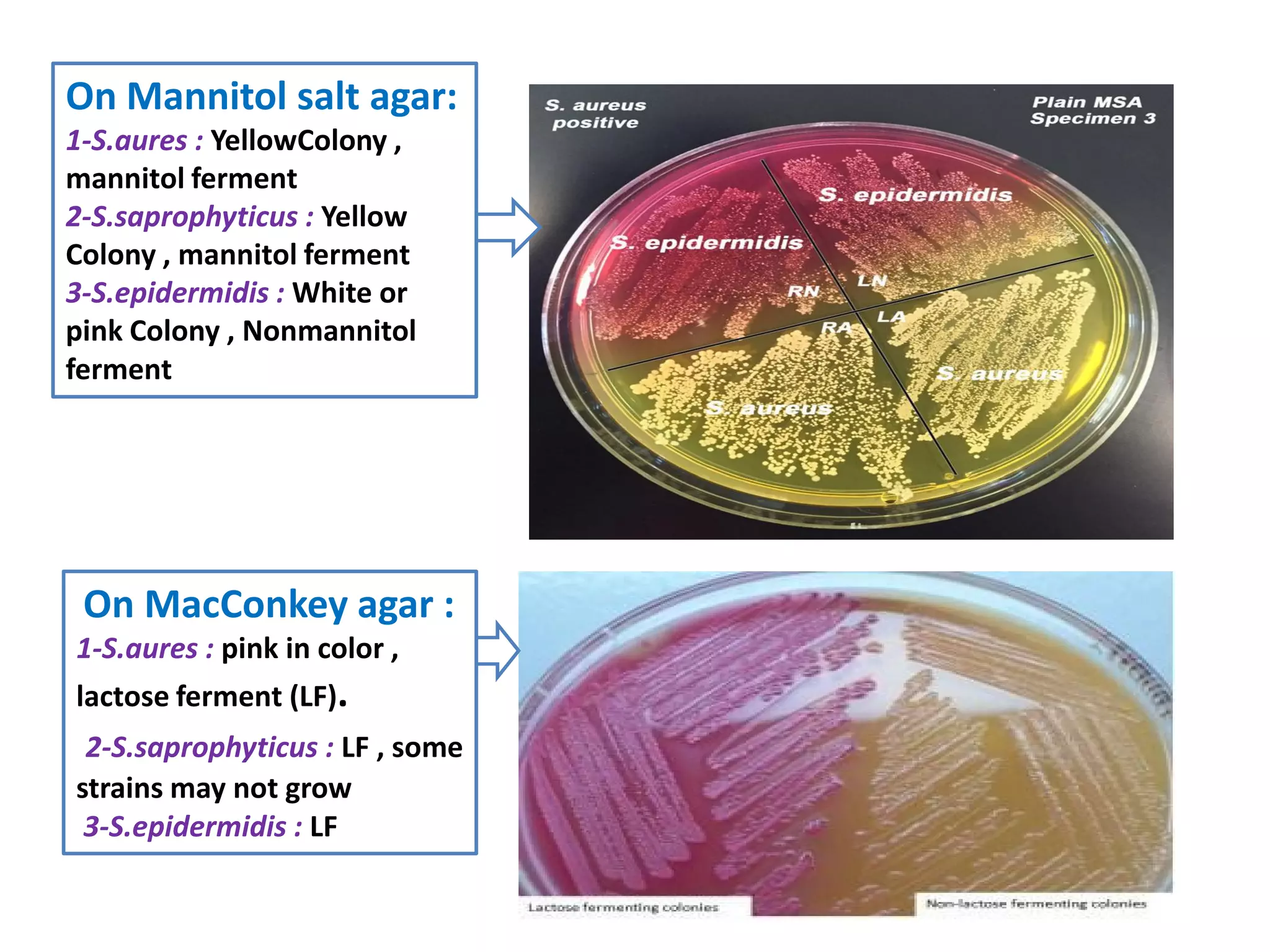
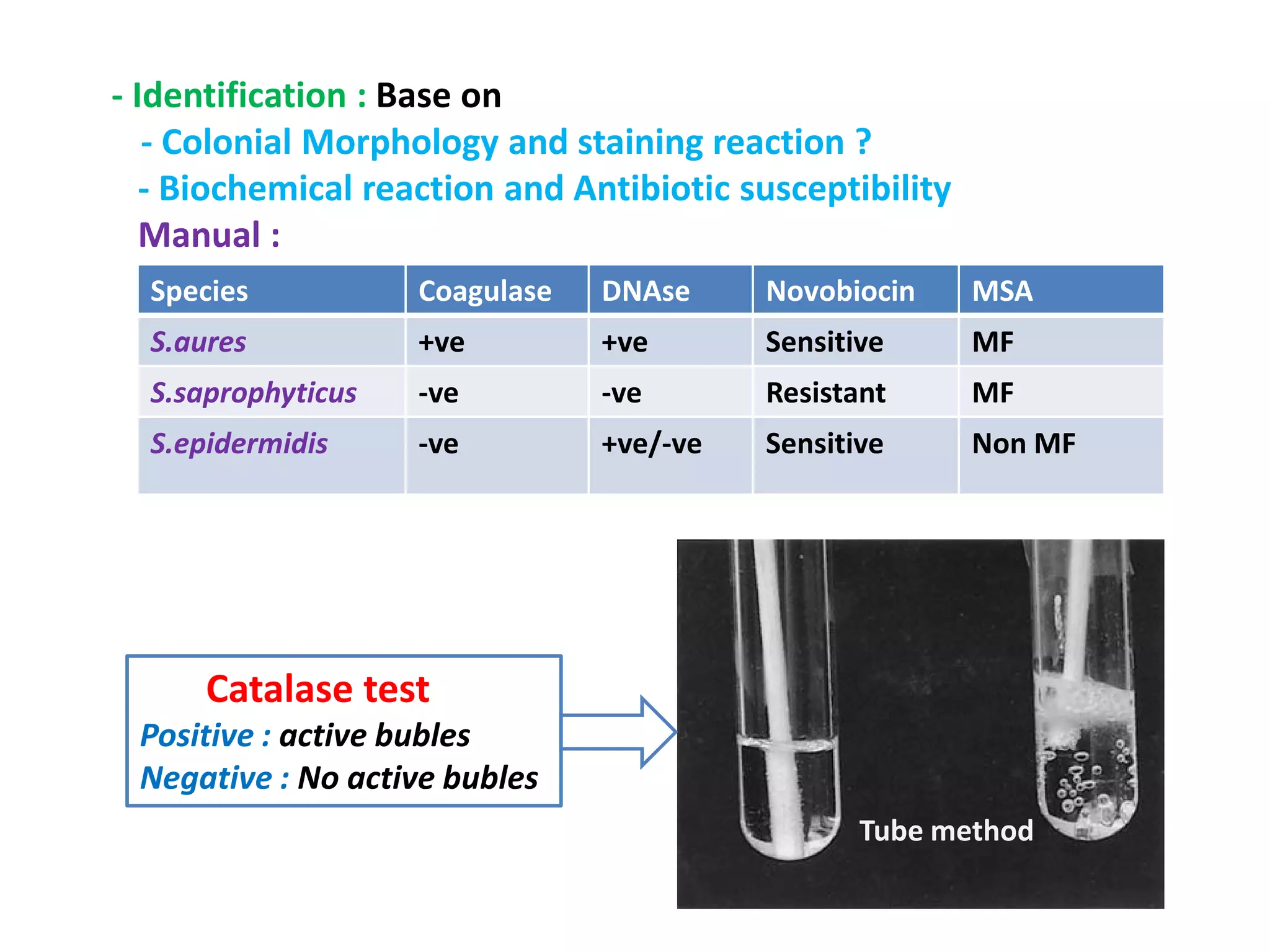
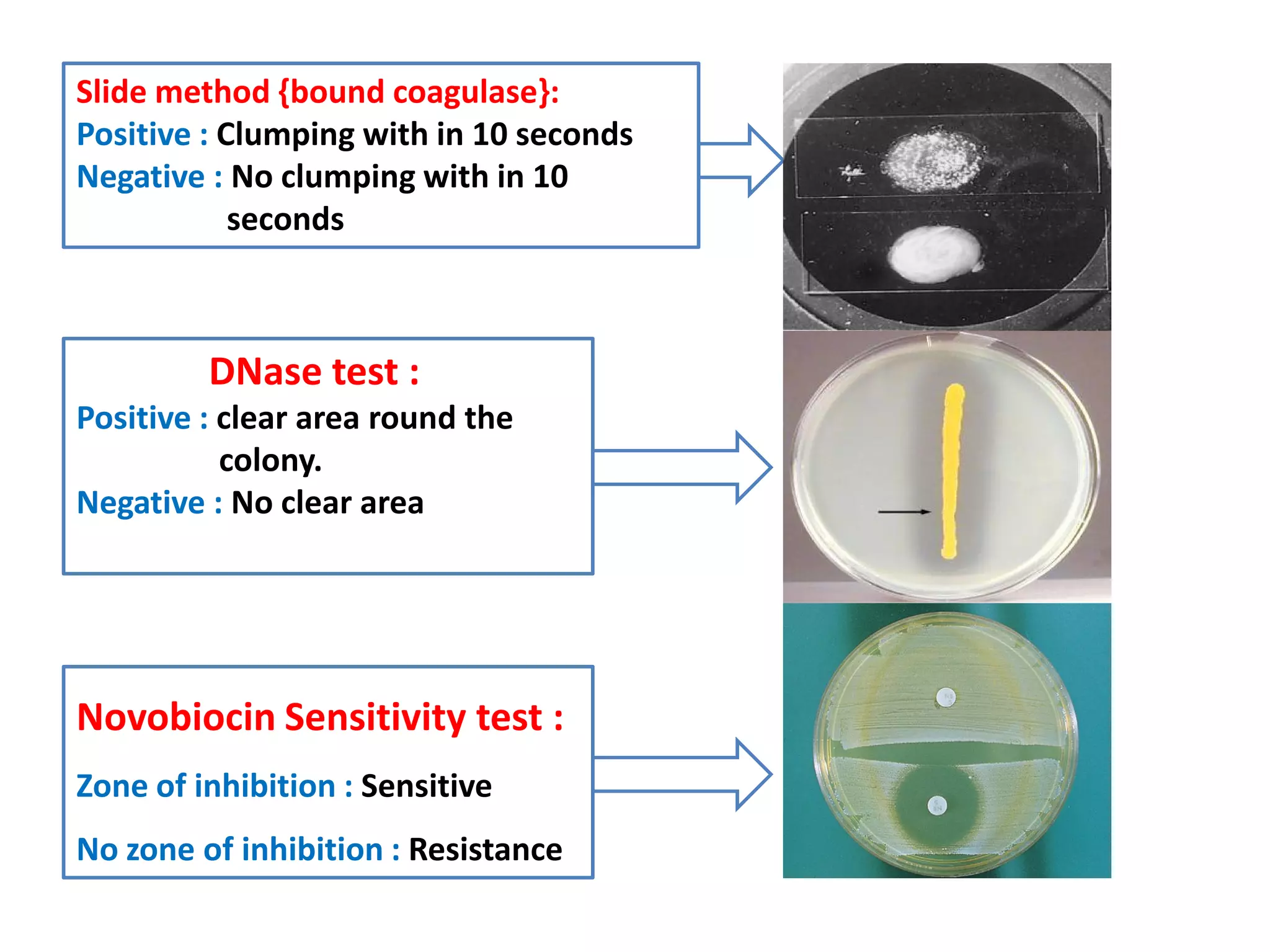
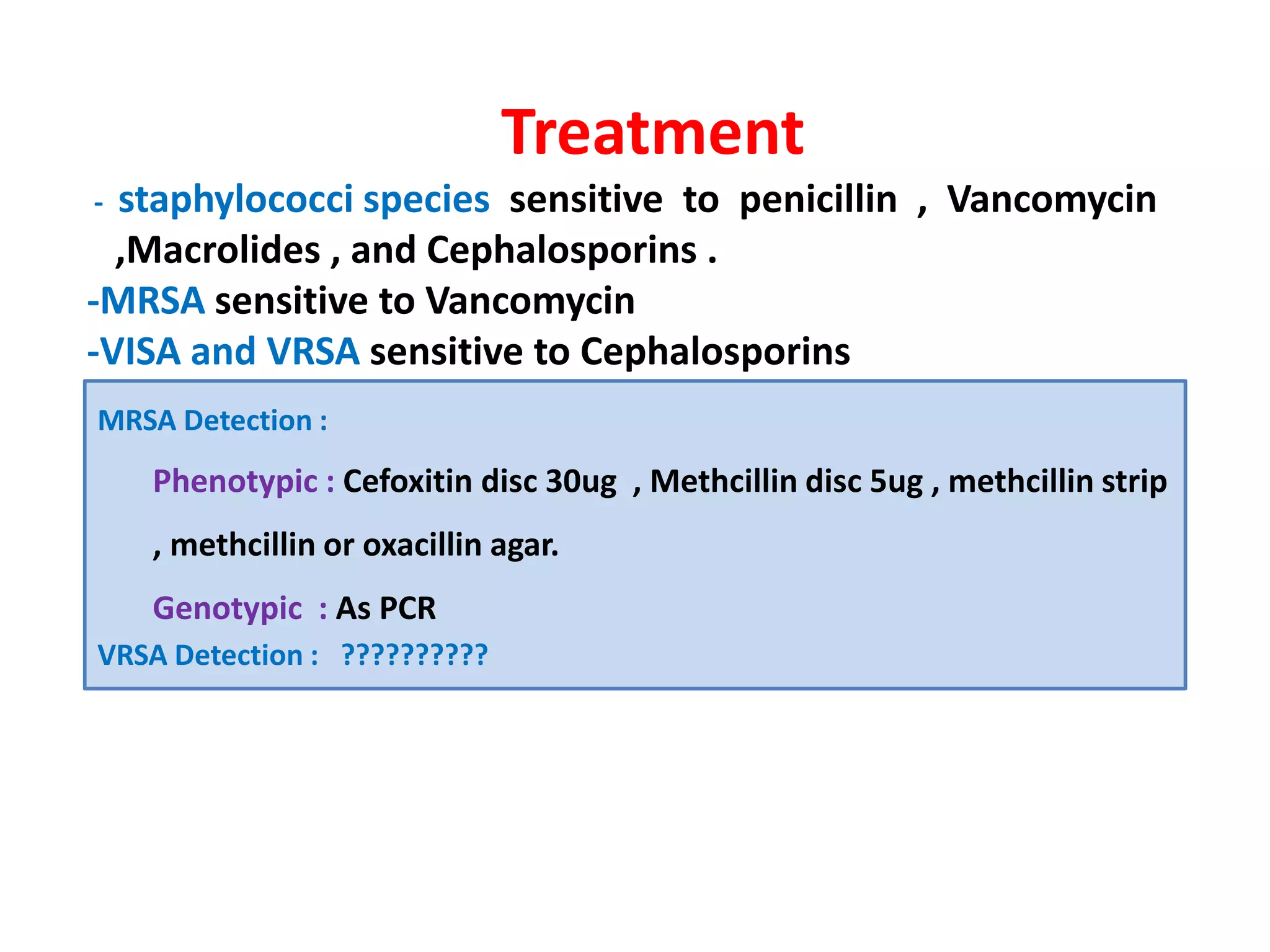
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Staphylococcus genus, detailing key properties, significant species like S. aureus, S. saprophyticus, and S. epidermidis, and their pathogenicity. It discusses laboratory diagnosis methods, including microscopy and culture techniques, alongside treatment options for staphylococcal infections. Key aspects like virulence factors and identification methods, including biochemical tests and automated systems, are also highlighted.