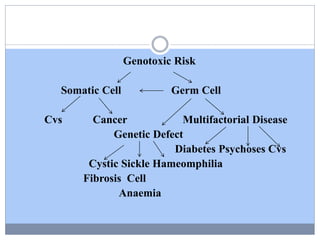
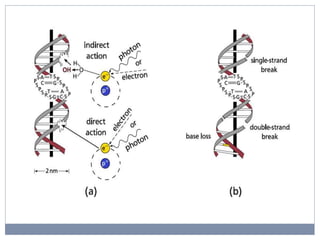
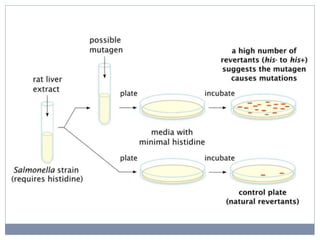
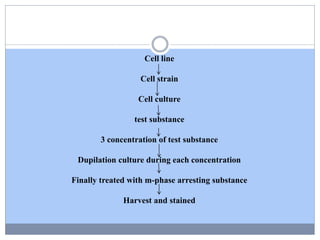
This document discusses genotoxicity, defining it as the harmful effects of substances on genetic material which can lead to mutations. Key methods for assessing genotoxicity, including the Ames Test, in vitro mammalian cell micronucleus test, and chromosomal aberration tests, are detailed to identify mutagenic and carcinogenic risks posed by various agents. The importance of these assays is emphasized in regulatory requirements to predict the potential of compounds as human carcinogens and mutagens.