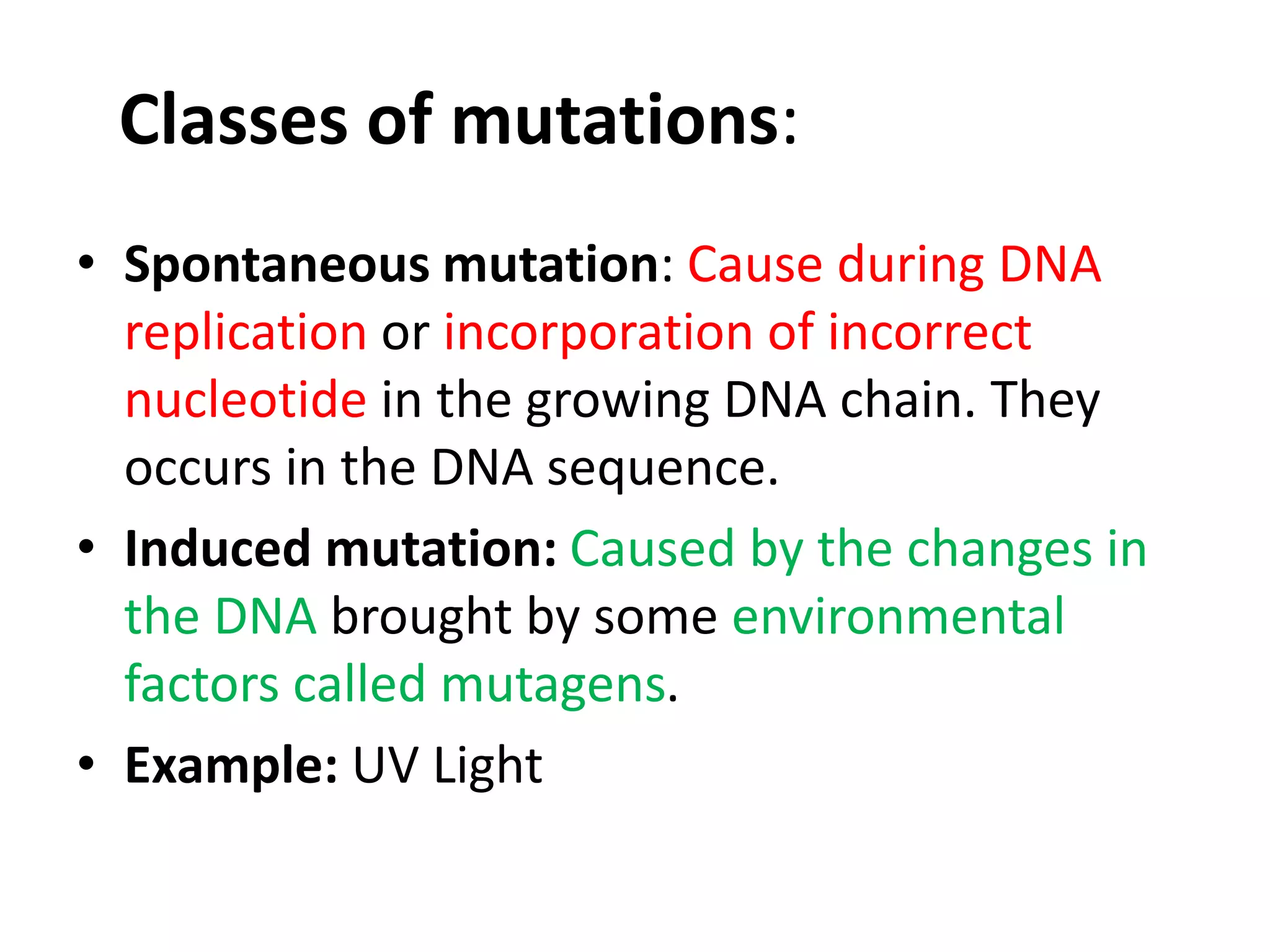
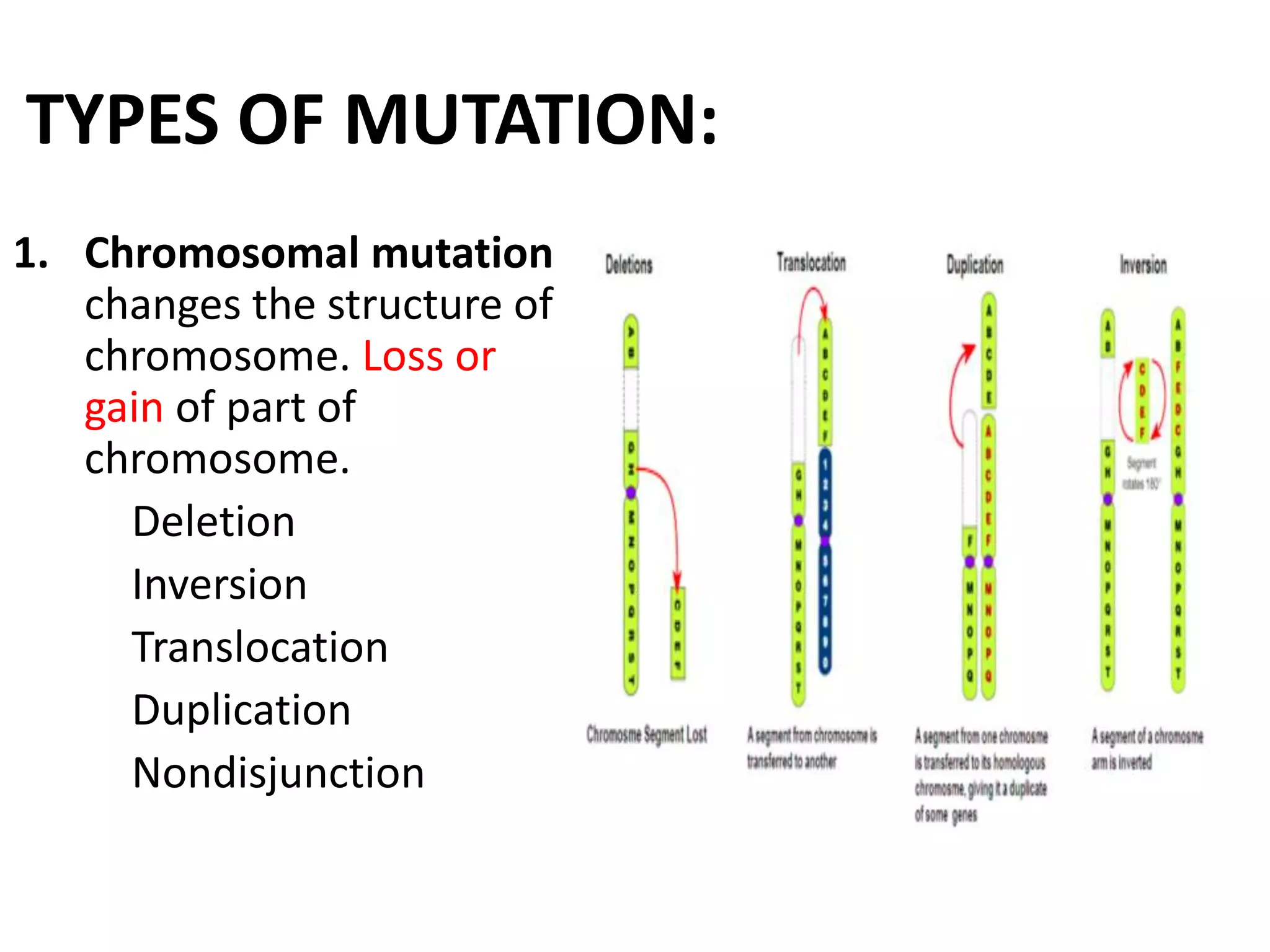
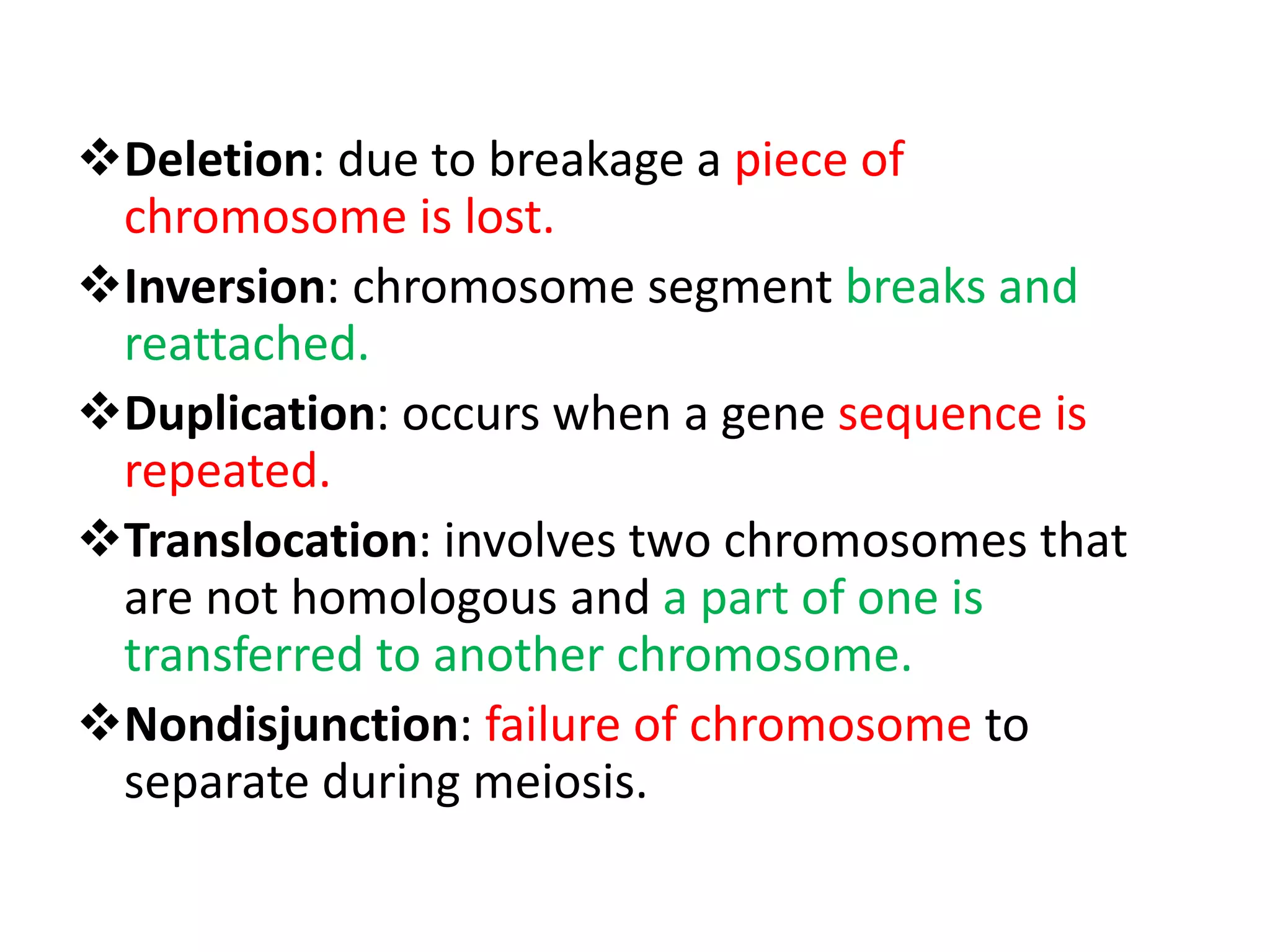
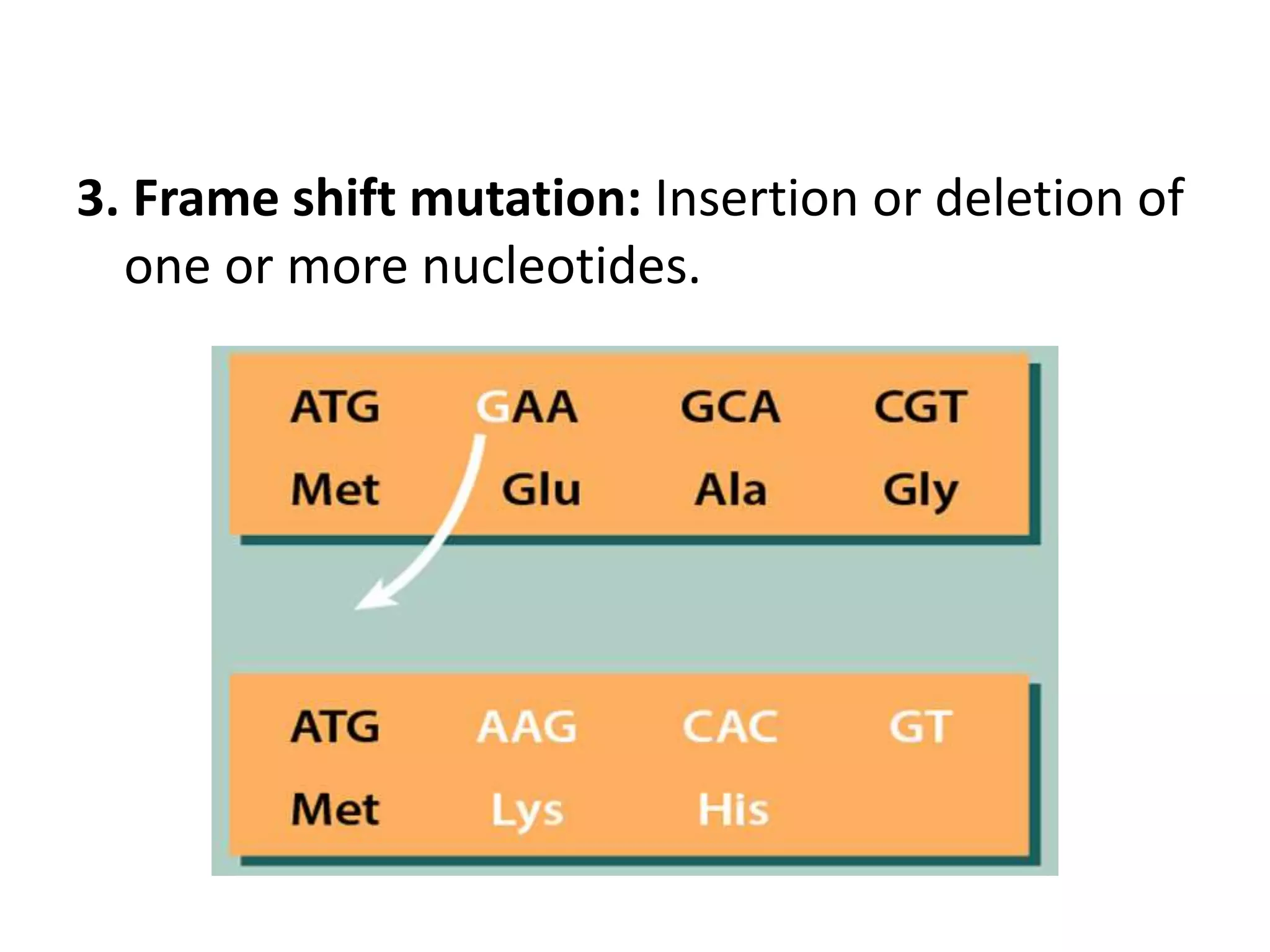
This document discusses mutagenicity and carcinogenicity testing that is done during drug discovery and development. It defines mutagenicity as the ability of chemicals to cause permanent changes to DNA, potentially leading to inherited mutations, and carcinogenicity as the ability to cause cancer. Common classes of mutagenic and carcinogenic compounds are described. Methods of mutagenicity testing include the Ames test, which uses Salmonella bacteria to identify mutagens, and other in vitro and in vivo assays. The document emphasizes the importance of screening drugs for these toxic effects before human use to avoid dangerous inherited mutations or cancer risks.






![ N- Nitroso compounds:
N- Nitrosodimethylamine
Aromatic Amines:
Benzidine
Aniline
o- Anisidine
o- Toluidine
Aromatic Hydrocarbons:
Benzene
Benz[a] anthracene
Bonzo[a] pyrene](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptmutagenicityandcarcinogenicity-200404075557/75/Ppt-mutagenicity-and-carcinogenicity-7-2048.jpg)