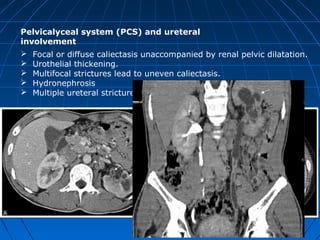
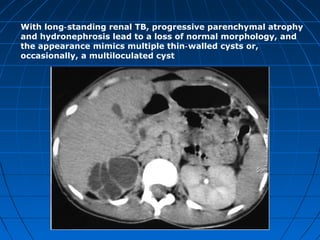
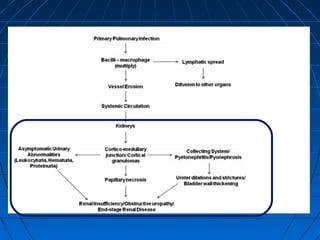
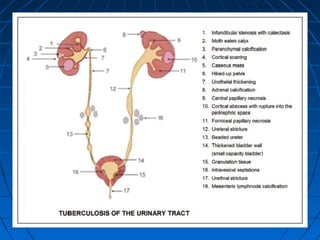
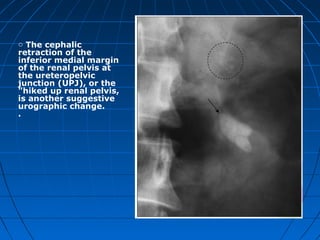
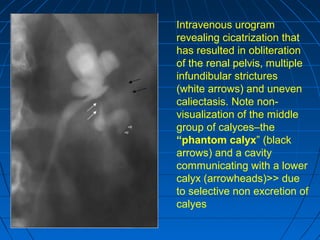
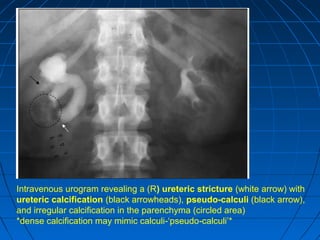
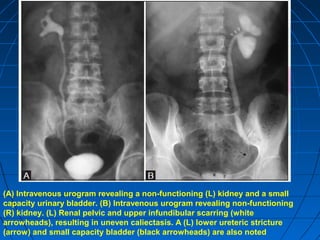
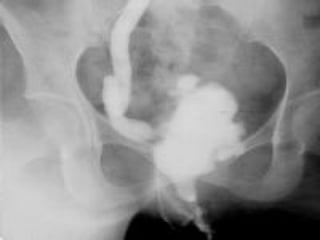
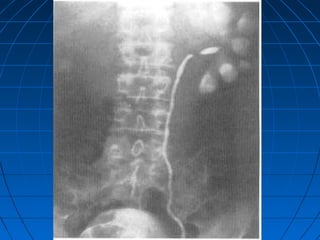
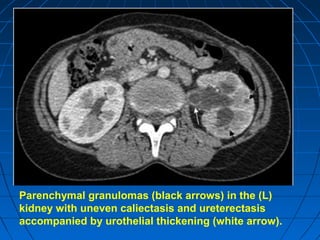
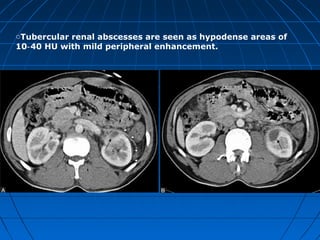
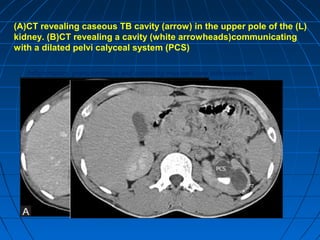
Tuberculosis can infect the genitourinary system and cause lesions in the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and genital organs. Radiographic imaging plays an important role in diagnosis and can reveal findings like renal calcifications, ureteral strictures, and bladder wall thickening indicative of genitourinary tuberculosis. The document discusses the pathology, clinical presentation, diagnostic tests including urine examination, tuberculin skin testing, and radiography that are used to identify genitourinary tuberculosis.








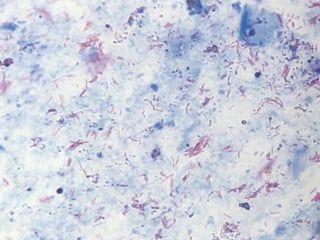




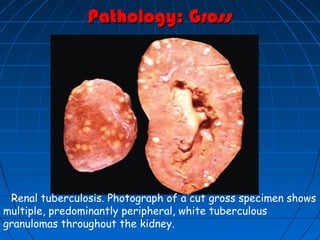
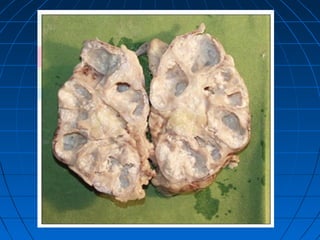



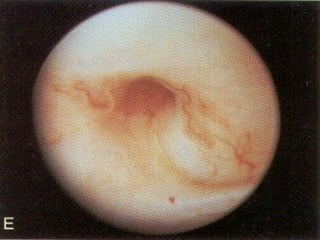
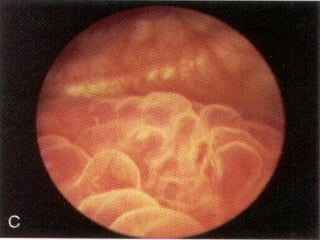
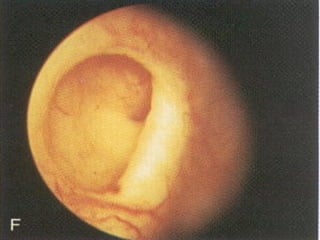

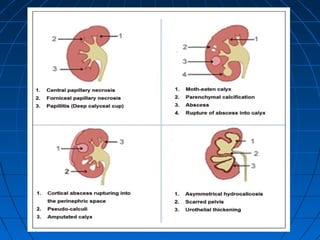
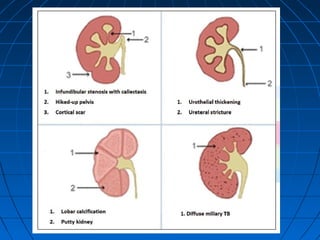











![(A) Non-contrast CT image showing fine cortical calcification in the (L)
kidney (white arrow). (B and C) non-contrast CT image showing
punctate calcification [arrows in (B) and soft (caseous) parenchymal
calcification arrowheads in (C)].
(D and E) axial CT revealing the lobar pattern of calcification
(arrowheads)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genitourinarytb-160504142104/85/Genitourinary-Tuberculosis-58-320.jpg)