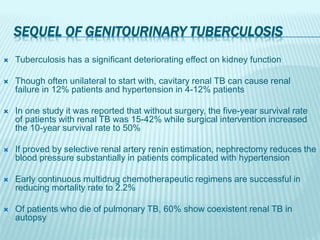
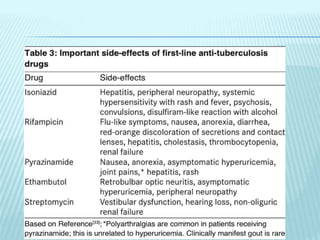
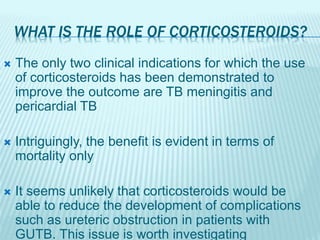
1) Genitourinary tuberculosis is a common form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, accounting for 4% of the total TB disease burden. It commonly involves the kidneys, fallopian tubes, epididymis, and prostate.
2) Clinical presentations are non-specific and include recurrent urinary tract infections, irritative voiding symptoms, renal or epididymal masses, and infertility.
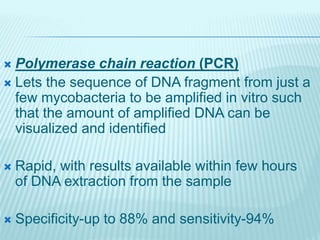
3) Diagnosis involves identifying the characteristic granulomatous lesions and caseous necrosis on biopsy of the involved organs, along with identifying the tuberculosis bacilli through microscopy or culture.


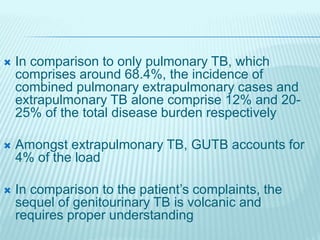
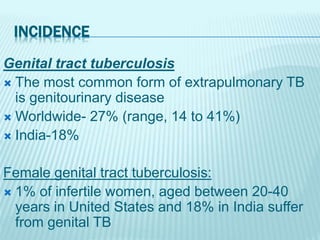




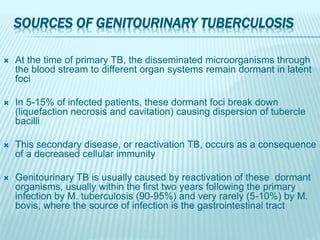












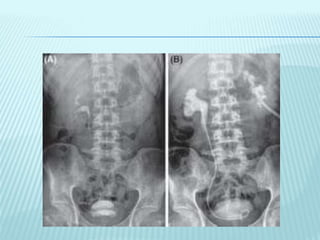
![GROSS PHOTOGRAPH OF KIDNEY SHOWS MULTIPLE NECROTIC AREAS INVOLVING THE MEDULLA AND AT PLACES
DESTROYING RENAL CALYCES [FIGURE 1A]. CHRONIC TB PYELONEPHRITIS WITH DESTROYED RENAL CALYCES
[FIGURE 1B]. EPITHELIOID CELL GRANULOMAS WITH DENSE CHRONIC INFL AMMATORY INFI LTRATE IN RENAL
CORTEX. [FIGURES 1C, D, H AND E, X100]. FOCALMFORMATION OF LYMPHOID FOLLICLES [FIGURE 1E, H AND E, X40].
CROSS-SECTION OF URETER SHOWING ULCERATED UROTHELIUM BY A GRANULOMATOUS PROCESS [FIGURE 1F, H
AND E, X40]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genito-urinarytuberculosis-151021181511-lva1-app6892/85/Genito-urinary-tuberculosis-24-320.jpg)















![RAPID IDENTIFICATION OF MYCOBACTERIUM
Radiometric systems
Radiometric liquid culture systems (i.e.,
BACTEC®) [Becton Dickinson, USA]) give
rapid results and are highly sensitive in the
identification of mycobacterium
But these methods have some inherent
diffculties in working with radioactive materials,
and the necessary apparatus used are really
expensive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genito-urinarytuberculosis-151021181511-lva1-app6892/85/Genito-urinary-tuberculosis-40-320.jpg)