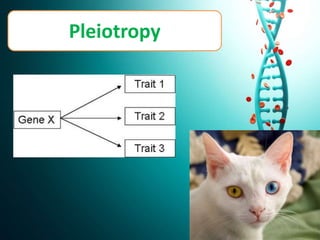
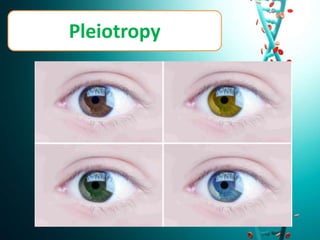
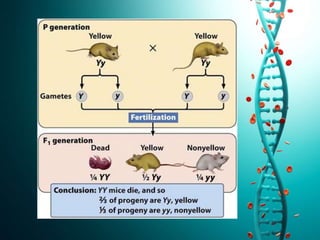
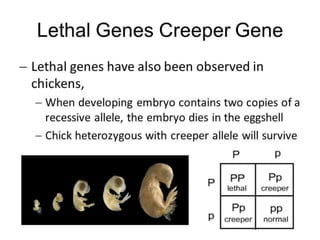
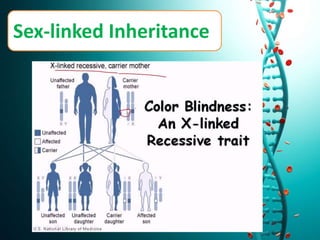
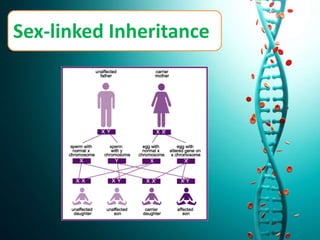
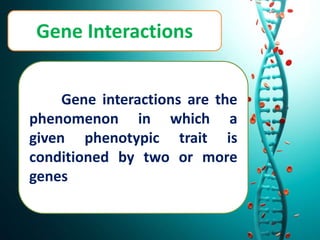
This document discusses several non-Mendelian patterns of inheritance including lack of dominance where the heterozygous phenotype differs from the homozygous phenotypes, multiple alleles where a single gene can have more than two alleles, pleiotropy where a single gene influences multiple traits, lethal genes which cause death, sex-linked inheritance determined by genes on sex chromosomes, gene interactions between two or more genes, complementary genes which act together to determine a trait, epistasis where one gene inhibits another, polygenic inheritance where multiple genes influence a trait, and pedigree analysis to trace traits within a family.