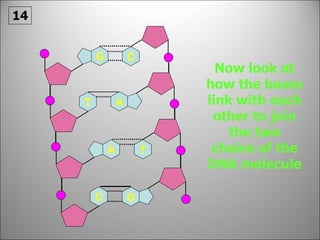
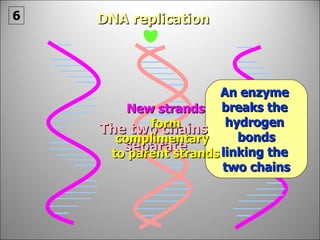
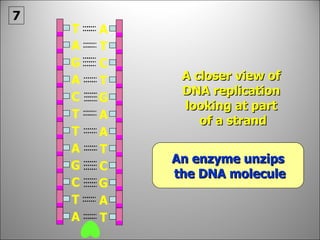
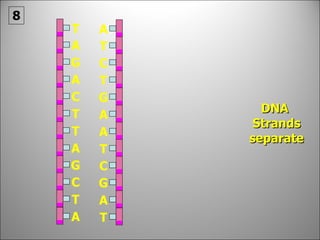
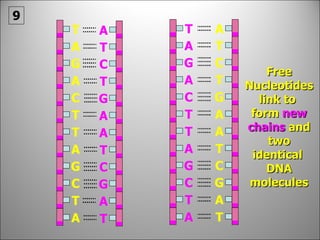
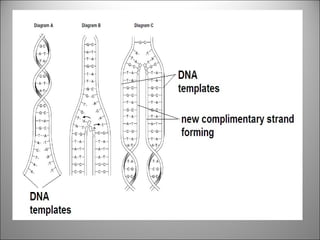
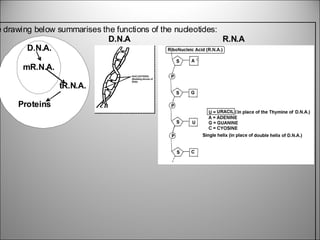
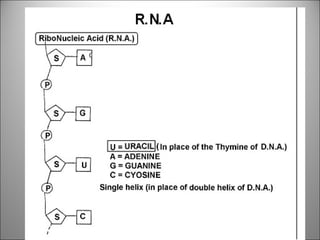
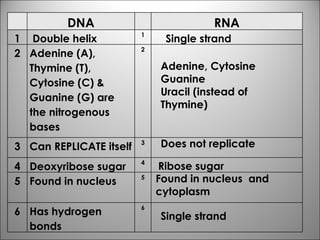
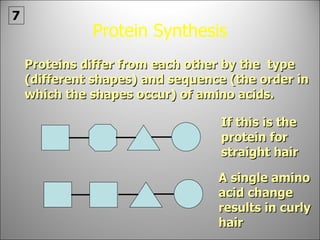
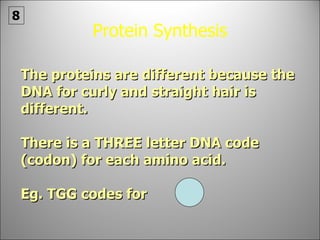
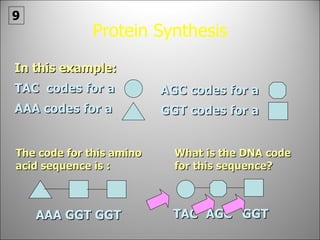
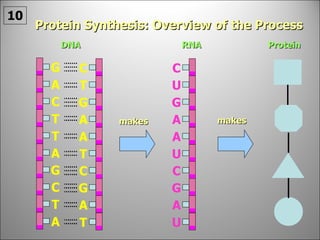
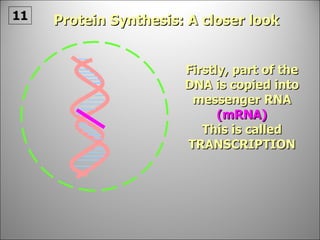
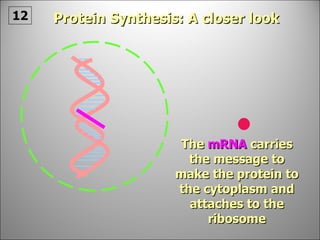
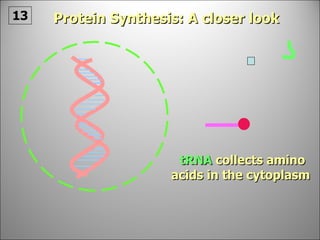
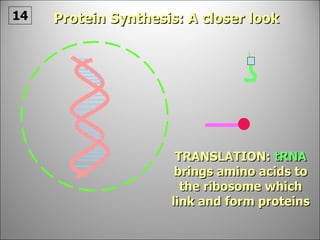
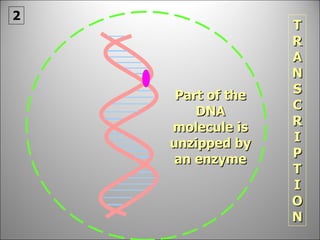
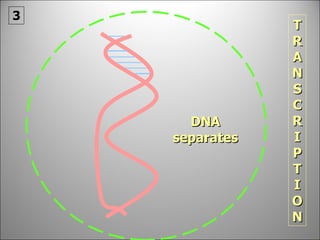
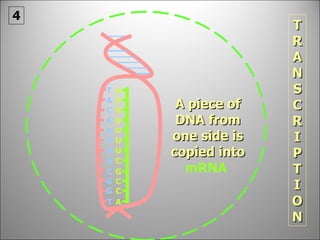
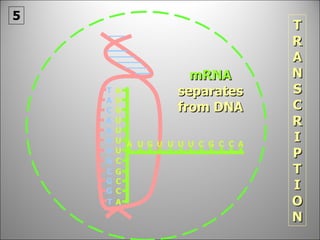
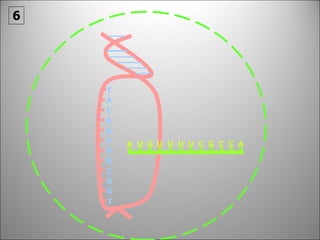
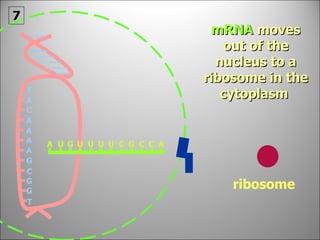
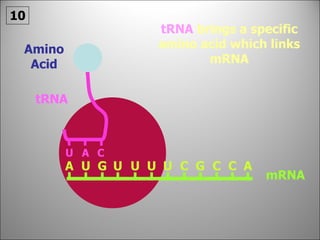
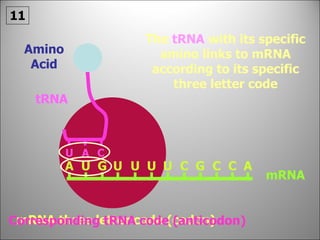
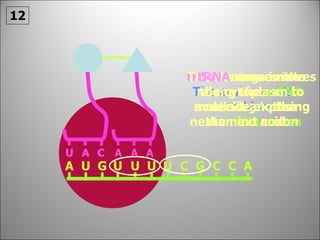
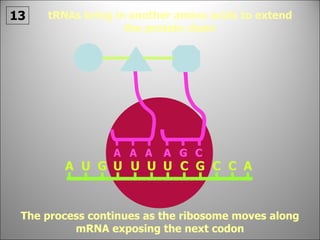
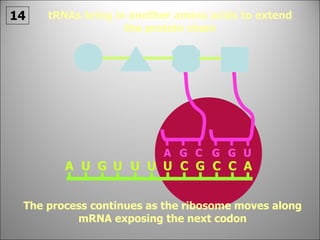
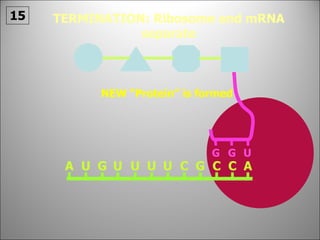
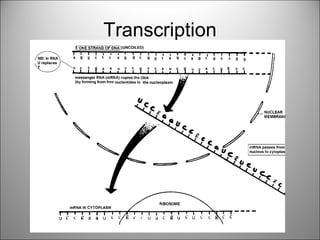
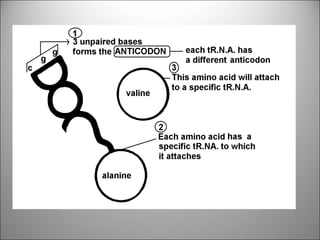
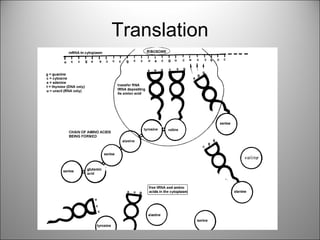
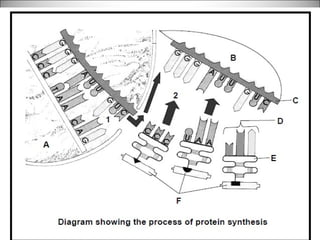
The nucleus contains DNA which directs the production of proteins through transcription and translation. DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) during transcription. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm where it is translated into a protein sequence. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules match amino acids to the mRNA codons to link them together into proteins.
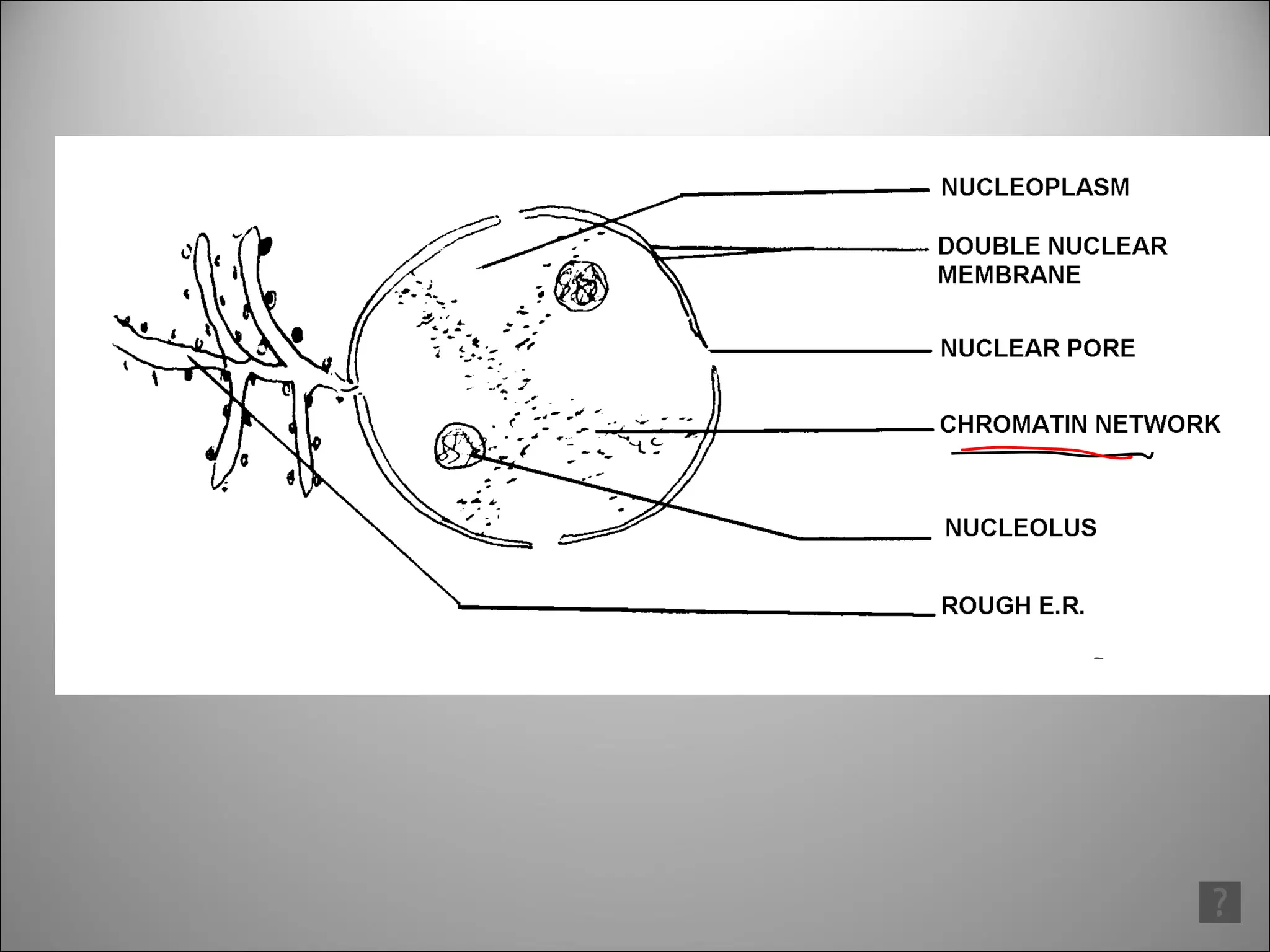
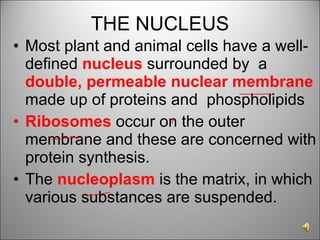
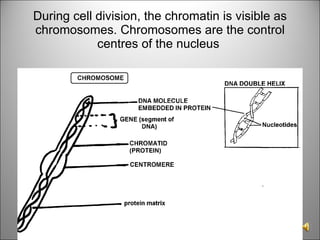
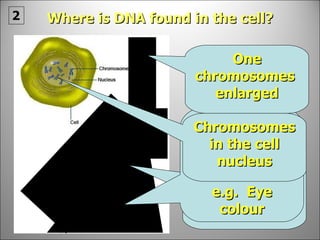
![There may be one or more nueleoli [singular = nueleolus] in the nucleus. These contain proteins and nucleic acids found within the nucleus and they manufacture RNA and are concerned with protein synthesis. Chromosomes are long threads made of DNA and some protein. They are the carriers of GENES which are responsible for our hereditary traits . When a cell Is not dividing the chromosomes are not visible but are in a very tangled mass, the chromatin network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dna20112-111023015314-phpapp02/85/Dna-2011-2-3-320.jpg)


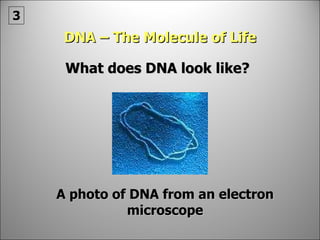



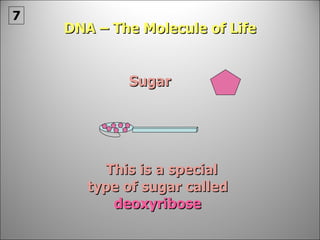
![DNA STRUCTURE D NA [deoxyribose nucleic acid] is known as the key to life. It is the hereditary material found in the chromosomes as well as other parts of the cell e.g. mitochondria.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dna20112-111023015314-phpapp02/85/Dna-2011-2-17-320.jpg)
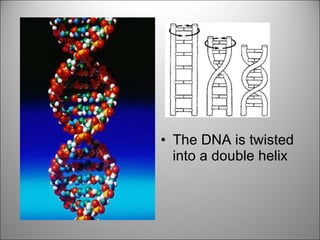
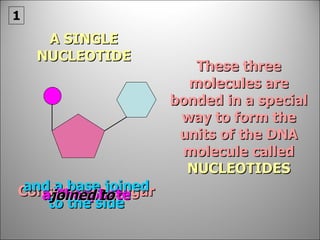
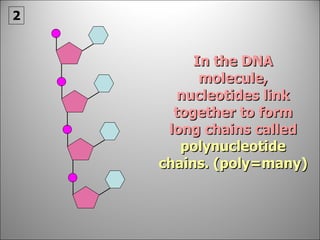
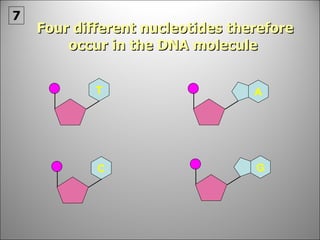
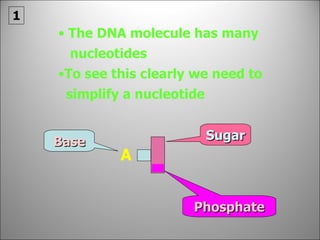
![It is a very long giant molecule made up of smaller units called NUCLEOTIDES . Watson & Crick were awarded the Nobel Prize for working out its structure [although a South African woman was just pipped at the post (1953-1962)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dna20112-111023015314-phpapp02/85/Dna-2011-2-18-320.jpg)
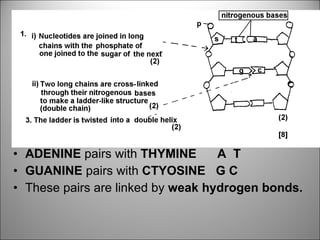
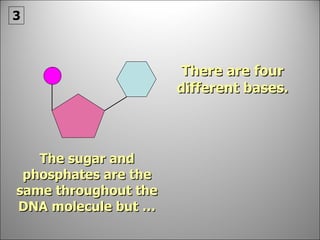
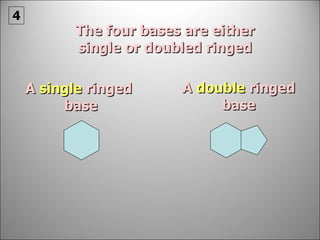
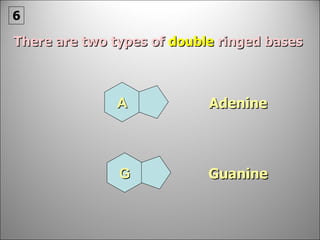
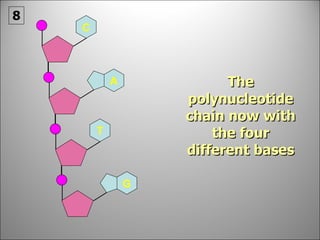
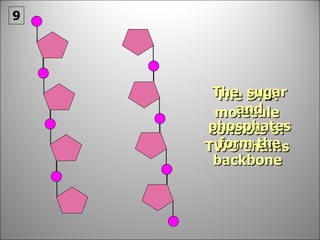
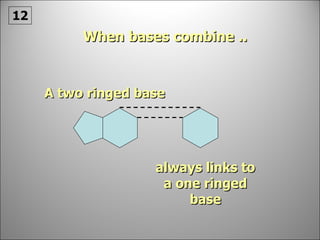
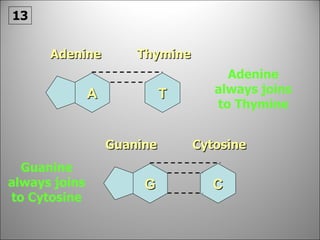
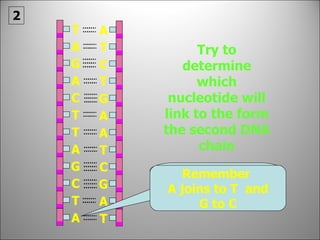
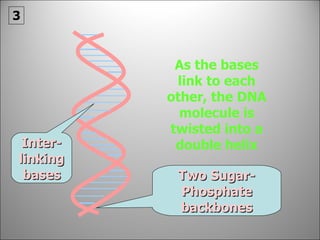
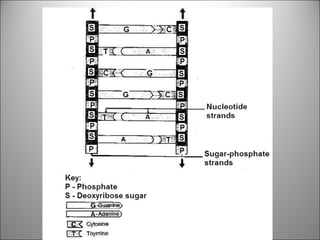
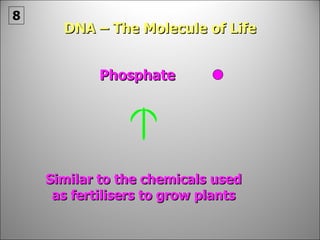
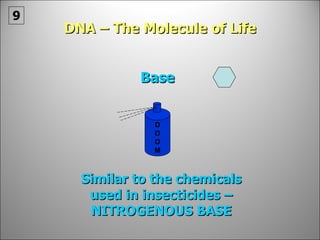
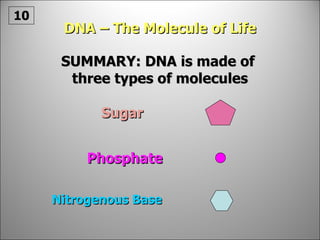
![Each side is made up of alternating SUGARS [ deoxyribose ] and PHOSPHATES . Forming the 'rungs' are PAIRED NITROGENOUS BASES ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dna20112-111023015314-phpapp02/85/Dna-2011-2-19-320.jpg)