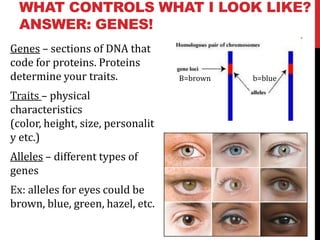
This document provides an introduction to genetics concepts including:
1) Genes located on chromosomes are segments of DNA that code for proteins which determine traits. Traits are physical characteristics influenced by alleles which are different versions of genes.
2) Genotype refers to the alleles an organism receives from its parents, while phenotype describes the physical traits that are expressed.
3) Dominant alleles will always be expressed over recessive alleles in determining an organism's phenotype, with the exception of traits only expressed in the homozygous recessive genotype.