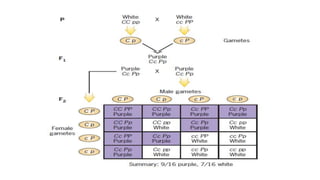
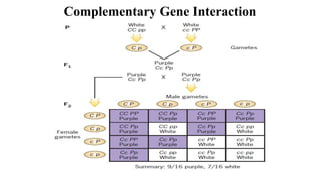
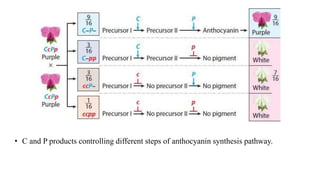
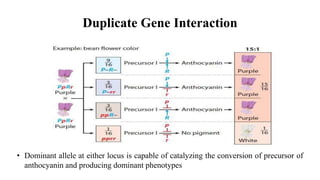
The document discusses gene interactions, explaining how different genes can influence the expression of a single trait, including dominance and epistasis. It describes various patterns of epistasis with examples, such as complementary and dominant gene interactions, detailing how certain genes can mask others. Multiple-choice questions illustrate these concepts in practical scenarios, focusing on traits in plants and animals.