Embed presentation
Downloaded 21 times





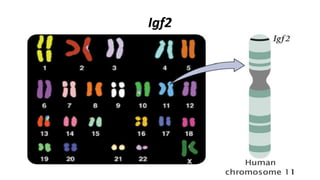


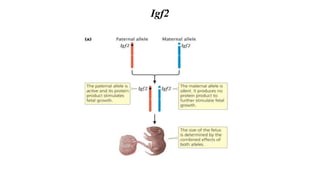








Genomic imprinting is the differential expression of a gene based on the sex of the parent that transmits it, primarily occurring in eutherian mammals. This phenomenon is crucial for fetal and brain development, exemplified by disorders such as Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome, which are caused by deletions on chromosome 15 inherited from the father and mother, respectively. Key imprinted genes include igf2, which plays a significant role in placental and fetal growth.
















