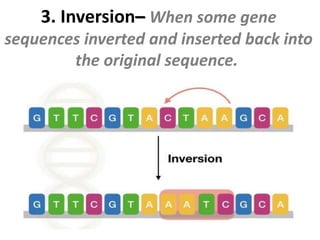
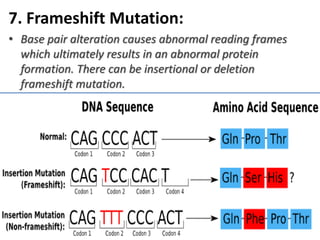
The document discusses different types of mutations including chromosomal mutations and genetic mutations. It defines gene mutations as mutations that change the function of a gene by altering its polynucleotide sequence. The types of gene mutations described include insertion, deletion, inversion, substitution, duplication, silent mutation, missense mutation, nonsense mutation, and frameshift mutation. Each mutation type results from a different change to the gene sequence, such as the addition, removal, inversion, or replacement of nucleotide bases.