1. A mutation is a change in DNA sequence that can occur due to errors when DNA is copied or environmental factors like UV light.
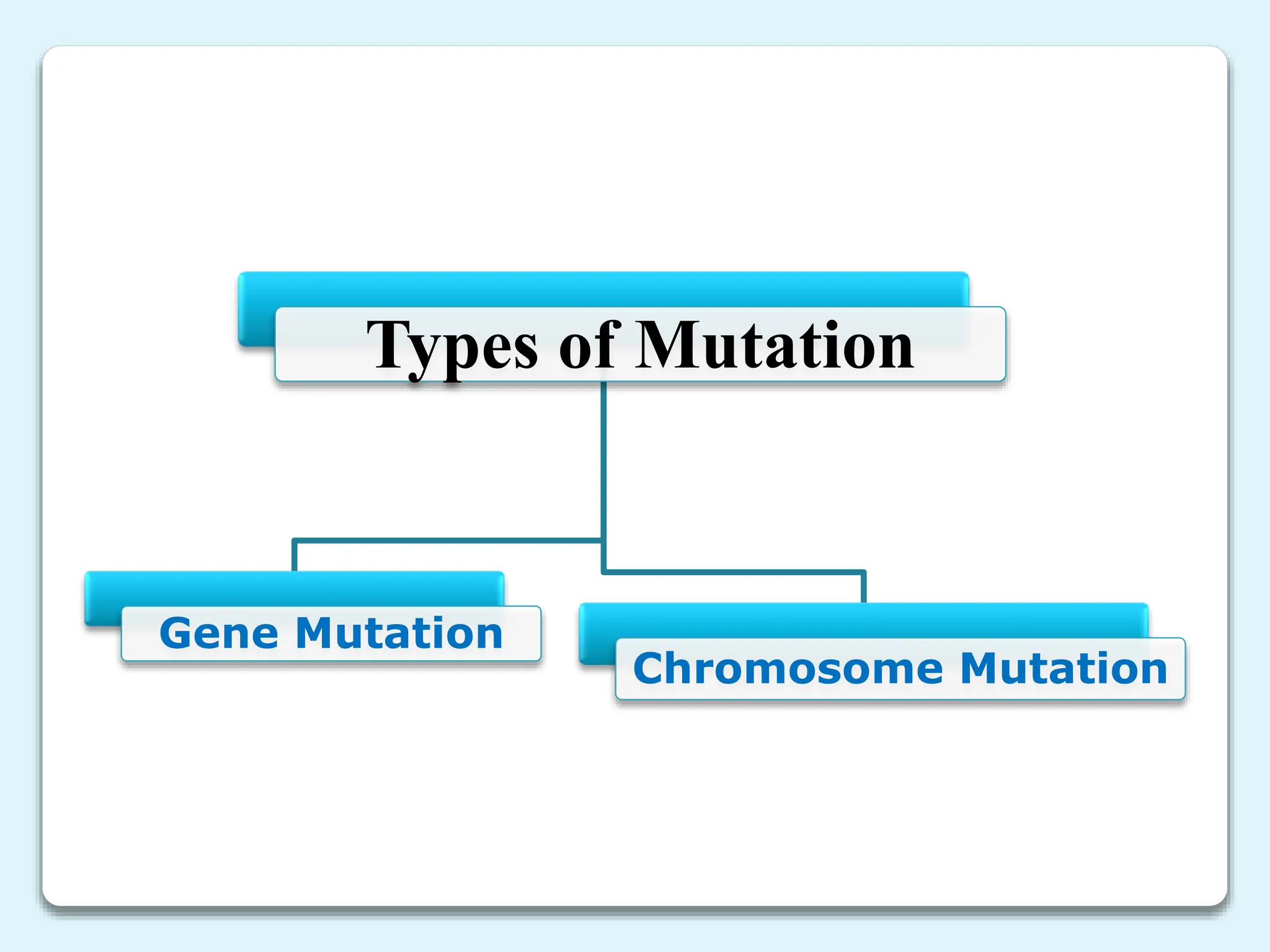
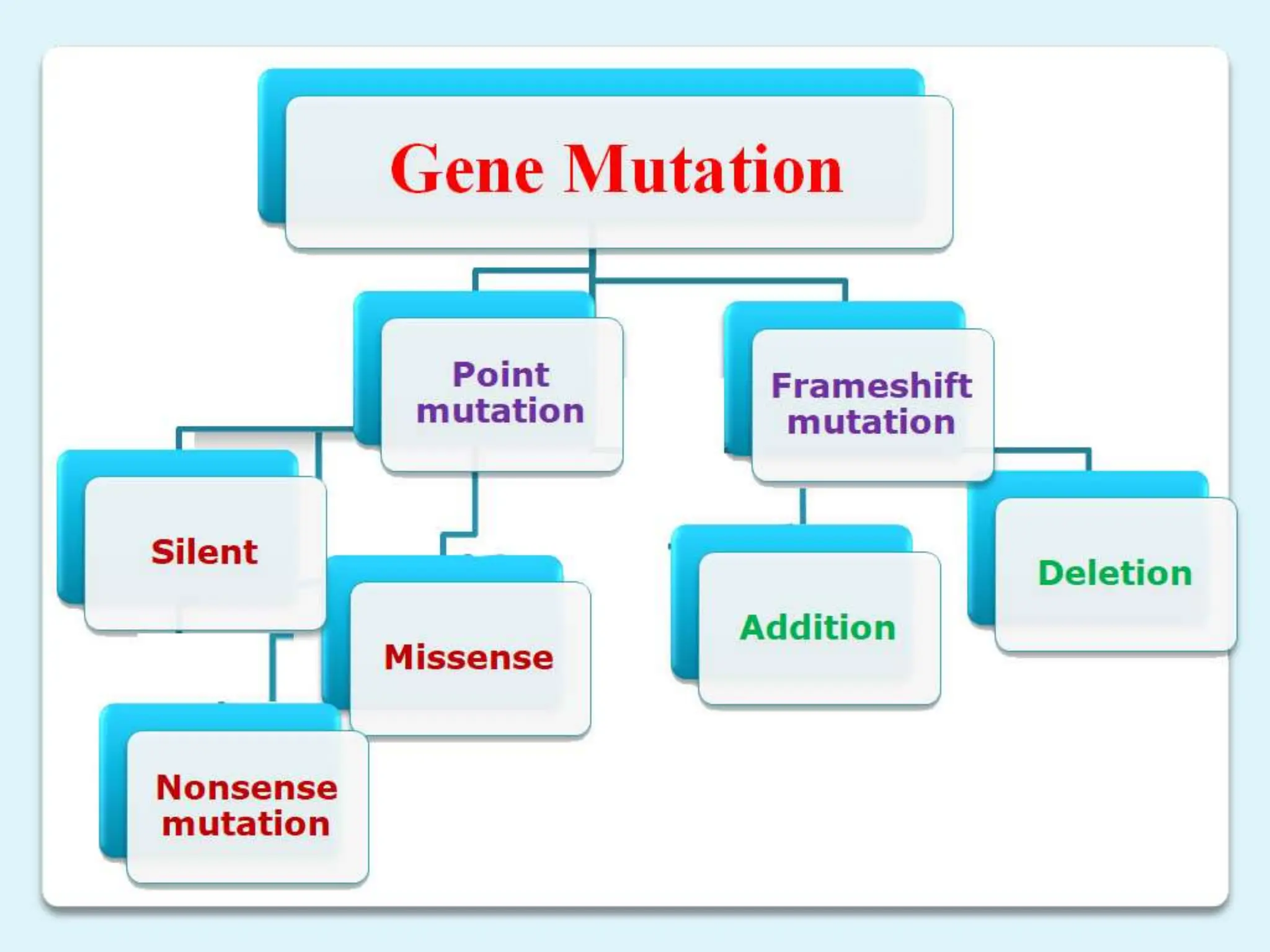
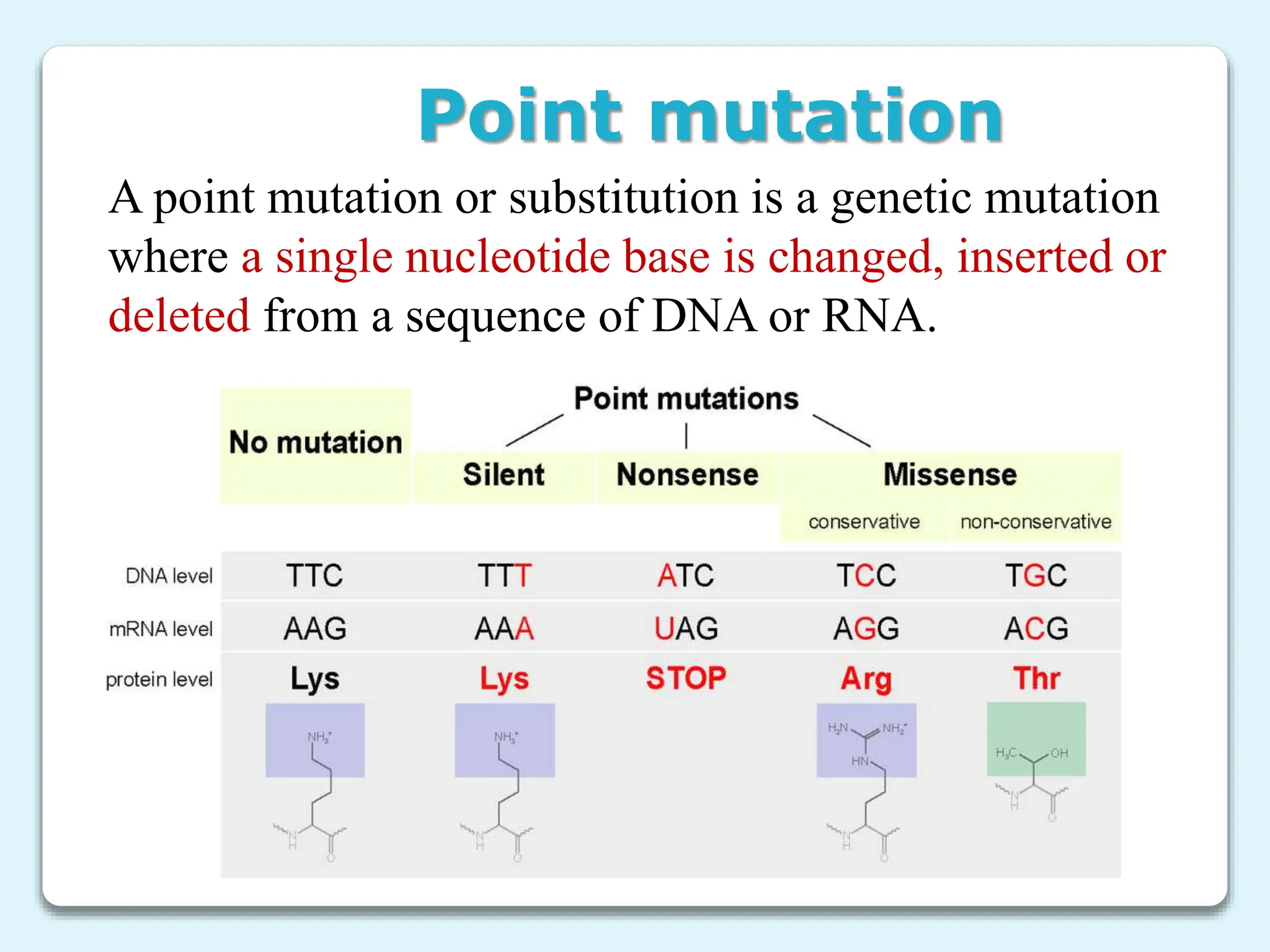
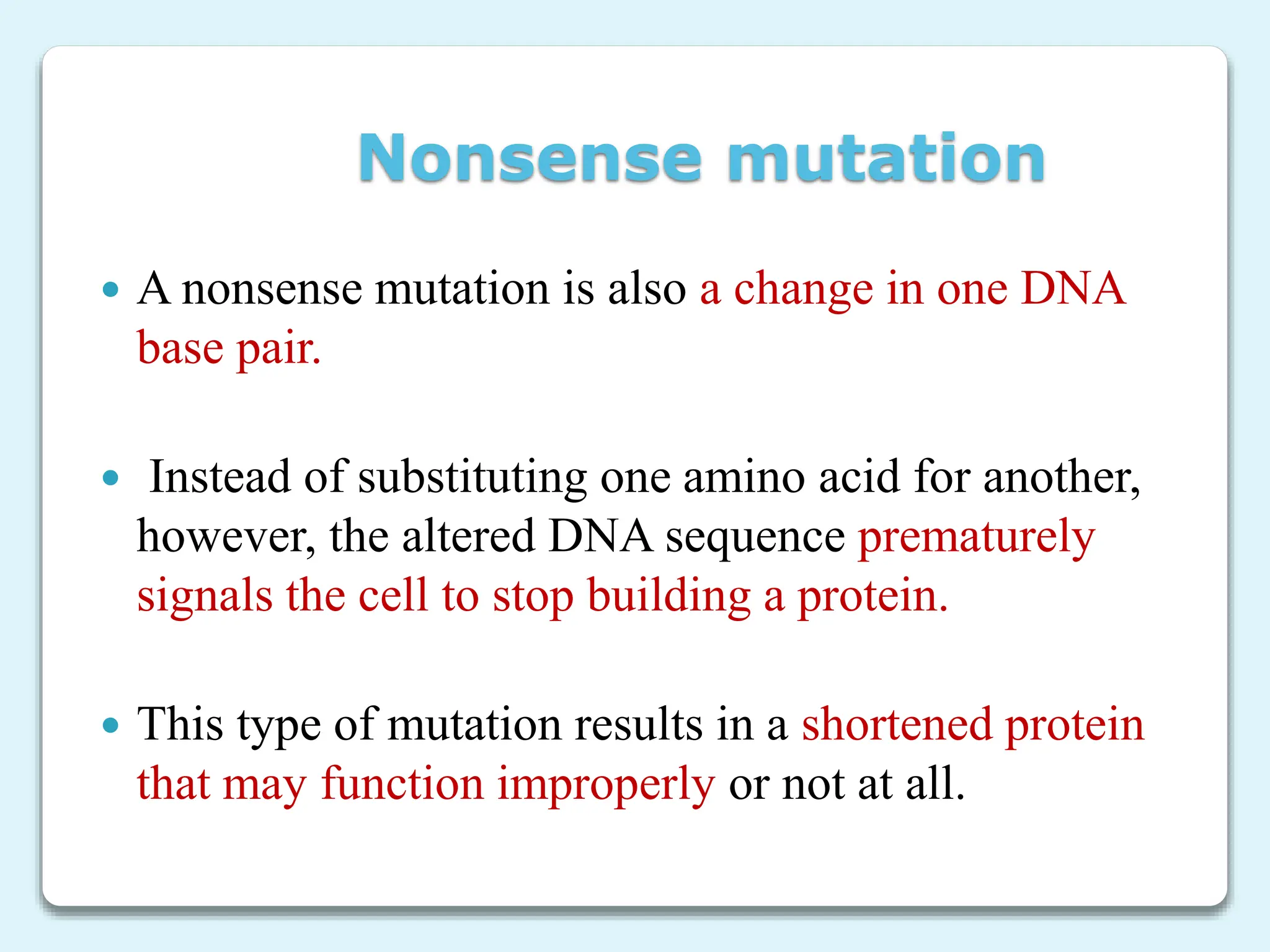
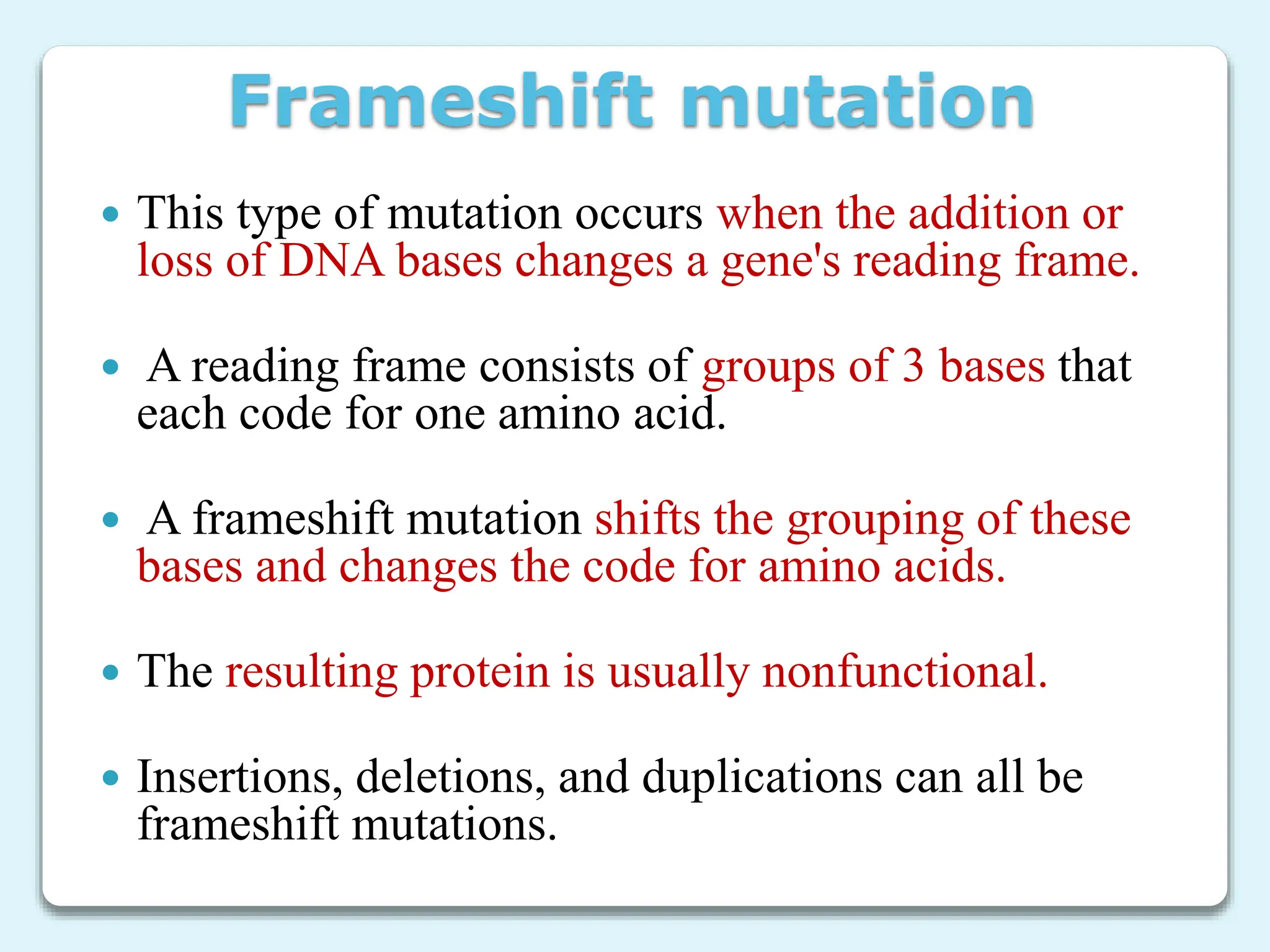
2. There are different types of mutations including point mutations, silent mutations, nonsense mutations, missense mutations, and frameshift mutations.
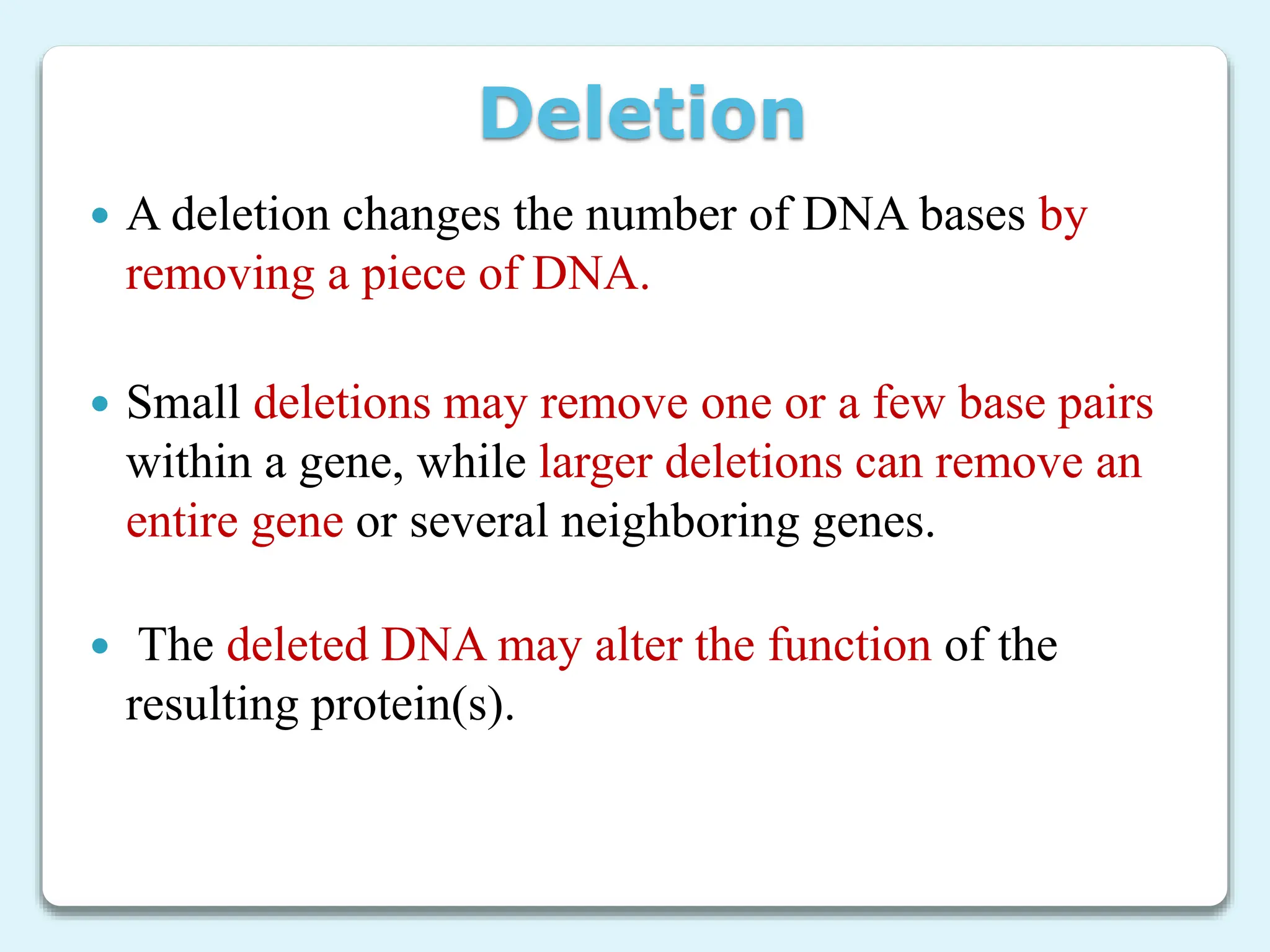
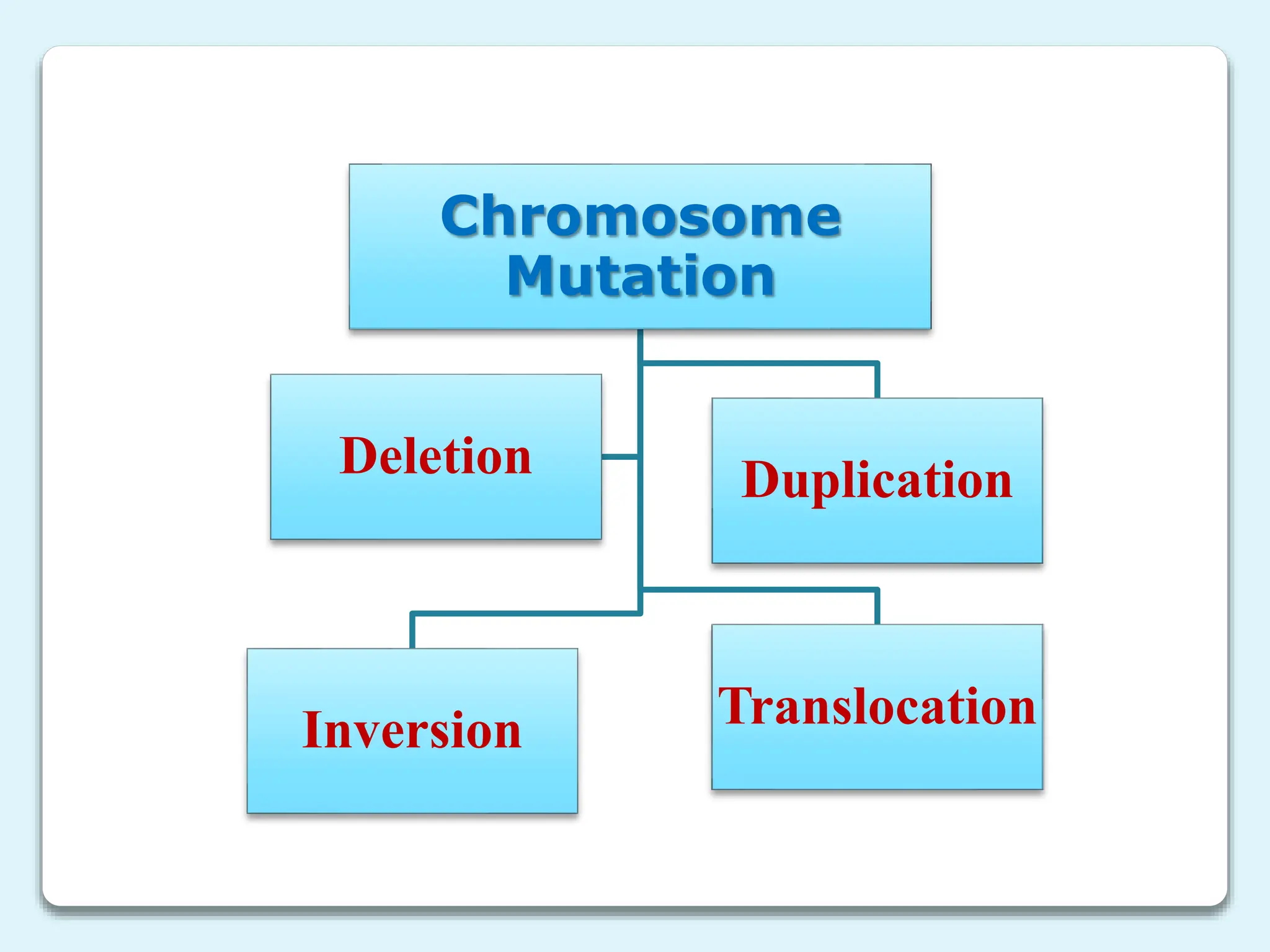
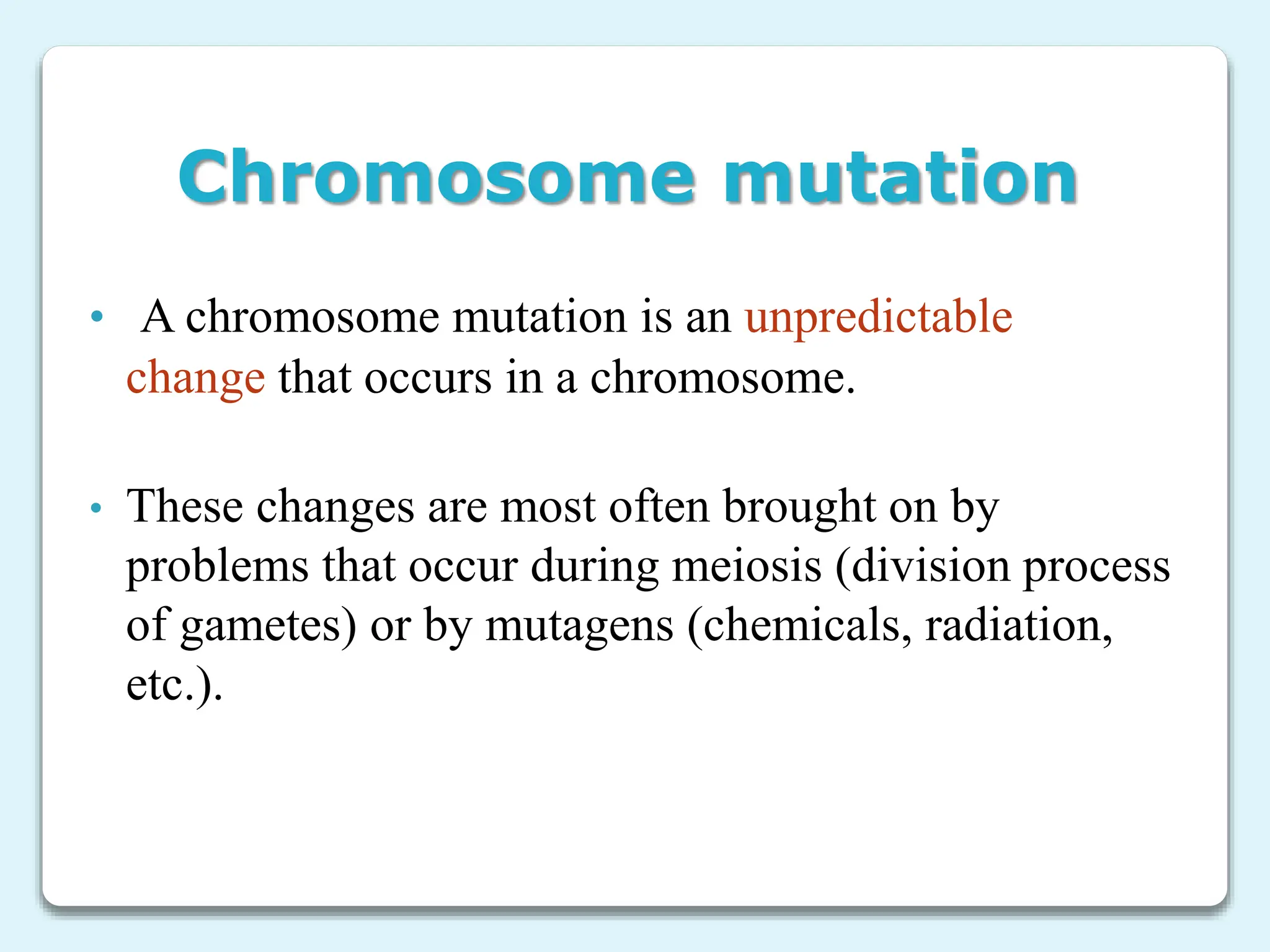
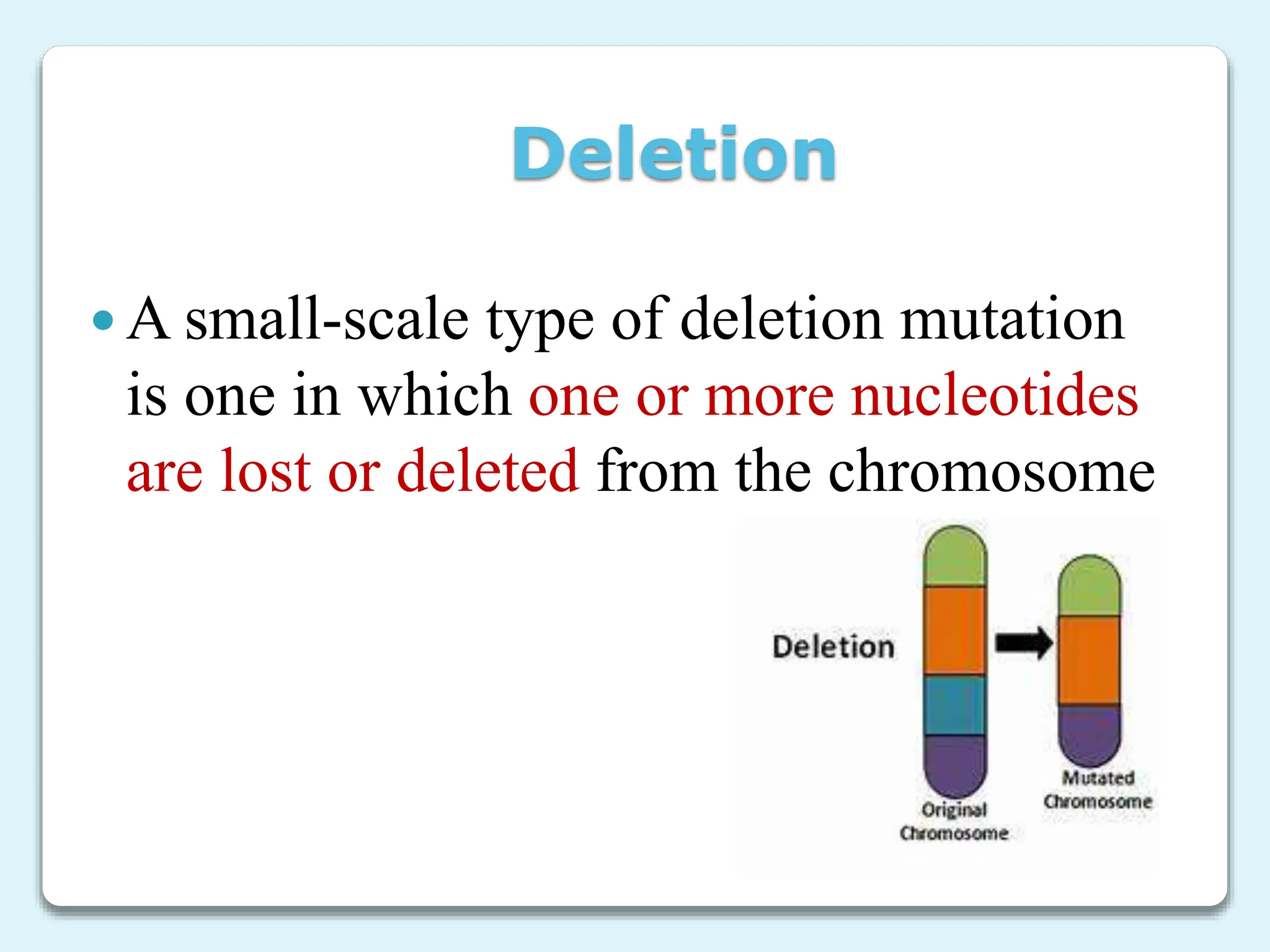
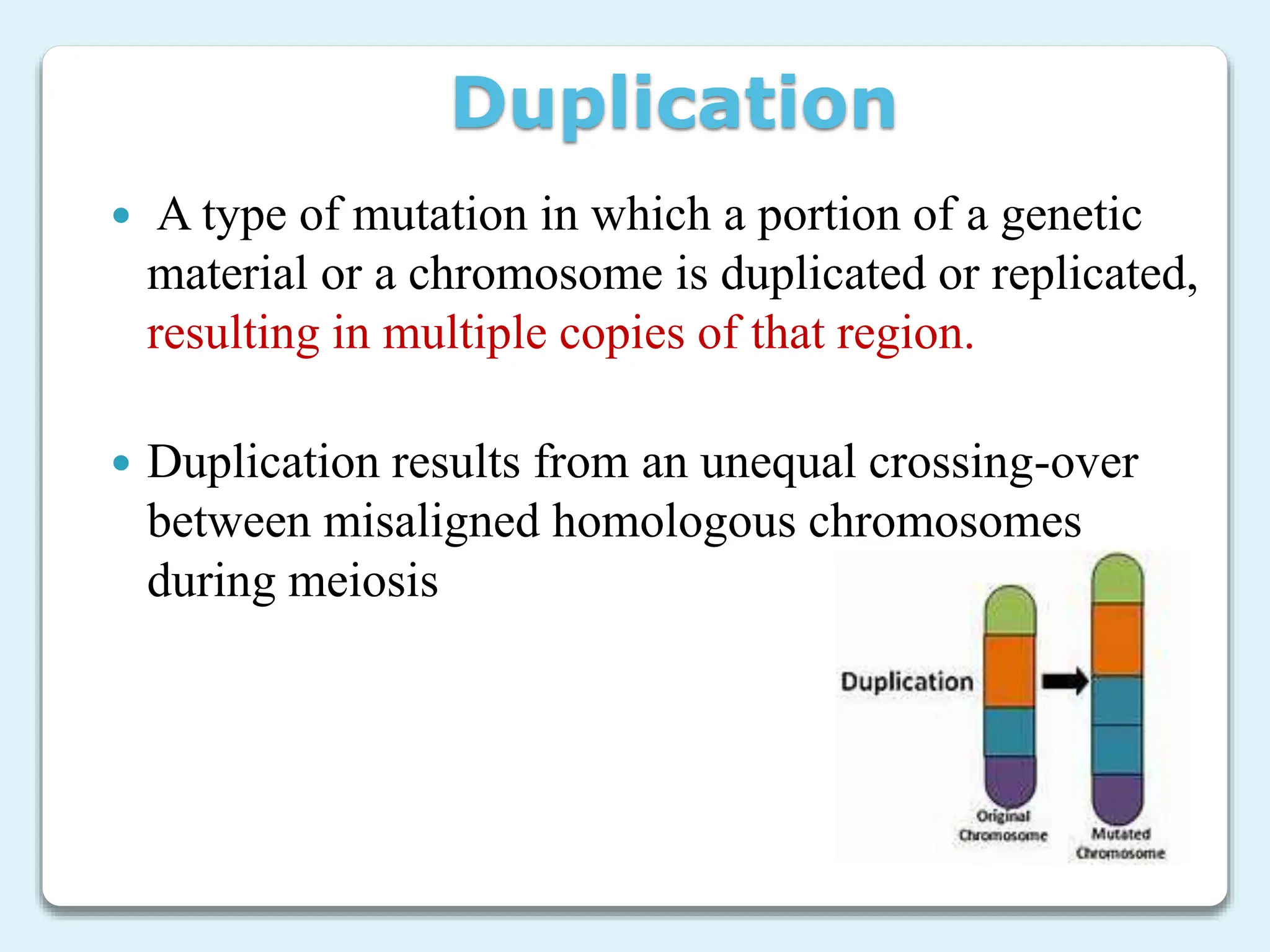
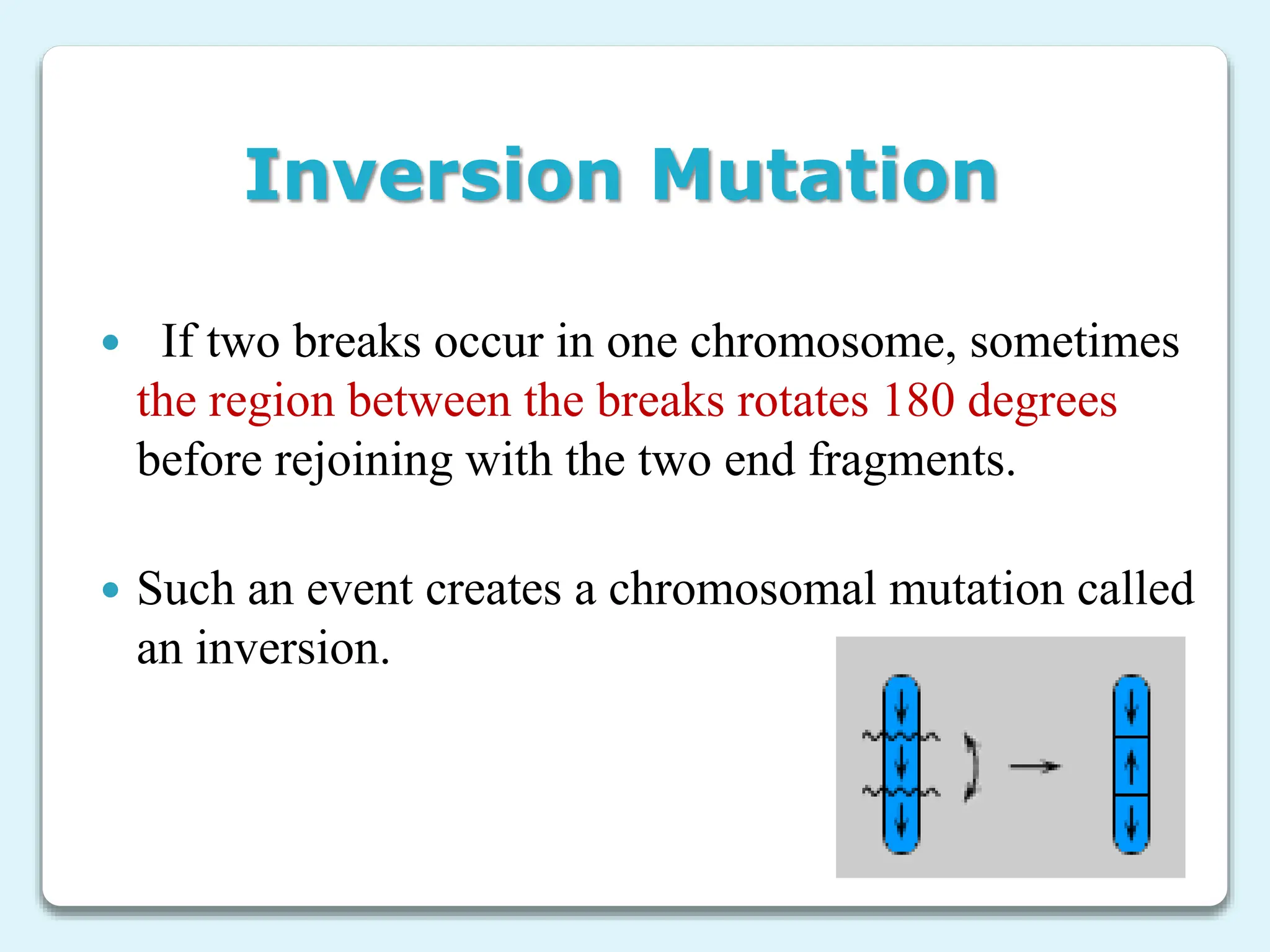
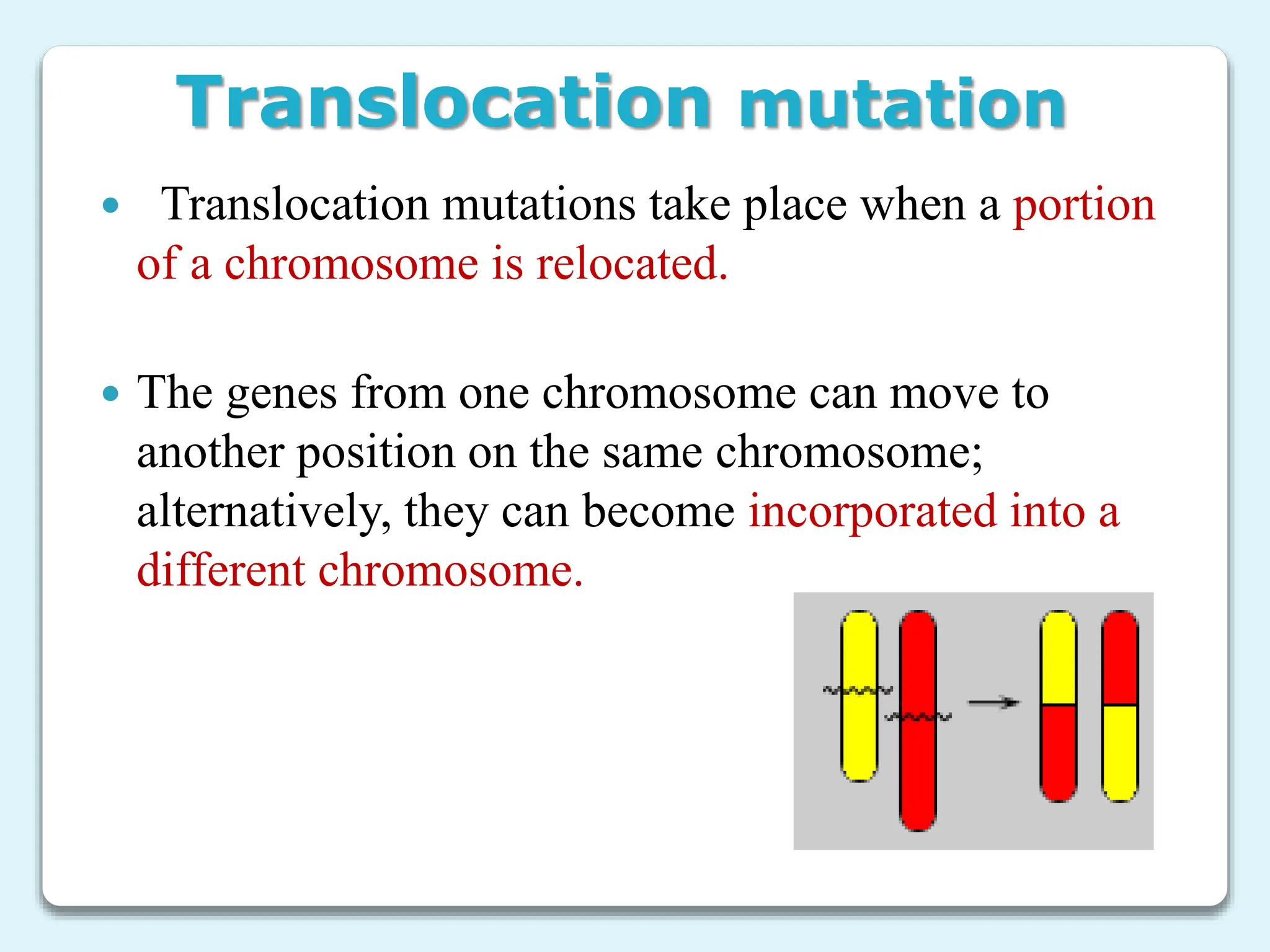
3. Chromosome mutations are changes that occur in chromosomes and include deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. These mutations can affect chromosome structure and gene function.