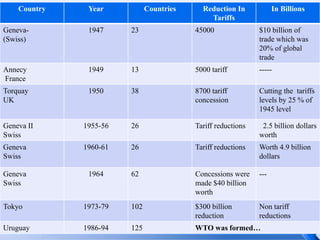
The document discusses the evolution of international trade agreements from GATT to the World Trade Organization (WTO). It notes that GATT was formed in 1947 by 23 countries as a set of multilateral trade agreements aimed at reducing tariffs and quotas. Over successive rounds of negotiations, GATT helped lower international trade barriers and increase global commerce. In 1995, WTO was established building upon GATT's achievements and providing stronger mechanisms for liberalizing trade and resolving disputes. Today, WTO oversees global trade rules and agreements covering goods, services, and intellectual property protection between its 153 member countries.