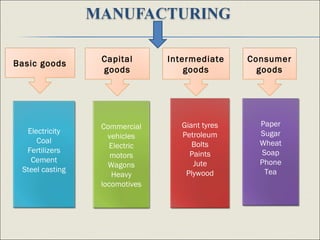
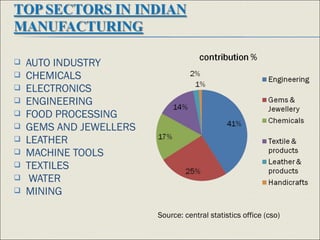
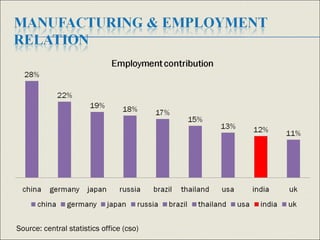
The document discusses India's manufacturing sector. It notes that manufacturing contributes 16% to India's GDP and includes sectors like automotive, chemicals, electronics, and food processing. The largest sub-sectors are discussed and statistics provided on manufacturing's contribution to GDP growth from 2007-2012. Challenges facing the sector are outlined like high costs and the need for skills development. Government initiatives to support manufacturing competitiveness are mentioned. Larsen and Toubro, a large Indian conglomerate active in construction, heavy equipment, and other areas is also summarized.