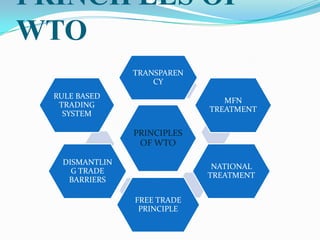
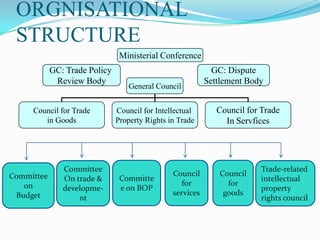
The document provides information about the World Trade Organization (WTO). It notes that the WTO was established on January 1, 1995 and succeeded the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). The WTO aims to supervise and liberalize international trade between its 153 member countries. It has an annual budget of 196 million Swiss francs and 629 staff members. The WTO seeks to promote free trade and resolve trade disputes between countries.