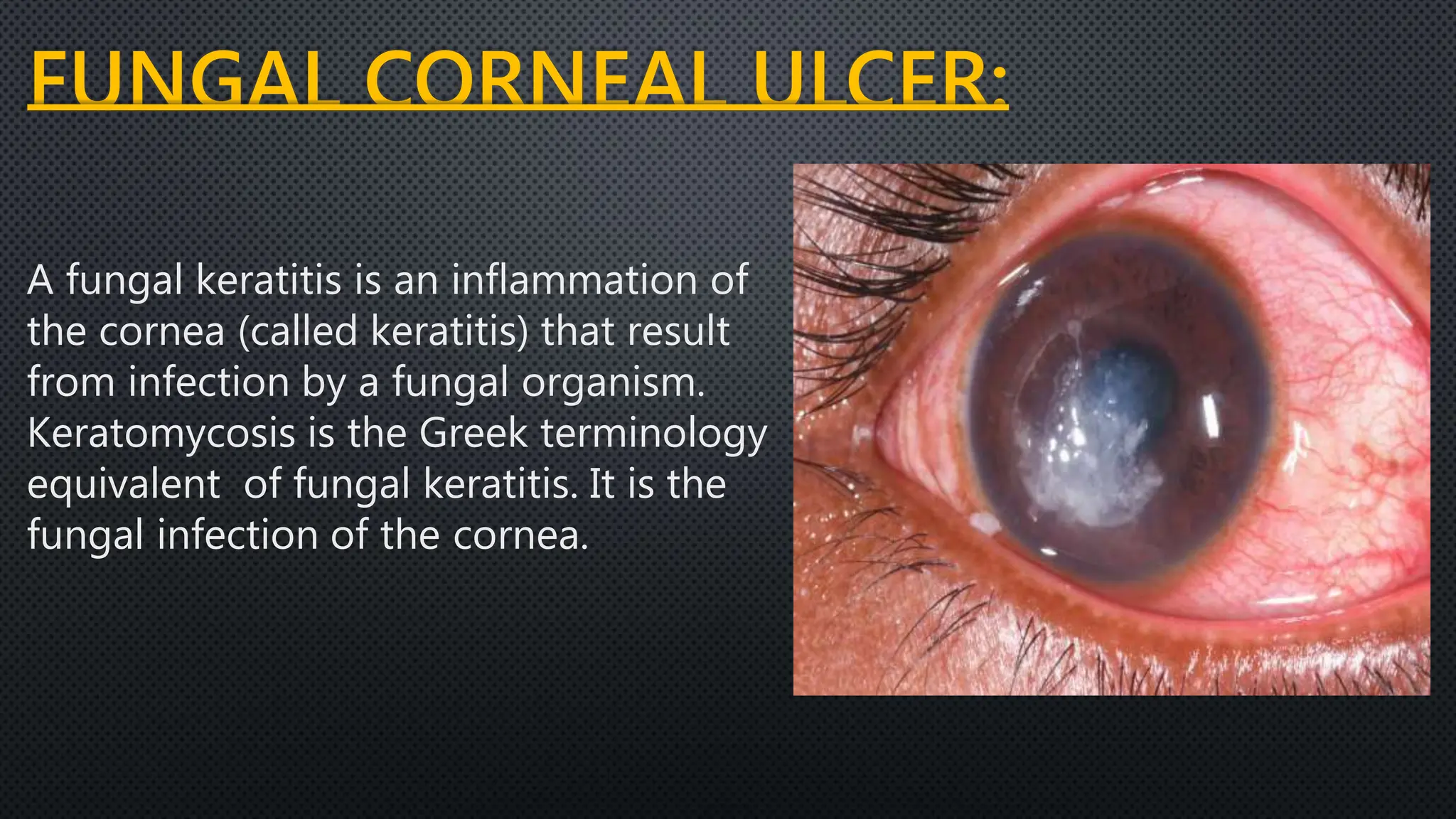
A fungal corneal ulcer is caused by a fungal infection of the cornea. Common causative organisms include Candida, Aspergillus, Fusarium, and others. Symptoms include pain, photophobia, blurred vision, and redness. Signs include a greyish-white ulcer with feathery extensions into the stroma. Diagnosis involves corneal scraping for KOH, Gram, or calcofluor white staining to identify fungal hyphae. Treatment consists of topical antifungal drops like natamycin or amphotericin B for 6-8 weeks, sometimes with adjunctive cycloplegics, analgesics, or systemic antifungals for severe cases. Unresponsive cases