This document provides information about nematodes, including their:
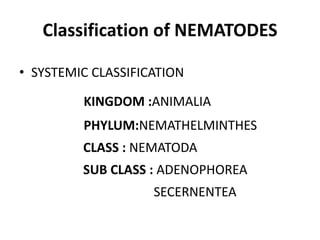
1) Classification within the kingdom Animalia and phylum Nemathelminthes.
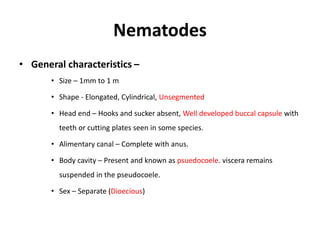
2) General characteristics such as size, shape, presence of a buccal capsule and teeth.
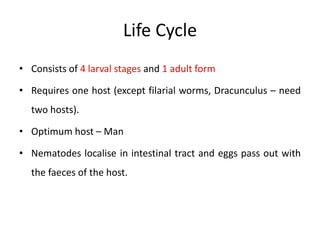
3) Life cycle which involves 4 larval stages and 1 adult form, and usually requires a single host like humans.
4) Modes of infection such as ingestion, skin penetration, or transmission by blood-sucking insects.