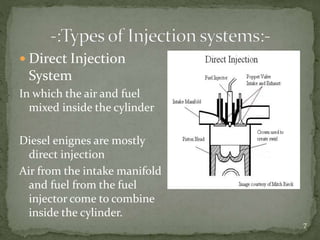
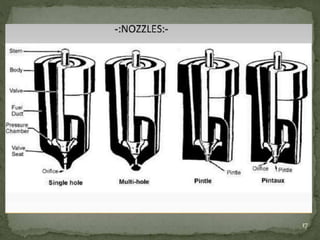
The document discusses fuel injection systems used in internal combustion engines. It describes the key components of a fuel injector including the nozzle, needle valve, and spring. It explains the differences between mechanical and electronic fuel injectors. Direct injection systems mix fuel and air in the cylinder, while indirect injection systems mix in the intake manifold. The document outlines the advantages of fuel injection over carburetion such as improved engine performance and fuel metering.