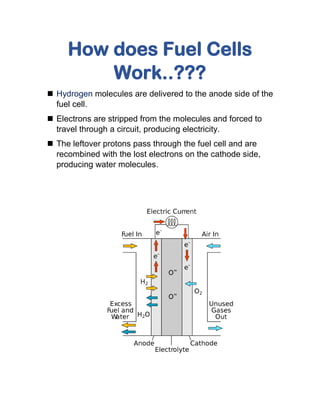
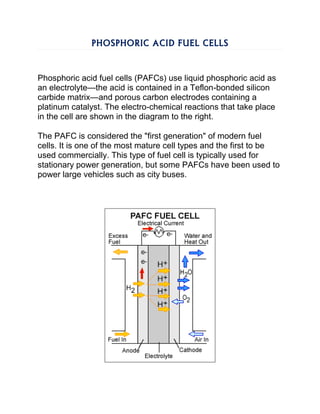
Fuel cells generate electricity through electrochemical reactions that combine hydrogen and oxygen, producing water and heat, making them more efficient than traditional combustion engines. They come in various types, including polymer electrolyte membrane and alkaline fuel cells, each with unique advantages, such as fuel flexibility and high power densities. Despite challenges like hydrogen availability and high capital costs, fuel cells hold potential for significant market growth in the automotive sector from 2015 to 2040.