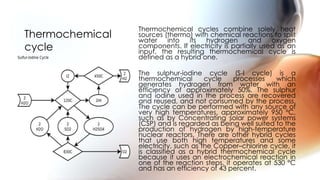
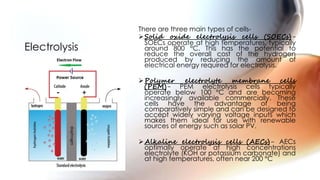
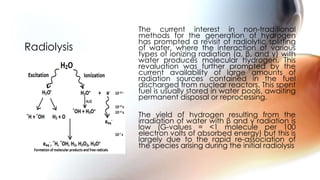
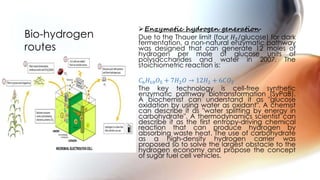
Hydrogen can be produced through various methods such as steam reforming of natural gas, partial oxidation of hydrocarbons, thermochemical water splitting using high temperatures, electrolysis of water, radiolysis of water through nuclear radiation, and biological and enzymatic conversion of biomass. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages related to efficiency, costs, environmental impacts, and scalability. Hydrogen is a very useful energy carrier due to its high energy content per unit mass and non-polluting nature when used.



![The partial oxidation reaction occurs when
a sub-stoichiometric fuel-air mixture is
partially combusted in a reformer, creating
a hydrogen-rich syngas. A distinction is
made between thermal partial oxidation
(TPOX) [ ≥ 1200°C] and catalytic partial
oxidation (CPOX) [800°C-900°C]. The
chemical reaction takes the general form:
𝐶 𝑛 𝐻 𝑚 +
𝑛
2
𝑂2 → 𝑛𝐶𝑂 +
𝑚
2
𝐻2
Idealized examples for heating oil and coal,
assuming compositions 𝐶12 𝐻24 and 𝐶12 𝐻12
respectively, are as follows:
𝐶12 𝐻24 + 6𝑂2 → 12𝐶𝑂 + 12𝐻2
𝐶24 𝐻12 + 12𝑂2 → 12𝐶𝑂 + 12𝐻2
Partial oxidation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrogengeneration-150909084746-lva1-app6891/85/Hydrogen-generation-4-320.jpg)