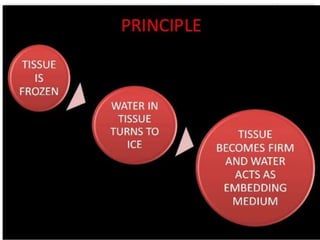
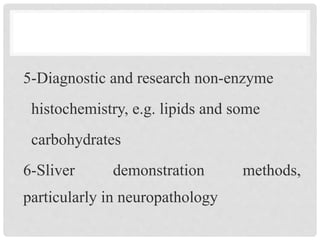
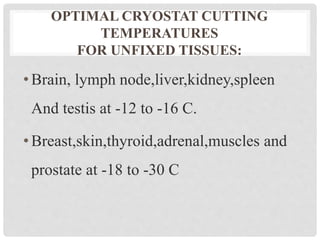
This document discusses frozen sections and cryostats. Frozen sections are prepared without dehydration or embedding to enable rapid diagnosis within 10 minutes. They have applications in intraoperative diagnosis, enzyme histochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and other techniques. Tissue is frozen using liquid nitrogen or other cryogenic methods, turning water within the tissue to ice which acts as an embedding medium for sectioning. Cryostats maintain low temperatures, typically -20 to -30°C, for sectioning frozen tissue blocks. Optimal cutting temperatures vary by tissue type and whether the tissue is fixed.