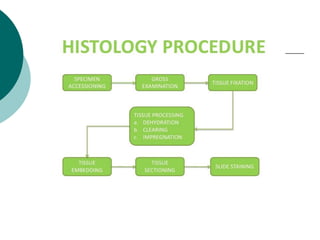
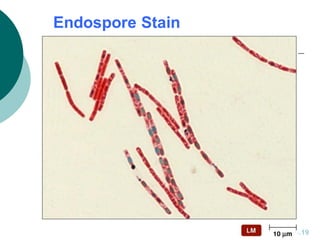
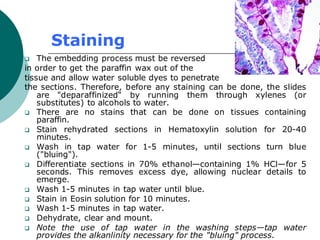
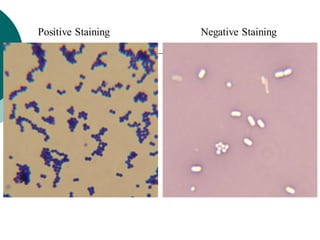
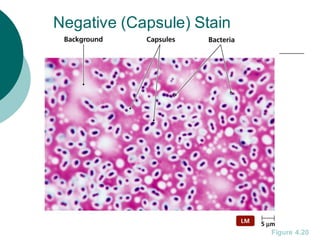
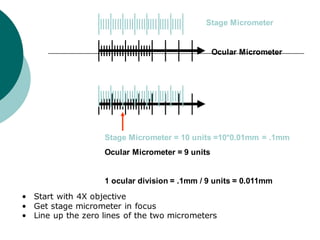
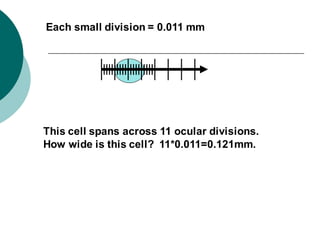
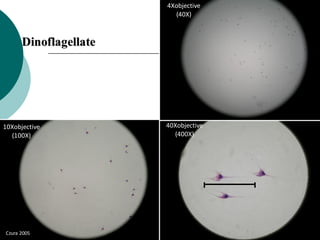
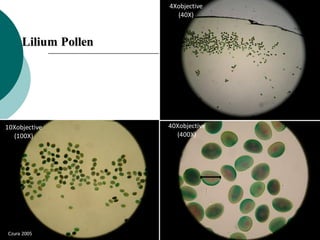
1. Histotechniques involve processing tissues through fixation, dehydration, clearing, embedding, section cutting, and staining to enable pathological examination under a microscope.
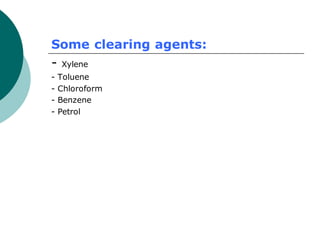
2. Tissues are first fixed in chemicals like formaldehyde to preserve their structure, then dehydrated with graded alcohols, cleared with solvents, and embedded in paraffin wax for section cutting with a microtome.
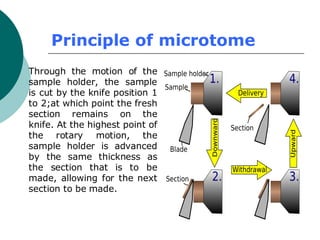
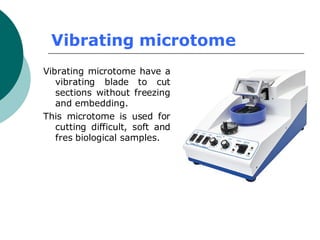
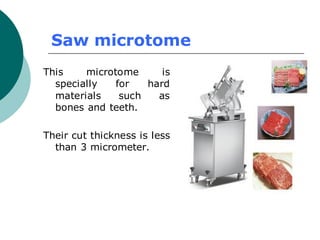
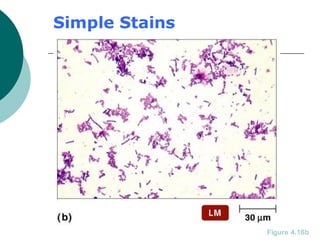
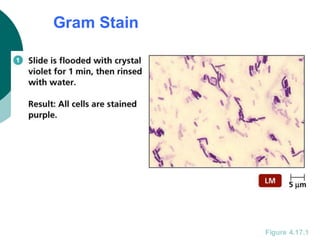
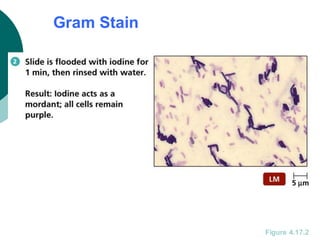
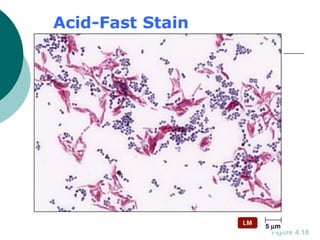
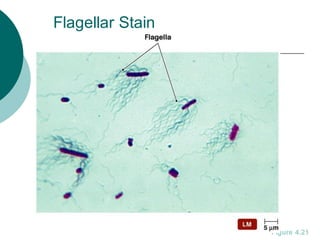
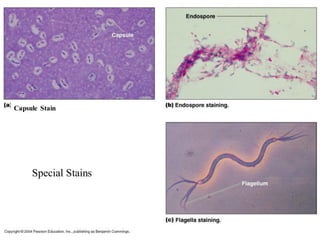
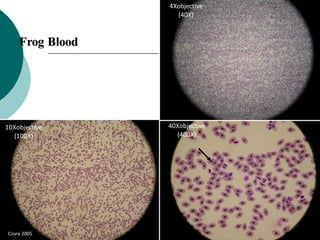
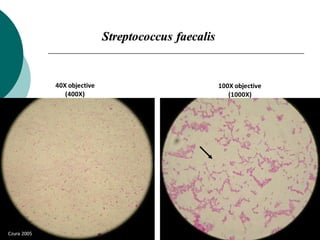
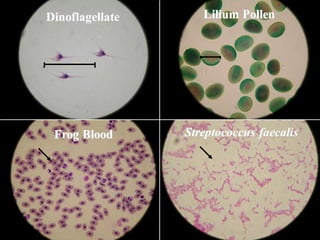
3. The microtome uses a knife to cut extremely thin sections of the wax-embedded tissue, which are then floated in water, mounted on slides, and stained for microscopic examination.