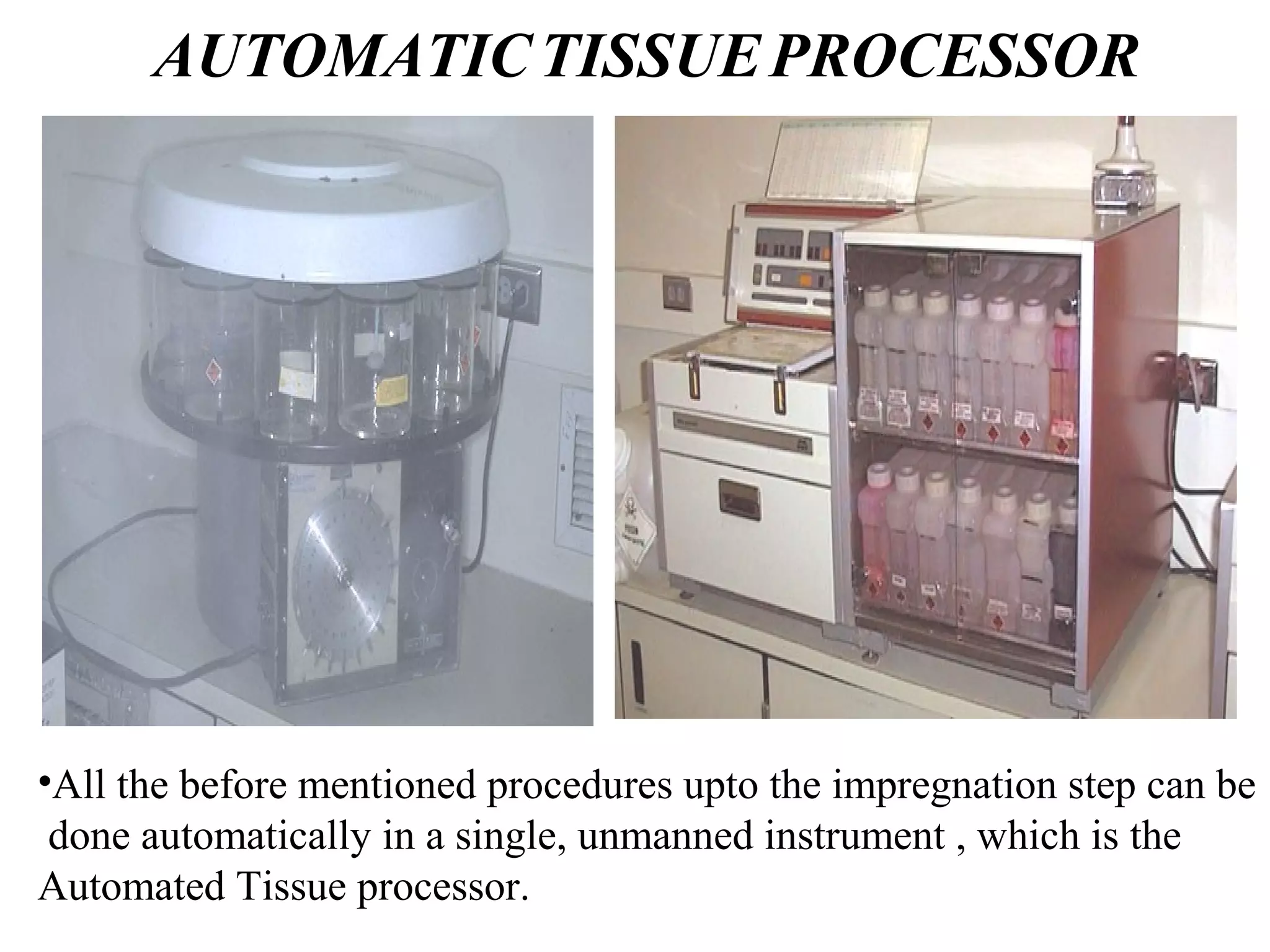
The document outlines the process of tissue processing in histotechnology, detailing key steps such as fixation, dehydration, clearing, impregnation, and embedding. It discusses the principles and reagents involved, various techniques for dehydration and clearing, and the importance of using appropriate methods to ensure the integrity of tissue samples. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity for precise processing to obtain diagnostic-quality sections.