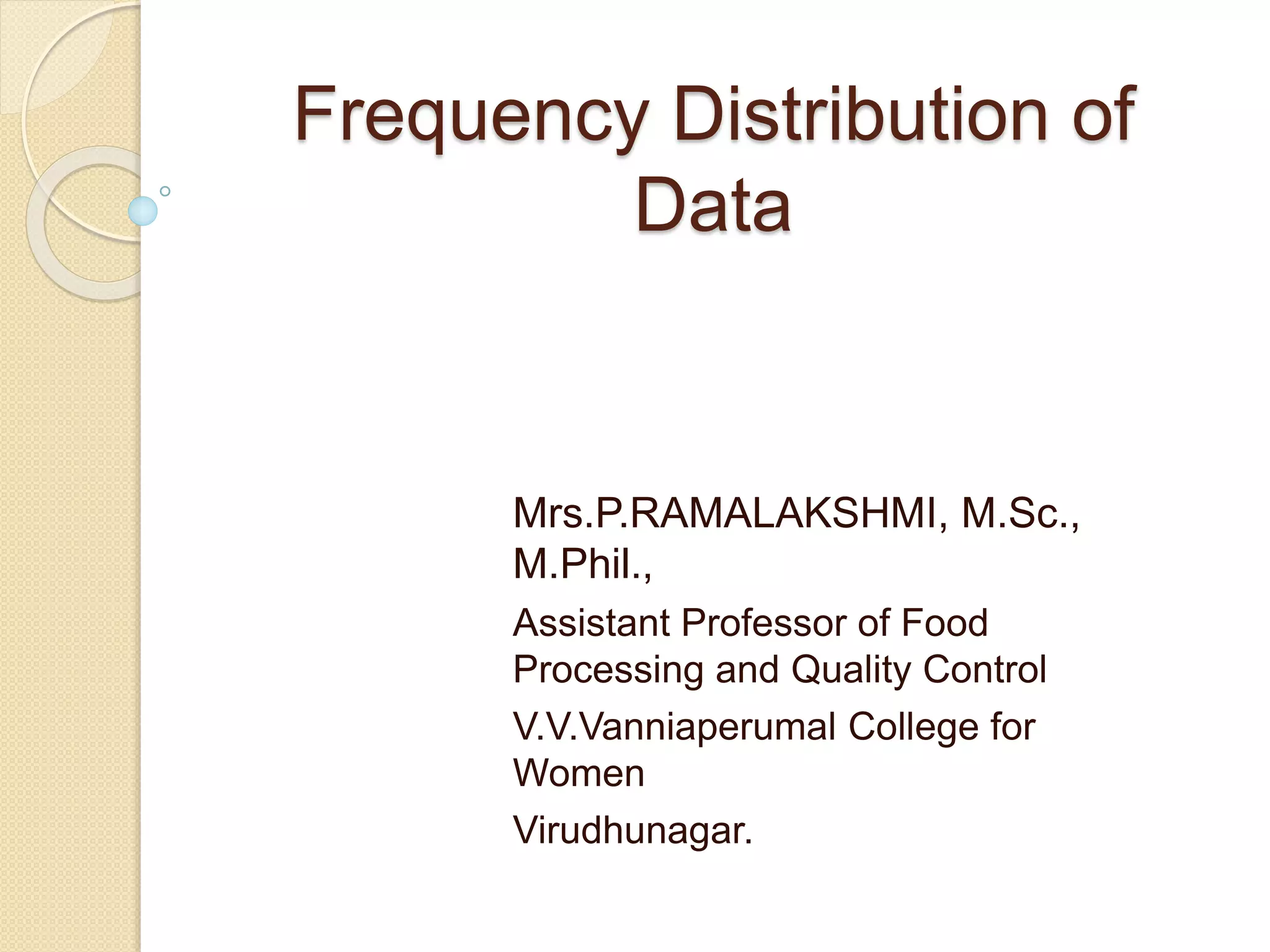
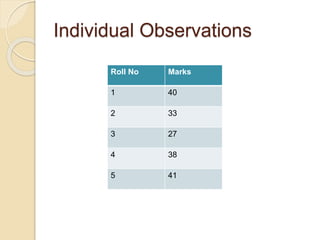
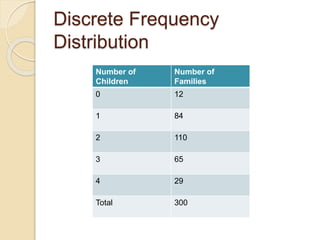
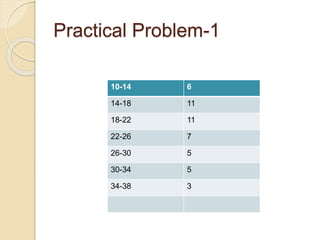
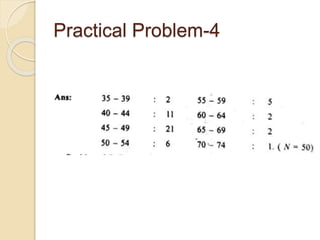
The document discusses frequency distribution, a method of classifying data based on the number of occurrences of specific values. It outlines three types of frequency distributions: individual observations, discrete frequency distribution, and continuous frequency distribution, along with examples of each. Additionally, it explains class limits, class intervals, and provides practical problems to illustrate the concepts.