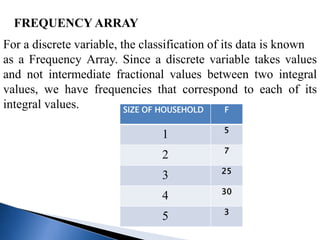
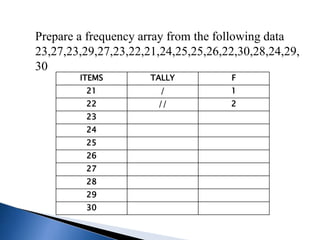
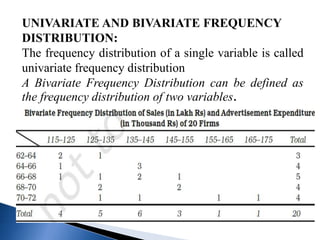
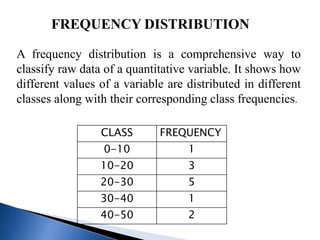
This document discusses different types of data classification and frequency distributions. It defines raw data and explains the objectives and types of classification, including chronological, spatial, quantitative, and qualitative. Variables are classified as continuous or discrete. A frequency distribution arranges raw data into classes and shows the frequency of observations in each class through tables or arrays. The key elements of a frequency distribution like class limits, midpoints, and intervals are also explained.

![RAW DATA
The unclassified data is called raw data
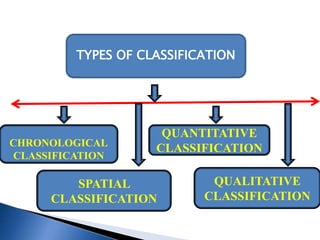
CLASSIFICATION OF DATA
The process of grouping data according to their
characteristics is known as classification of data
Objectives of Classification:
a] To simplify complex data
b] To eliminate unnecessary details
c] To help comparison
d] To make analysis and interpretation easy.
e] To arrange the data according to their common
characteristics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organisationofdata-240213170625-357645e2/85/ORGANISATION-OF-DATA-pptx-2-320.jpg)



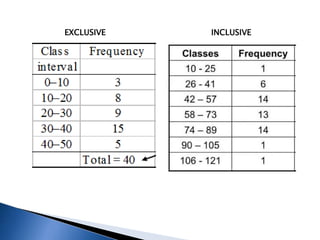
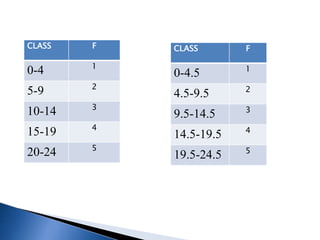
![CLASS INTERVAL
Class interval: Difference between upper limit and lower limit
Class interval=upper limit-Lower limit
Example 10-20
Class interval=20-10=10
FREQUENCY
Number of items [observations] falling within a particular
class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organisationofdata-240213170625-357645e2/85/ORGANISATION-OF-DATA-pptx-8-320.jpg)