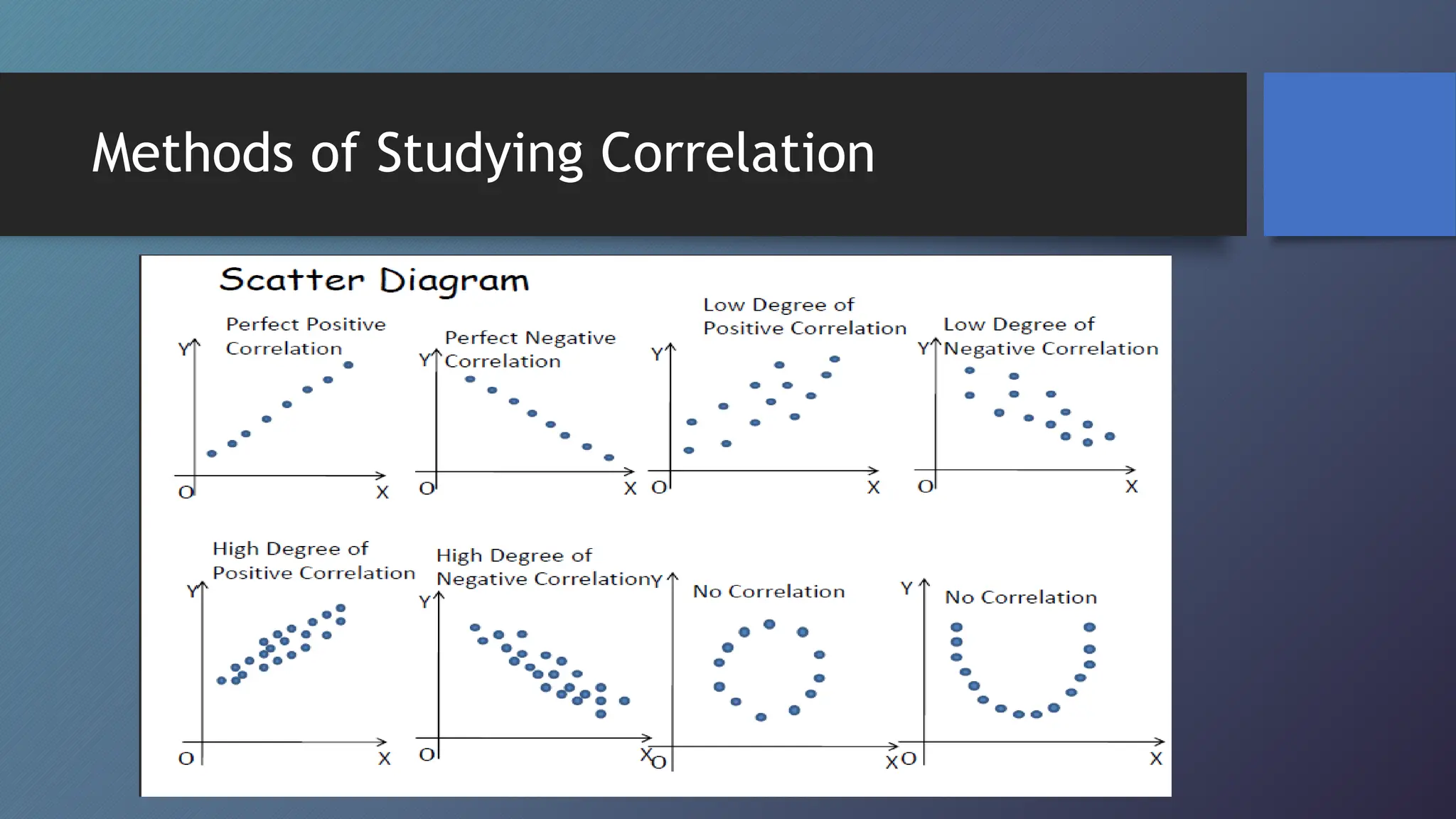
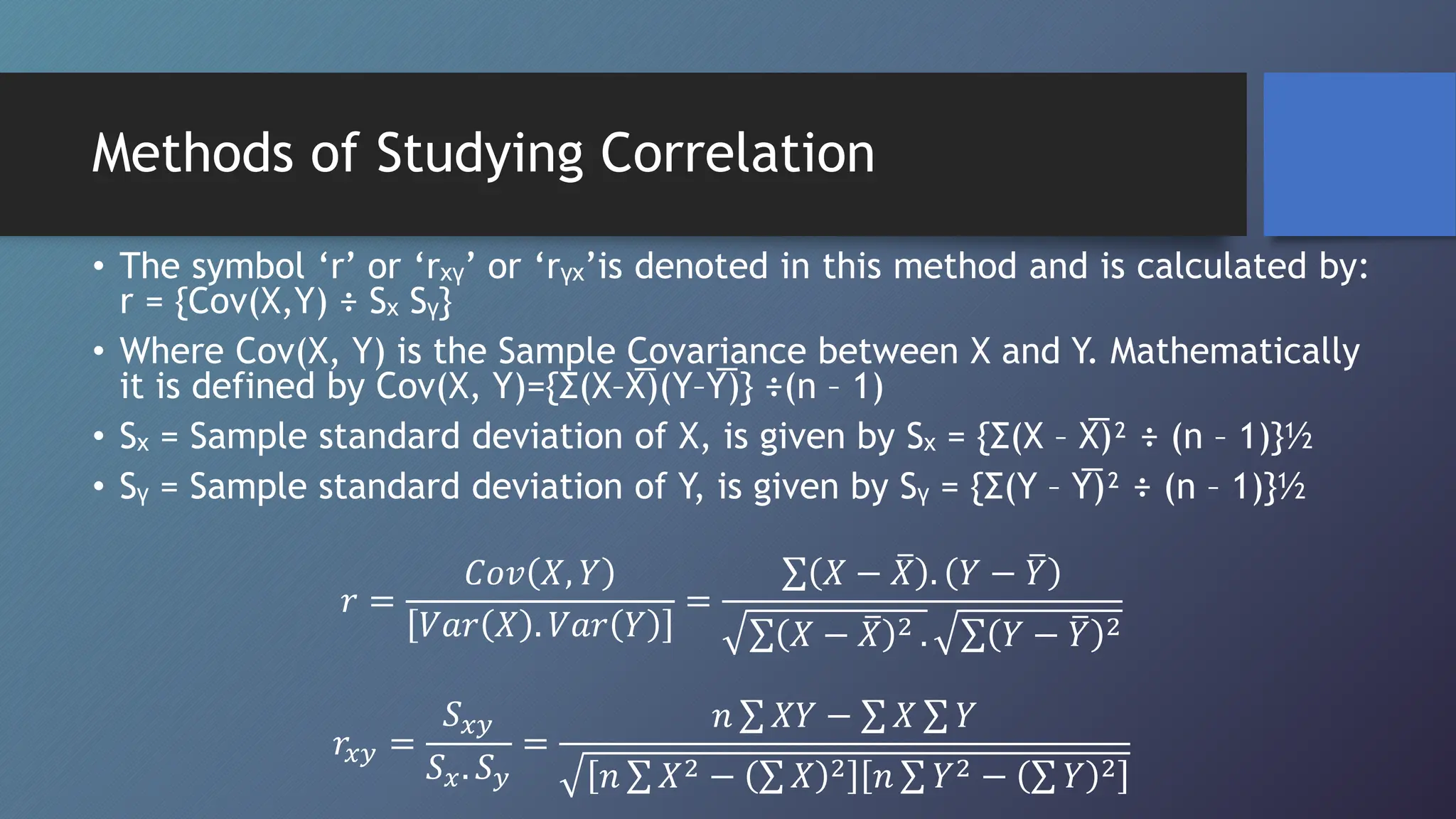
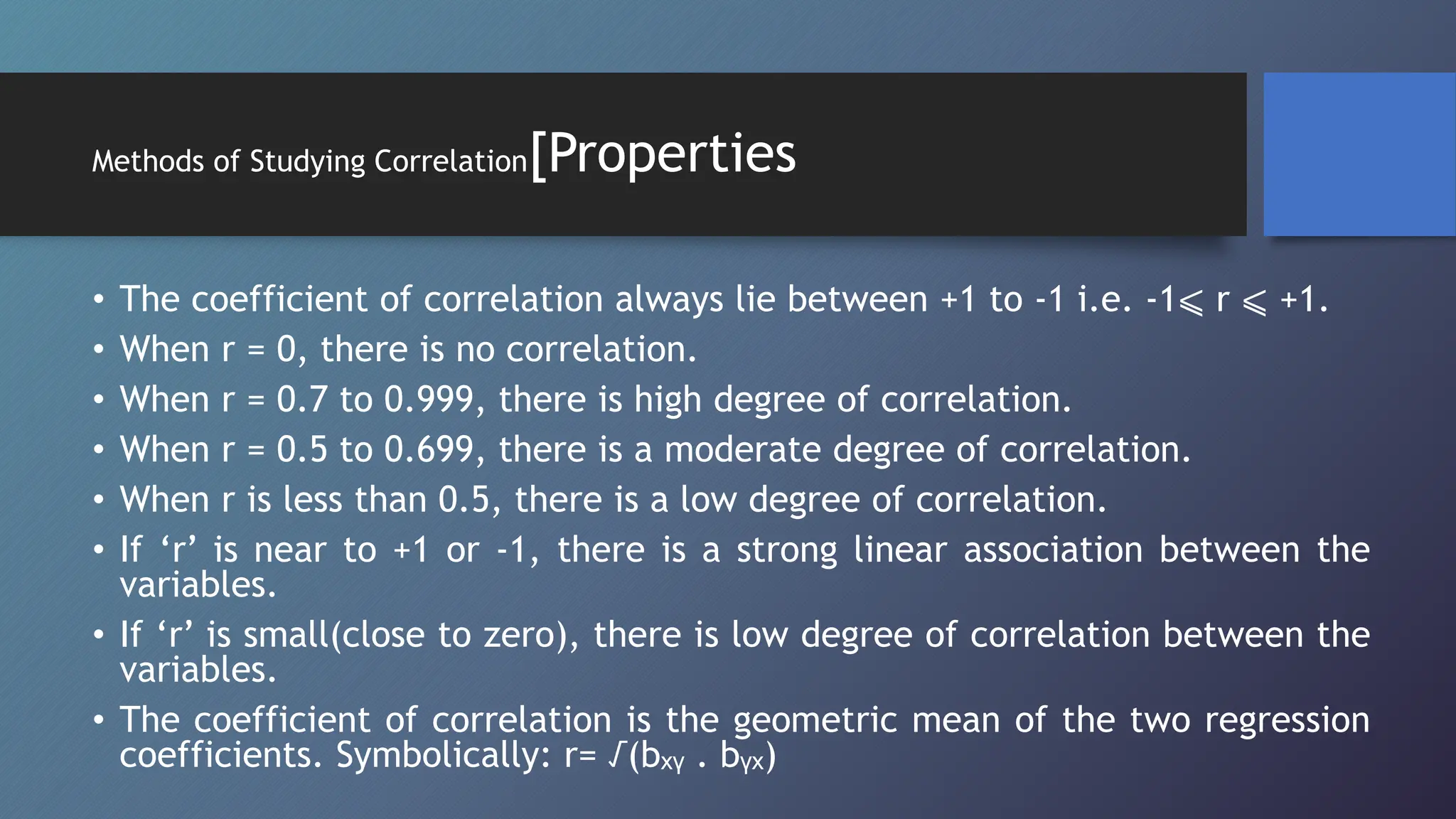
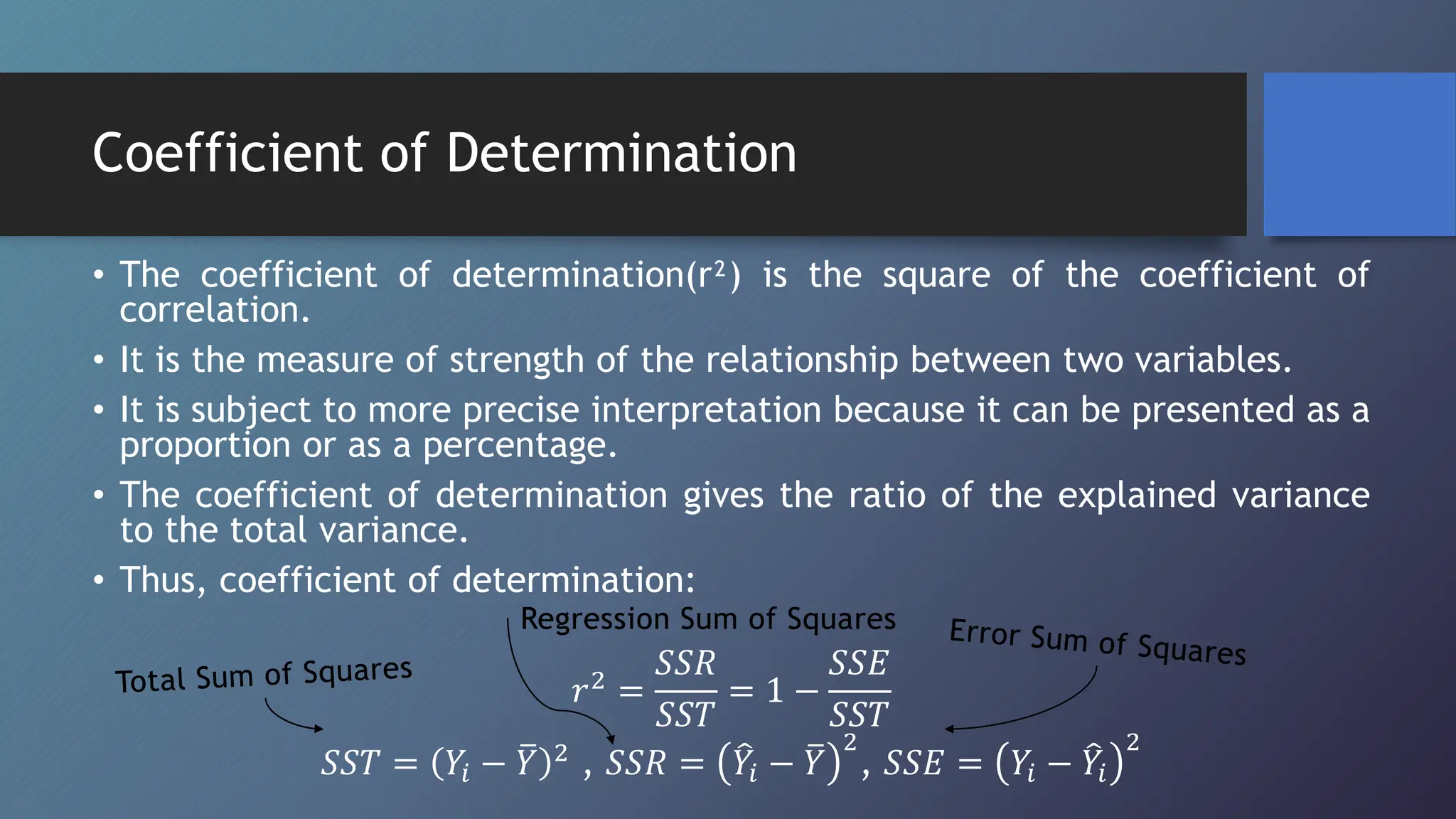
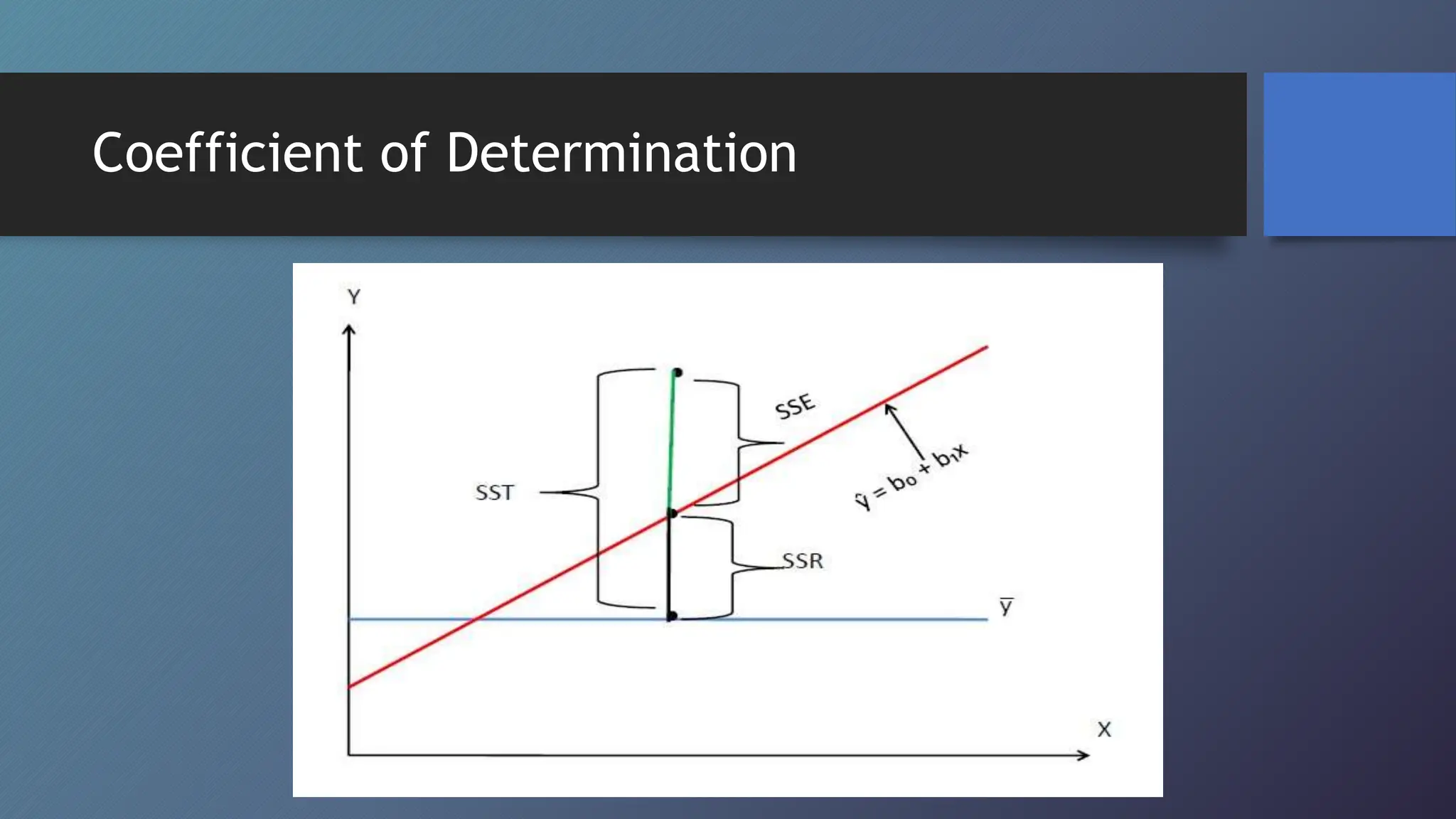
This document discusses correlation and methods for studying correlation. Correlation refers to the relationship between two variables, where a positive correlation means the variables change in the same direction and a negative correlation means they change in opposite directions. Methods for studying correlation include scatter plots, Karl Pearson's coefficient of correlation (denoted r), and the coefficient of determination (denoted r2). The coefficient of correlation quantifies the strength and direction of the linear relationship between variables while the coefficient of determination indicates how much variability in one variable can be predicted from the other variable.