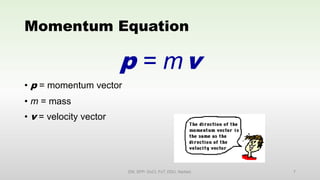
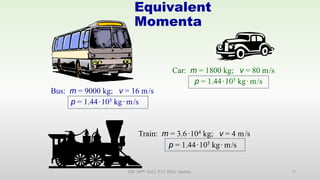
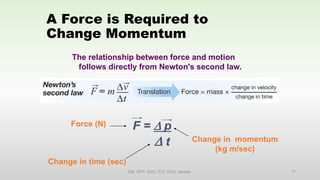
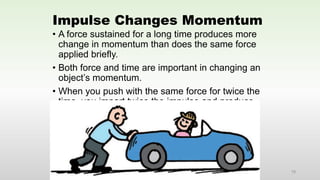
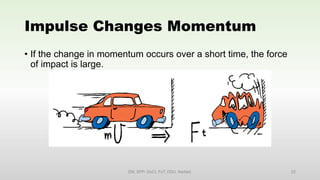
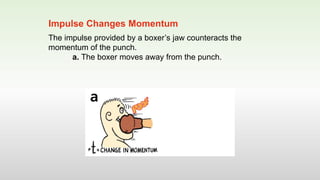
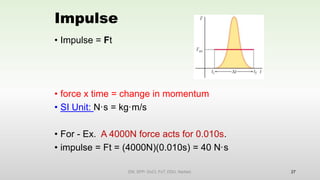
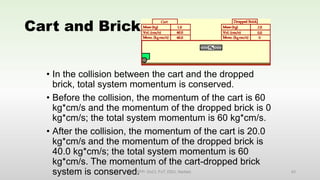
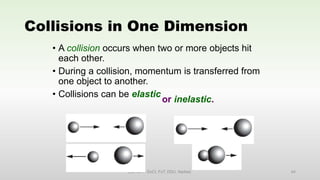
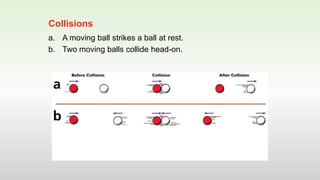
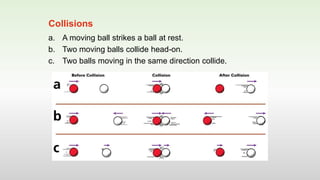
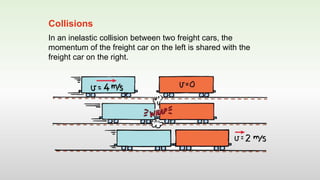
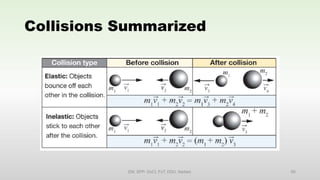
This document discusses momentum and impulse. It defines momentum as a property of moving objects that describes their tendency to continue in the same direction and at the same speed. Momentum is calculated as mass times velocity. Impulse is defined as the product of force and time. The document also discusses how impulse causes changes in momentum based on Newton's second law, and how momentum is conserved in collisions according to the law of conservation of momentum.