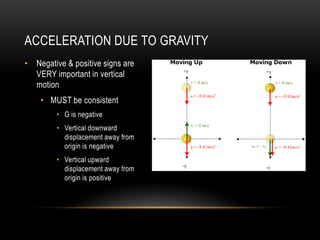
This document discusses the physics of falling objects. It defines physics as the study of matter, energy, and their interactions. It states that near the Earth's surface, in the absence of friction, all objects experience a constant downward acceleration due to gravity of about 9.81 m/s2. It provides the kinematic equations for analyzing vertical motion under constant acceleration due to gravity and emphasizes the importance of sign conventions in such problems. Finally, it works through an example problem of calculating the distance fallen by a ball dropped from a tower over different time intervals.