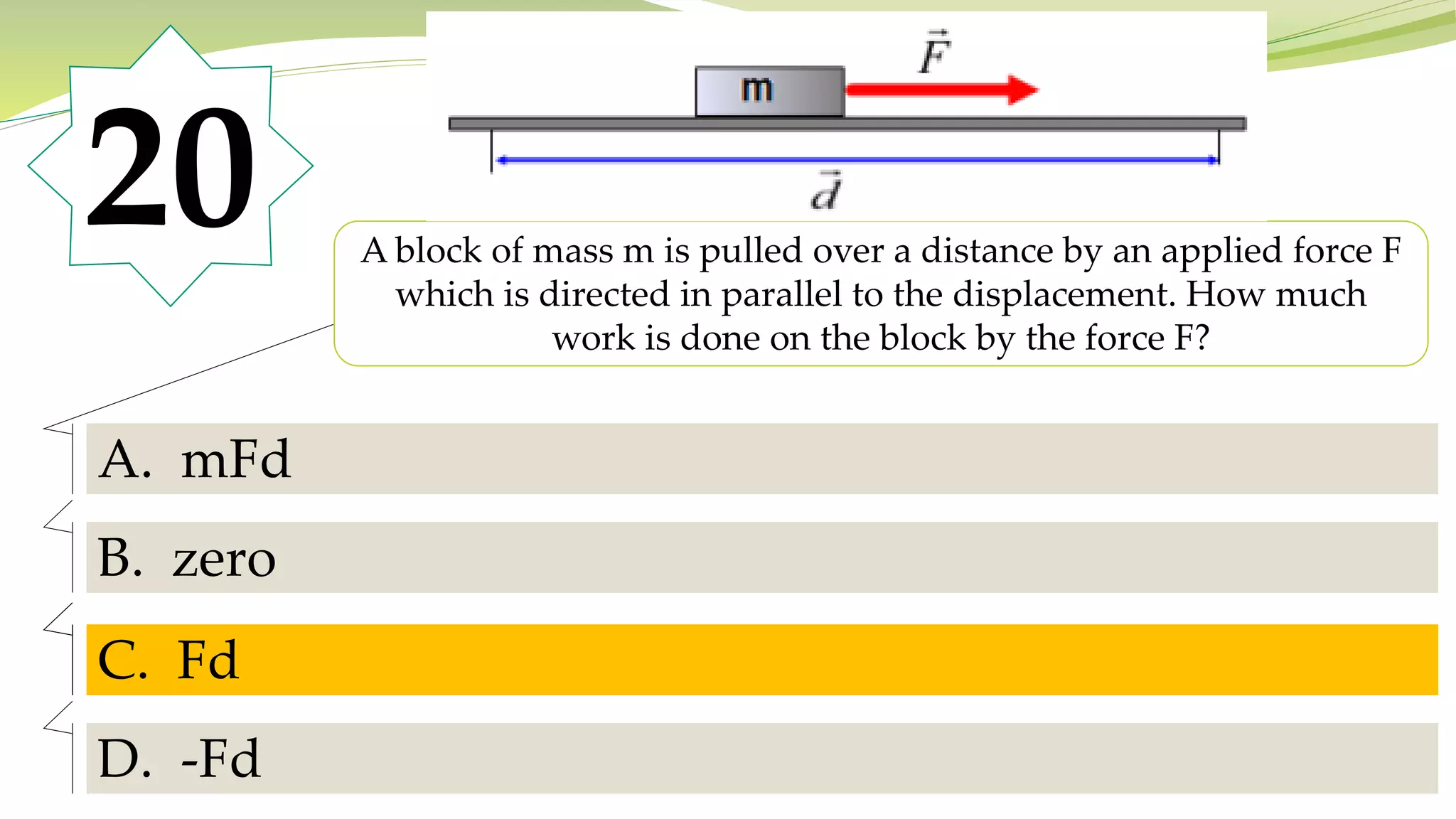
The document consists of multiple-choice questions related to general physics concepts, specifically focusing on quantities, units, vectors, and motion. Key topics include the distinction between vector and scalar quantities, displacement calculations, Newton's laws of motion, and the principles of momentum and work. The questions test foundational knowledge in physics, often requiring the application of formulas and definitions.