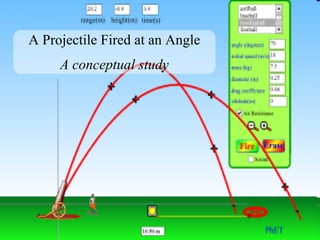
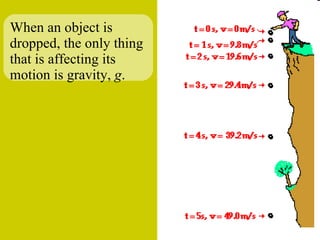
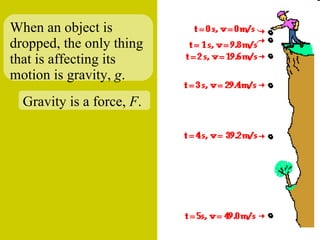
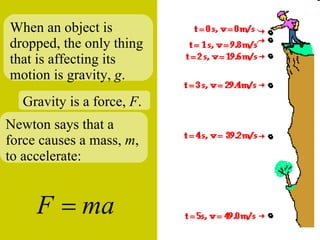
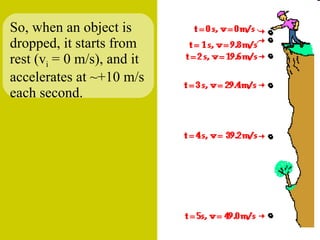
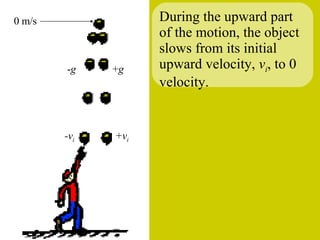
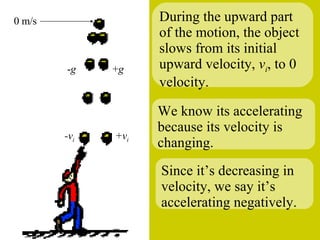
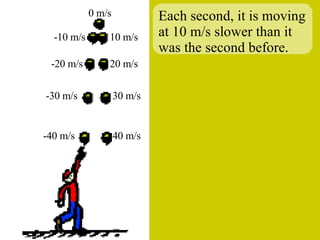
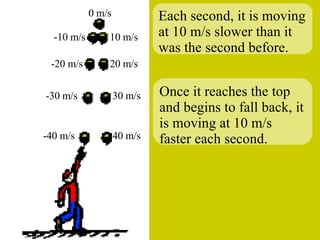
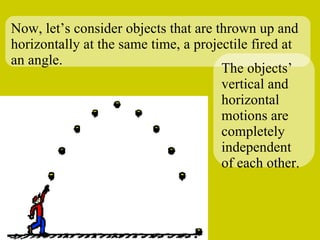
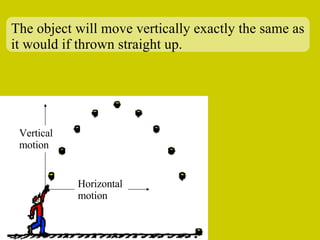
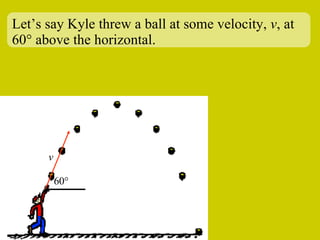
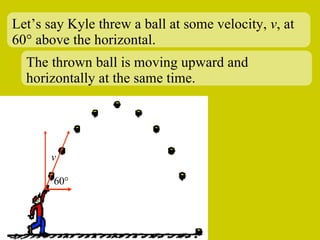
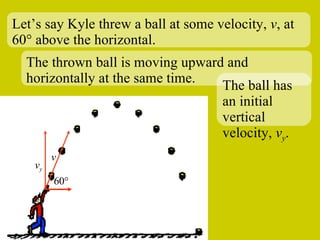
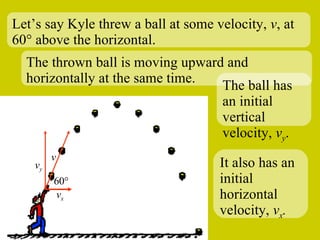
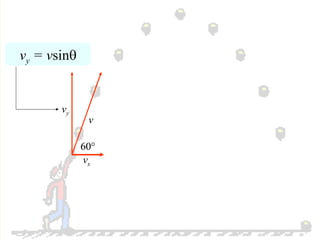
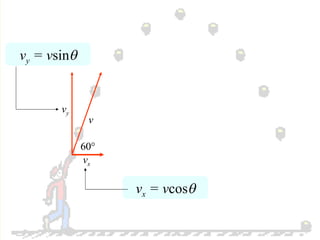
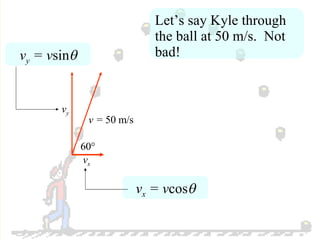
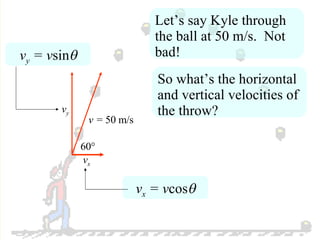
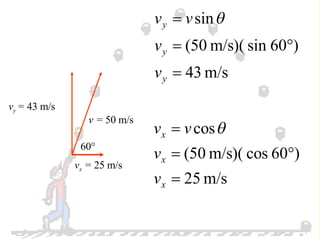
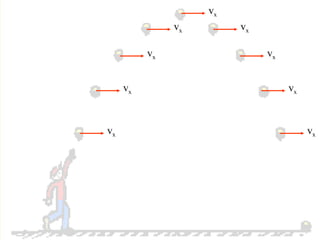
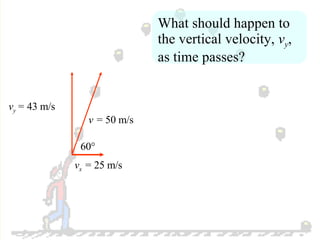
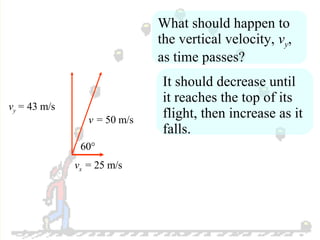
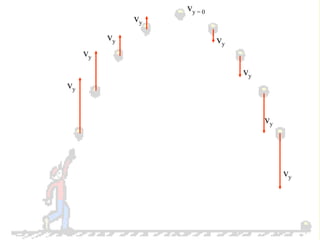
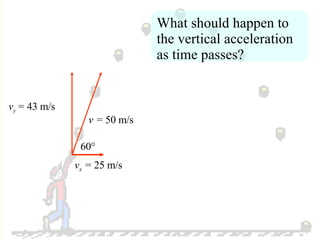
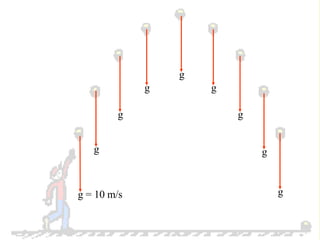
The document discusses the motion of projectiles fired at an angle. It explains that a projectile has both vertical and horizontal motion, with the vertical motion identical to if thrown straight up, undergoing acceleration from gravity. The horizontal motion is unaffected by gravity and maintains a constant velocity. The document provides an example of a ball thrown at a 60 degree angle, calculating its initial vertical velocity as 43 m/s and horizontal velocity as 25 m/s.