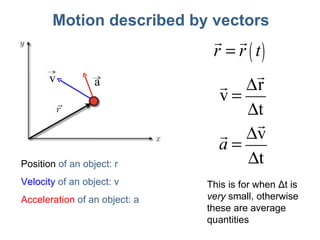
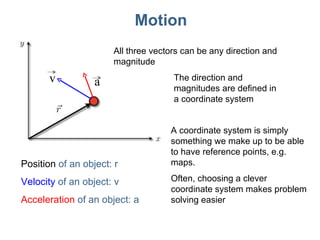
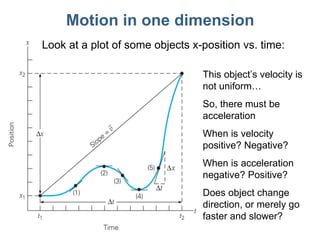
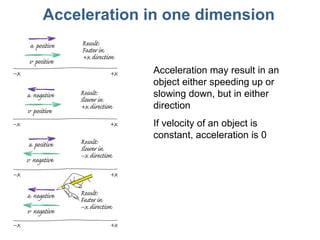
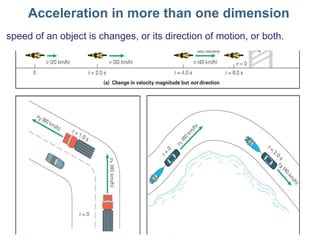
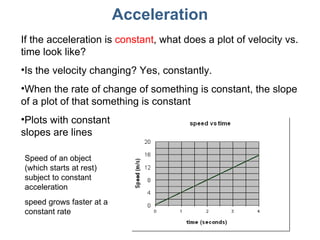
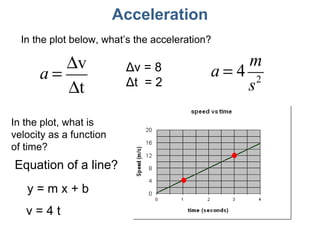
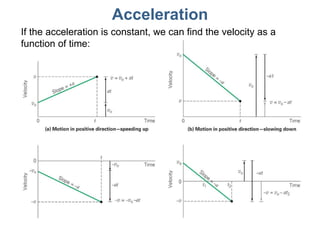
This document discusses motion, position, velocity, and acceleration. It defines these terms and explains how they relate to each other. Specifically:
- Position refers to where an object is located. Velocity refers to how fast and in what direction an object is moving. Acceleration refers to whether an object's speed or direction is changing.
- Motion, position, velocity, and acceleration can all be described as vectors that have a magnitude and direction within a coordinate system.
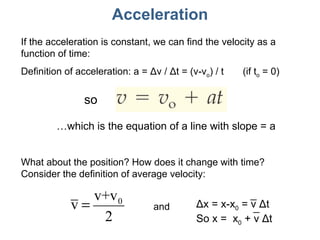
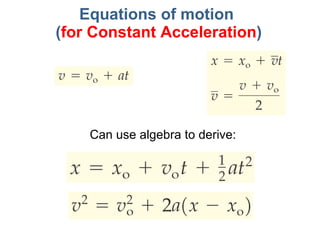
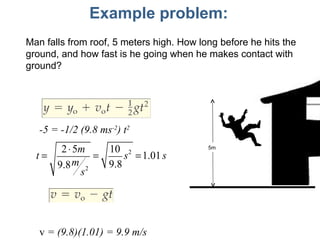
- Equations are provided that define the relationships between these quantities, such as the equations of motion that describe how velocity and position change over time under constant acceleration like gravity.