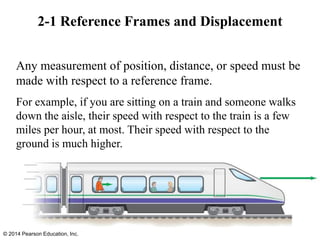
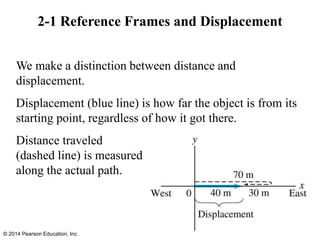
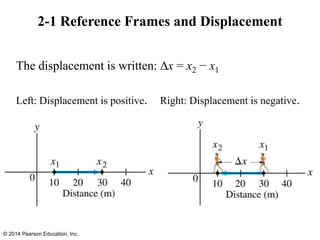
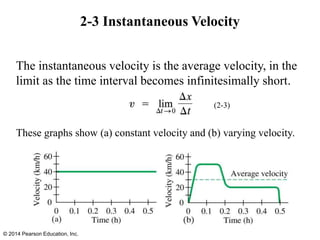
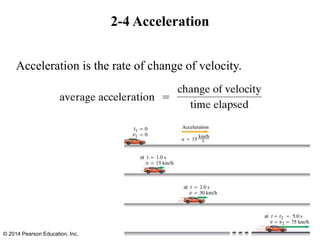
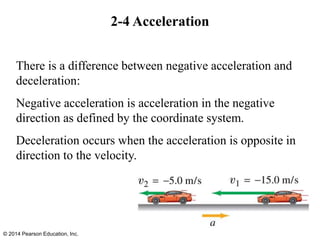
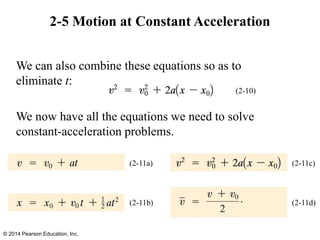
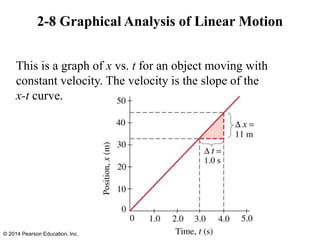
The document is a chapter from a physics textbook about one-dimensional motion. It covers key concepts like reference frames, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity, acceleration, motion with constant acceleration, freely falling objects, and graphical analysis of linear motion. Equations for constant acceleration are derived and explained. Problem-solving strategies are outlined. Copyright information indicates this content is intended solely for classroom instruction.