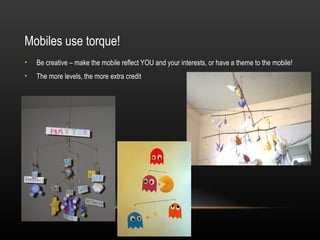
1. The agenda includes physics presentations on light, an extra credit opportunity to build a multi-level mobile involving torque, and information about the physics olympics presentations.
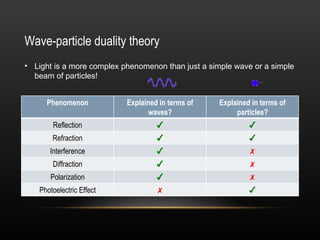
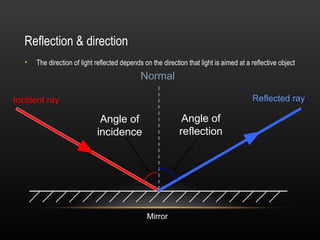
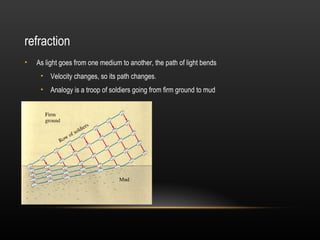
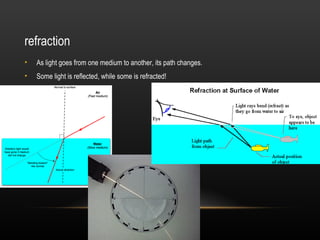
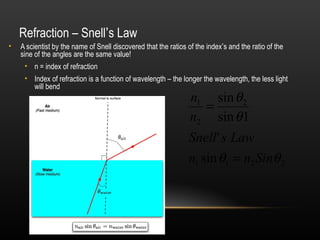
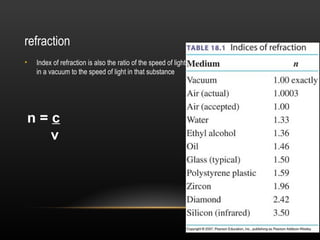
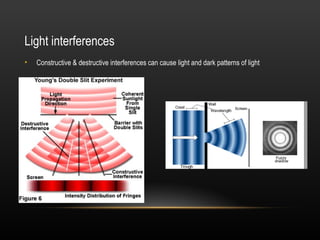
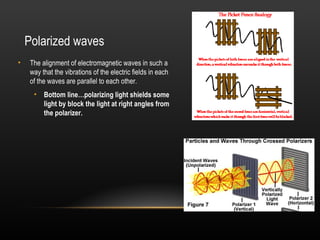
2. Light demonstrates both wave and particle properties. It can reflect, refract, diffract, interfere and polarize which supports the wave model, but it also explains the photoelectric effect as particles.
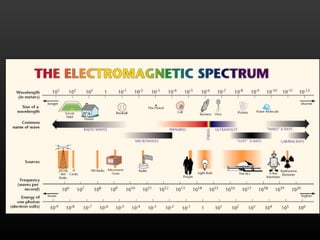
3. Visible light is a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and its wavelength corresponds to color from red to violet with shorter wavelengths having higher frequencies and more energy.