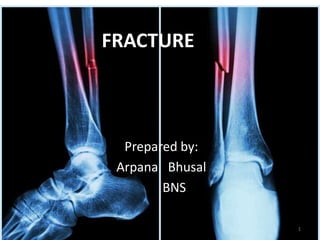
The document provides a comprehensive overview of fractures, including definitions, causes, types, signs, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. It categorizes fractures into various types such as simple, compound, open, closed, and others while detailing the symptoms and diagnosis methods. Additionally, it outlines emergency and medical management treatments, including cast immobilization, traction, and fixation methods, as well as potential complications.