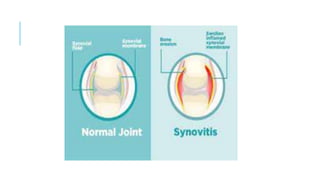
Bursitis is inflammation of fluid-filled sacs called bursae located around joints. It is caused by repeated pressure or overuse of a joint. Common types include prepatellar bursitis around the kneecap, trochanteric bursitis near the hip joint, and retrocalcaneal bursitis in the heels. Symptoms include pain, swelling, warmth, and restricted movement near the affected joint. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging tests, and fluid aspiration. Treatment focuses on rest, ice, braces, anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, and physical therapy. Prevention emphasizes proper posture, warming up before exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding repetitive motions.